Indian Navy, also known as the Bharatiya Nau Sena, is a naval branch of the Indian armed forces whose history can be traced back to 1612. It is a wonderful way of seeing the world while serving the country.
It is the world’s fifth largest and trustworthy 3-dimensional force capable of operating above, on and underwaters. A fleet of destroyers, submarines, freights and other vessels function under the Indian Navy. The Indian Navy is responsible for the defence and protection of maritime interests of India.
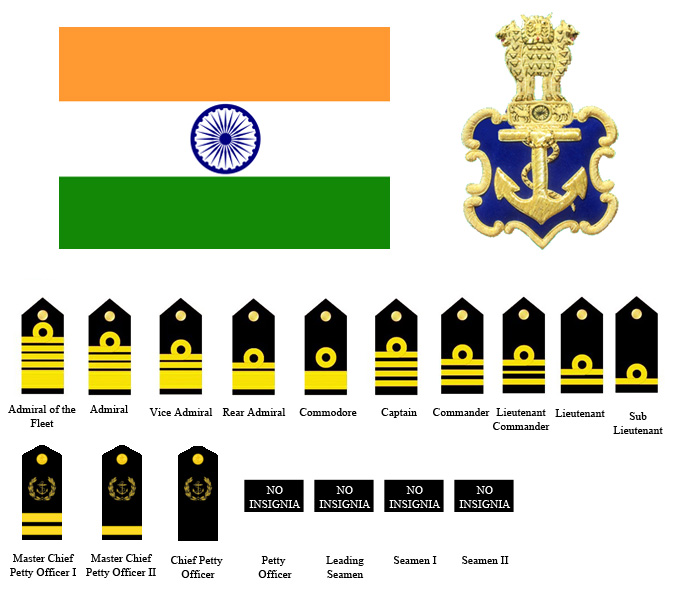
Ranks in the Indian Navy
The ranks in the Indian Navy are divided into Commissioned, Junior Commissioned, and Non-Commissioned Officer.
Commissioned Officer Ranks
1. Admiral of the fleet: Admiral of the fleet is a military naval officer of the highest rank in the Indian Navy. It is an honorary rank, which is reserved for wartime or ceremonial appointments. Till now, no officer in the Indian Navy has been bestowed with this rank.
2. Admiral: The Chief of the Naval Staff (Admiral) is the commander and the highest-ranking officer in the Indian Navy. The position of the Chief of the Naval Staff is held by a four-star officer in the rank of Admiral.
3. Vice Admiral: Vice Admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, senior to a rear admiral and junior to an admiral.
4. Rear Admiral: Rear Admiral is generally regarded as the lowest of the “admiral” ranks, sometimes referred to as “flag officers” or “flag ranks”. It is a rank above Commodore, and below a Vice Admiral.
5. Commodore: Commodore is a naval rank, superior to a navy captain, but below a rear admiral.
6. Captain: Captain is equal to the army rank of colonel. Any naval officer who commands a ship is addressed by naval custom as “captain”.
7. Commander: Commander is a naval officer rank equal to a lieutenant colonel in the Indian army. Commander is also a generic term for an officer commanding any armed forces unit.
8. Lieutenant Commander: The Lieutenant Commander is a commissioned officer rank in the Indian Navy. This rank is superior to a lieutenant and subordinate to a commander.
9. Lieutenant: Lieutenant is a commissioned officer rank in the Indian Navy. It is typically the most senior of junior officer ranks. The navy rank of lieutenant is equivalent to an army captain.
10. Sub Lieutenant: A sub-lieutenant is a commissioned officer in the Indian Navy, ranking below a lieutenant.
Junior Commissioned Officers Ranks
1. Master Chief Petty Officer (1st Class): Master Chief Petty Officer (1st Class) is the senior rank of junior commissioned officer in the Indian Navy. Although they are commissioned officers but fulfill a role similar to that of the most senior non-commissioned officers.
2. Master Chief Petty Officer (2nd Class): A Master Chief Petty Officer (2nd Class) is an officer in the Indian Navy who is designated as a junior commissioned officer distinguished from the commissioned ones, and a non-commissioned officer who is designated often by virtue of seniority.
3. Chief Petty Officer: Chief petty officer is a junior commissioned rank in the Indian Navy. They are below commissioned ranks and above non-commissioned ranks. A Chief Petty Officer is responsible for the training of junior officers and leading his division of sailors and petty officers.
Non-Commissioned Officers Ranks
1. Petty Officer: A petty officer is a non-commissioned officer in the Indian Navy. This rank is equivalent to a sergeant in the Indian Army and Indian Air Force.
2. Leading Seaman: Leading seaman is a junior non-commissioned rank equivalent to the army and air force rank of corporal.
3. Seaman 1 and 2: Seaman is a naval rank and is either the lowest or one of the lowest ranks in most navies around the world.
Careers in Indian Navy
The brilliant and challenging career in the Indian Navy is completely different from other professions. Apart from giving an opportunity to the youngsters to display their leadership skills, this career also entrusts one with a huge amount of responsibility. A career in the Indian Navy offers great facilities, a first-class lifestyle, an phenomenal way of exploring one’s life and of course, honor in serving the country. If you are prepared to deal with the stress of being on a ship and away from your loved ones for a long time while protecting your country on the Indian waters, then a career in navy could be for you. You can either join as an officer or a sailor in the Indian Navy.
Officers
An Indian Navy officer plays an essential role in the intricate system that governs a warship and also uses the ship as an equipment of strategic warfare. An officer of the Indian Navy is trained in the specializations like anti-submarine warfare, communications, navigation, logistics, gunnery, diving, and hydrography. One can also go for the aviation or submarine arm.
Women are also allowed to join the Indian Navy in the categories of Air Traffic Control, Logistics Cadre, Law Cadre, and Education.
Sailors
Sailors are responsible for running and keeping up of the propulsion machinery, weapons, sensors etc. Sailors in the Navy are imparted with requisite training at various intervals during their service. The branch and trade allotted to sailors are Executives, Electrical, Engineering, Aviation, and Submarine.
Recruitment Process in the Indian Navy
Officers
Methods for applying: The entry to this position is either through a Permanent Commission or Short Service Commission.
Permanent Commission: Selection for Permanent Commission through NDA/NA cadet and CDSE (Graduate), you have to undergo a written examination conducted by the UPSC followed by an interview with the Service Selection Board.
Short Service Commission: The candidates applying through Short Service Commission may skip the written examination. Women can only apply through this method.
Duration of the Short Service Commission: 10 years, extendable up to 14 years.
Sailors
The selection of sailors is done on the basis of a written test, followed by a physical examination and a medical examination. There are several ways of entry for a
sailor:
Direct entry for diploma holder: Subject to certain medical standards and a physical fitness test, the Navy recruits candidates who have completed a three-year diploma from a Government of India-recognised institute in one of the following fields: Mechanical, Electrical, Electronics, Telecommunications, Aeronautical, Ship Building, Instrumentation Engineering, and Metallurgy.
Artificer Apprentice: The educational qualification for an Artificer Apprentice is Class XII pass with Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics.
Senior Secondary Recruits: The qualifications of the Senior Secondary Recruits are similar to those of Artificer Apprentice.
A sailor can become a commissioned officer subject to certain conditions, depending on his performance and exam results.
Join Indian Navy and be a part of this prestigious organisation.
Explore More…………