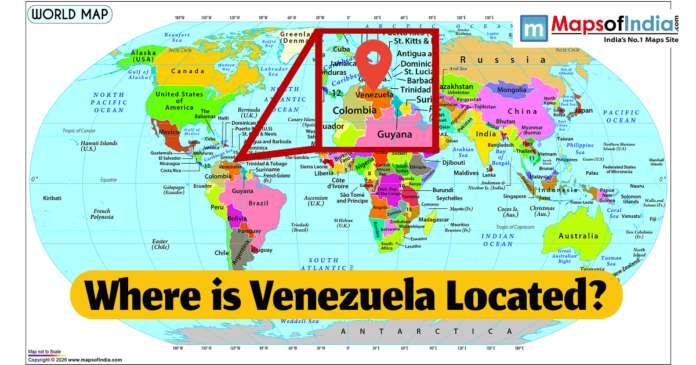
Venezuela, formally referred to as the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a state located on the northern side of South America. It is a country that enjoys a variety of geography, sources of natural resources, and a strategic position, which connects the Caribbean Sea to the mainland of South America. So its geographical position is very important to its cultural, economic and geopolitical value.
Geographically, Venezuela is situated between the latitudes of 0° and 13°N and the longitudes of 59° and 73°W. Three countries border it, and they are Colombia to the West, Brazil to the South and Guyana to the East. It borders the Caribbean Sea to the north, thus having access to various significant islands and sea routes. The coastal belt of the country is approximately 2,800 kilometres long and provides Venezuela with an assortment of ports and harbours, which are crucial in commerce and trade.
The nation is subdivided into three major regions, namely the coastal region, the central plains, and the southern highlands. Great cities on the northern coast of the Caribbean Sea include the capital, Caracas, and Maracaibo, which serves as a major oil industry hub. The Llanos or the central plains are expansive grasslands that produce food and cattle rearing. In the meantime, the southern region of the country is covered by the Guiana Highlands, where Angel Falls, the highest waterfall in the world and tropical rainforests are located.
The natural setting of Venezuela has also made it one of the wealthiest nations in the world concerning natural resources. It has the biggest proven oil reserves in the world and has huge natural gas, gold and mineral deposits. It has a strategic location in the Caribbean region that has historically resulted in it being a key player in regional trade and global politics.
Venezuela’s climate depends on its geography. Tropical climate is experienced in the coastal areas with high temperatures of humidity, whereas the highlands are cooler and temperate. Llanos also undergoes seasonal flooding that sustains a great biodiversity and a large-scale agricultural activity. This geographical heterogeneity has been playing a role in the way the country lives, its culture, and economy, throughout the centuries.
Besides physical geography, Venezuela has geopolitical significance with regard to location. It lies in Northern South America, and close to the Caribbean, thus acting as a channel between Latin America and the rest of the Atlantic world. It has international trade based on ports, and its closeness to oil-rich states has been traditionally of global economic and political concern.
Finally, Venezuela is a country in northern South America, with Colombia, Brazil, Guyana and the Caribbean Sea as its neighbours. It is an important country in the region because of its geography, natural resources and strategic position. It is characterized by its location, as it has been able to define its cultural richness, economic potential and political relevance through its locations that range from tropical coasts to highlands.