
Where is Assam?
Assam is located along the valleys of the Brahmaputra and Barak River in the southern direction of the eastern Himalayan mountain range.
What is the Geography of Assam?
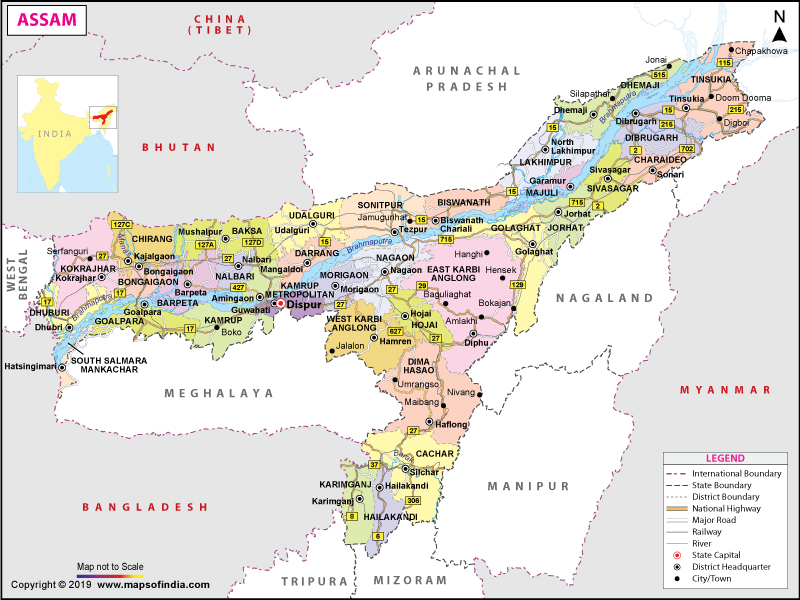
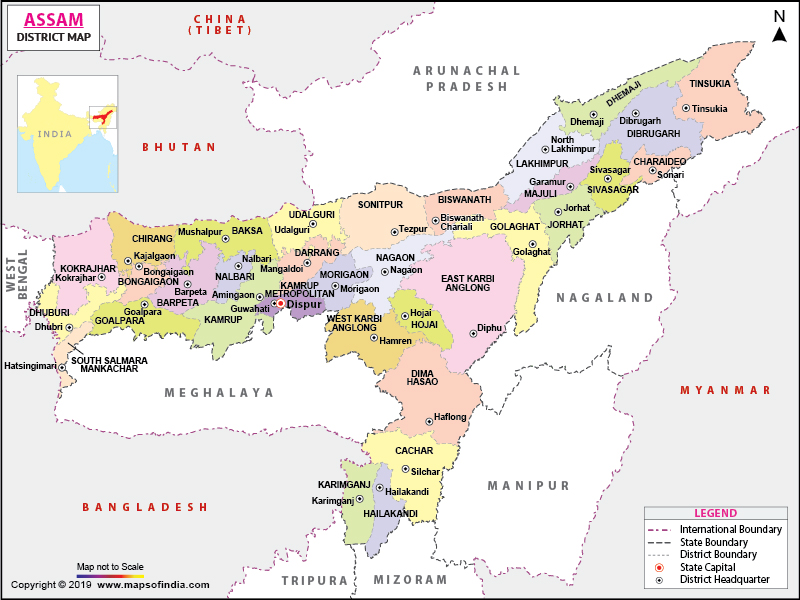
The state of Assam is spread across a total area of 78,438 sq. km (30,285 sq. mi). It shares its borders with Arunachal Pradesh in the north, Manipur and Nagaland in the east, West Bengal in the west, and Mizoram, Tripura, and Meghalaya in the south.
The major geographical characteristic features found in the country are the Northern Plains (Brahmaputra plain), the Northern Himalayas (Eastern Hills), and the Deccan Plateau (Karbi Anglong). The Brahmaputra is the main river in this state, leading to heavy rainfall throughout the year. The climate also remains cold because of the river. This river is older than the Himalayas and is the lifeline of the state.
The Brahmaputra river creates a flood plain. The Brahmaputra Valley is 1,000 km (600 mi) long and 80-100 km (50-60 mi) wide. Parts of the South Indian Plateau system are also found in this northeastern state in the forms of North Cachar and Karbi Anglong hills as well as the Khasi-Garo Hills in Guwahati.
The Barak River originates in the Barail Range along the border of Assam and Nagaland in the south. Before entering Bangladesh as Surma River, it flows by forming a 40-50 km (25-30 mi) valley through the Cachar Valley.
An unnamed peak near Laike in Dima Hasao District is the highest elevation point at 1,960 m (6,430 ft) in Assam. The lowest elevation point is at 45 m (148 ft). Some of the major rivers in the state are Brahmaputra, Burhidihing, Danshiri (South), Subansiri, Kopili and Dihang.
Read More: Geography of Assam
What is the Climate of Assam?
A Tropical Monsoon Rainforest Climate prevails in Assam. A temperate region is found in the state with heavy rainfall as well as humidity. The season of winter starts in late-October and continues till late-February. During winter, the minimum temperature varies from 6-8 ˚C (42.8-46.4 ˚F) and the rain is scanty. Early morning, as well as night, remains foggy.
The season of summer starts in mid-May. Both high humidity and rainfall accompany summer. During the summer, the maximum temperature reaches 35-38 ˚C (95-100.4 ˚F). However, frequent rain cools down the weather. It is during June when the monsoon reaches its peak. During the afternoon, thunderstorms called Bordoicila takes place.
Assam gets one of the highest amounts of rainfall in India. The average annual rainfall is around 1,800 mm (70 in) in the western parts and over 3,000 mm (120 in) in the eastern regions.
What is the Economy of Assam?
The economy of Assam is based mainly on agriculture and oil. Over half of the tea production in India is done in Assam itself. In 2018-19 (till Feb’19), the total tea production in Assam was 653.52 thousand MT. A quarter of the oil reserves in India are located in the Assam-Arakan basin, resulting in the production of 12% of the total petroleum in India. Some of the major industries of the state are tea, oil and gas, coal, cement, limestone, tourism, food processing, sericulture, and horticulture.
Around 95% of the total global Muga silk production takes place in Assam. It is also a significant producer of Eri silk (accounting for 65% of the total Eri silk production in India). During 2018-19 (till Dec’18), the output of total raw silk in Assam/Bodoland was 4,587 MT.
The nominal GSDP of the state was INR 251,588 crore (around US$ 35,051,139) in current prices in 2017-18. Assam’s Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) increased at a compound annual growth rate of 11.78% from 2011-12 to 2016-17. The total export in Assam was US$ 382.35 million during 2017-18. It was US$ 316.80 million during 2018-19 (till February 2019).
The findings of the survey (done by the Union Ministry of Labour and Employment) for the year 2009-10 shows that the unemployment rate in Assam was 6.4%, better than the national average of 9.5%. The data released by the Planning Commission shows that the level of poverty in this northeastern state had increased from 34.4% in 2004-05 to 37.9% in 2009-10.
What is the Transportation System of Assam?
Assam has 69,000 km (42,875 mi) long roadways. National highways connect all the major towns in this state. Over 2435.13 km (1513.12 mi) extended railway network is there in Assam. Broad-gauge railway tracks connect all major towns.
The most crucial airport in Assam is Lokapriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport. It connects the state with all other important Indian cities including New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, and Mumbai. There are over six civil airports in this northeast Indian state, and they are located in Guwahati, Silchar, Dibrugarh, Jorhat, Tezpur, and North Lakhimpur.
Brahmaputra River is the second National Waterway of India. On a commercial basis (for both passenger and goods transportation), two government-owned organizations (Directorate of Inland Waterways and Central Inland Waterways Corporation) operate water transport services on both Brahmaputra and Barak Rivers. The internal waterway network of Assam gives it access to multiple domestic and international ports such as Kolkata port, Haldia port, and Chittagong port.
What are the Popular Tourist Attractions in Assam?
Some of the most popular tourist spots to visit in Assam are Kaziranga National Park, Kamakhya Temple, Tocklai Tea Research Centre, Majuli Island, Manas National Park, Padam Pukhuri, Hoollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary, Panimoor Falls, Haflong Lake and Nameri National Park.
Read More: Places to Visit in Assam
![]()