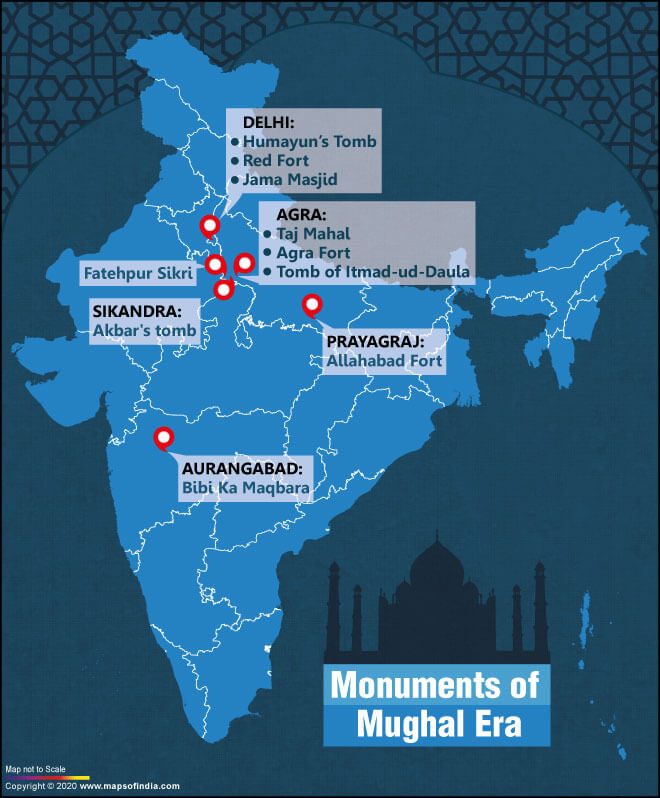

The Mughal architecture has a special place in the chapters of Indian heritage. Most of the Mughal emperors were fond of paintings, and they incorporated their experiments in Mughal art studios in the architecture they created. For this reason, it is considered that Mughal kings developed Indo-Persian architecture. In most of the architecture created by the Mughals, there are some common features like the bulbous domes, minarets, massive halls, the delicate ornamentation, large vaulted gateways, and so on.
Mughals built various types of monuments
The Mughal emperors had built forts, mosques, palaces, mausoleums, gardens, tombs in many parts of the country. Shahjahan was so fond of architecture that he was called the ‘king of architecture’. His era was also known as the ‘the Golden Era of the Mughal Empire’. Visitors from all over the world come to see such glorious structures built by the Mughal Kings.
Here is a list of some prominent Mughal structures which are famous worldwide for their beauty and superb architect work.
1. Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal is an epitome of eternal love. This fantastic building was built in 1632 by Mughal king Shahjahan in memory of his beloved wife, Mumtaz Mahal. It is the perfect example of the excellence of Mughal architecture of the period.
The white marble mausoleum is situated on the bank of river Yamuna in Agra. More than two decades were spent in the completion of this remarkable building. It was constructed in 1632. This colossal monument is the perfect example of the combination of Islamic, Turkish, and Persian architectural designs.
The chief architect of the Taj Mahal was Ustad Ahmad Lahori, and Isa was the mason. The Taj Mahal is a true wonder that impresses all who have seen this unique building. Taj Mahal came under the category of UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1983.
2. Humayun’s Tomb
Humayun, the second Mughal king, sat on the throne after the death of his father, Babur. Humayun’s tomb in Delhi is another magnificent building of the Mughal age. It was constructed by his widow Hamida Banu Begum after the death of Humayun. The construction of Humayun tome commenced in 1565 and was completed in 1572.
The Humayun Tomb was the first building that established the well-defined Mughal architecture. The architectural style of Humayun’s tomb is Persian brought by the Persian architect Mirak Mirza Ghiyuath and his son, Sayyid Muhammad.
It was probably the first garden-tomb of the Indian subcontinent. Another feature of the Humayun tomb is that it was the first structure where a large scale of red sandstone was used. This impressive garden tomb got UNESCO World Heritage status in 1993.
3. Agra Fort
Agra Fort is another remarkable structure built by the Mughal king Akbar. The unique feature of the building is the perfect combination of South-Asian, Persian, Islamic, and Turkish architecture. Agra Fort is also known as ‘Fort Rouge’ or ‘Qila-i-Akbari’. It was built as a military base of the Mughal emperor Akbar. The courtyards of the fort are eye-catching, decorated with famous pietra dura inlays. It is just 2.5 km northwest of the Taj Mahal.
The external walls of Agra Fort are made of burgundy sandstone. There are many monuments inside the fort-like Diwan-e-Aam and Diwan-e-Khas while Moti Masjid and Sheesh Mahal are also situated inside the Agra Fort. Akbar’s son Jahangir converted the fort into a royal residence. The remarkable architectural beauty of Agra Fort lures worldwide visitors. The Agra Fort also comes in the list of UNESCO World Heritage sites.
4. Red Fort (Delhi)
The Red Fort is another Mughal masterpiece monument constructed under the leadership of Shahjahan. The construction of the Red Fort was completed in 1648. Since then it was the principal residence of the Mughal emperors. Delhi’s Red Fort is built of red sandstone. Its wall is a massive 75 feet high.
In this eye-catching palace, there is an entertainment hall, baths, and indoor canals, a mosque but geometrical gardens of the complex increase the beauty of the fort. The complex comprises two halls for a public audience: Diwan-i-Am has 60 red sandstone pillars while Diwan-i-Khas has a pavilion of white marble.
The Red Fort has a glimpse of Persian and Islamic architecture. The Red Fort shows the pinnacle of Mughal’s artistic creativity. This historical building is where the Prime Minister of India unfurls the national flag on August 15, on the occasion of Independence Day every year. In 2007, UNESCO added Red Fort in its list as a World Heritage Site for its spectacular architecture.
5. Fatehpur Sikri
Fatehpur Sikri was founded by Mughal king Akbar in 1569. It is a fortified city in Agra. Emperor Akbar met a Muslim hermit Salim Chishti in Sikri and requested him to pray for a male heir. Akbar’s son Salim (Jahangir) was born in Sikri later. Therefore, the place Sikri proved auspicious for Akbar, so he decided to make it his capital. Fatehpur Sikri served as the capital of the Mughal Empire for a short stint (from 1572 to 1585). It is situated near Agra.
The open courtyards of the complex are worth seeing. There are several historical monuments inside the complex, and all of them are a treat to watch. Some of the essential monuments inside the Fatehpur Sikri complex are Buland Darwaza, the tomb of Salim Chishti, Jama Masjid, Panch Mahal, Palace of Jodha Bai, Birbal’s House Diwan-i-Khas and many more. Fatehpur Sikri was inscribed to the UNESCO list in 1986.
6. Akbar’s Tomb
Akbar’s Tomb is another masterpiece of Mughal architecture. Akbar, in his lifetime, selected a suitable site for his grave. But it was constructed in 1605-13 by his son Jahangir in Sikandra which is near Agra. The complex is spread in 119 acres. The structure is the blend of all religions like – Hindu, Islamic, Jain, Christian, and Buddhist styles of architecture.
The south gate of the complex is the biggest with four white marble minarets. The Akbar’s Tomb is surrounded by a walled enclosure of 105 square metres. The entrance of the tomb is exquisite, excellent jali work, fine Persian style calligraphy, and the char bagh garden reflect the zenith of Mughal architecture. The absence of domes and the use of chhatris (small canopies) reflected the local influence.
7. Tomb of Itmad-ud-Daula
Itmad-ud-Daula was a Persian noble, and he was also known as Mirza Ghiyas Beg. His daughter Nur Jahan married Mughal king Jahangir. In 1622, he died, and his daughter Nur Jahan decided to build a mausoleum in memory of his father in Agra. It was built in 1628.
The significant element of the monument Tomb of Itmad-ud-Daula is its dome, which is of the Persian style. Part of the structure is furnished with geometric structures. The tomb is replete with marble lattice screens and fine carvings. Apart from this, there is a lovely garden inside the complex called Char Bagh.
8. Jama Masjid (Delhi)
Jama Masjid was constructed in 1650-56 by the Mughal king Shahjahan. The splendid structure is the blend of white marble and red sandstone. It also comprises three imposing gates, four towers, two 131 feet gigantic minarets, and three massive domes. The mosque can accommodate about 25,000 people at a time for the prayer. Shahjahan invited Imam Syed Abdul Ghafoor Shah Bukhari from Bukhara (modern-day Uzbekistan) to inaugurate the mosque.
After the 1857 revolt, the British captured the mosque and kept their soldiers in the mosque premises. They also threatened to destroy the mosque. But could not damage the mosque due to strong opposition.
9. Allahabad Fort
The Allahabad Fort was built by the Mughal king Akbar at Allahabad in 1583. It stands on the confluence of two rivers, Ganga and Yamuna. The fort comprises massive walls, high towers, a large palace, and a temple as well.
The interior of the fort is the blend of Islamic and Hindu architecture. This fort is a significant tourist attraction, especially for the historians. Currently, Allahabad Fort is being used by the Indian Army, and only limited areas are open for the visitors.
10. Bibi Ka Maqbara
The Bibi ka Maqbara is a tomb situated in Aurangabad, Maharashtra. The tomb was commissioned by the Mughal king Aurangzeb in the 1660s in memory of his first wife, Dilras Banu Begum. It is similar to the Taj Mahal. Therefore, Biwi ka Maqbara is called ‘Dakhini Taj’ due to its strong resemblance with the Taj Mahal.
The architects of this mausoleum were Ataullah and Hanspat Rai, Attaullah was an engineer and the son of Ustad Ahmad Lahori, the chief architect of the Taj Mahal. The marble for this tomb was brought from Jaipur. The front of the mausoleum has fantastic foliage designs. The main structure is decorated with flora designs and remarkable trellis works.



