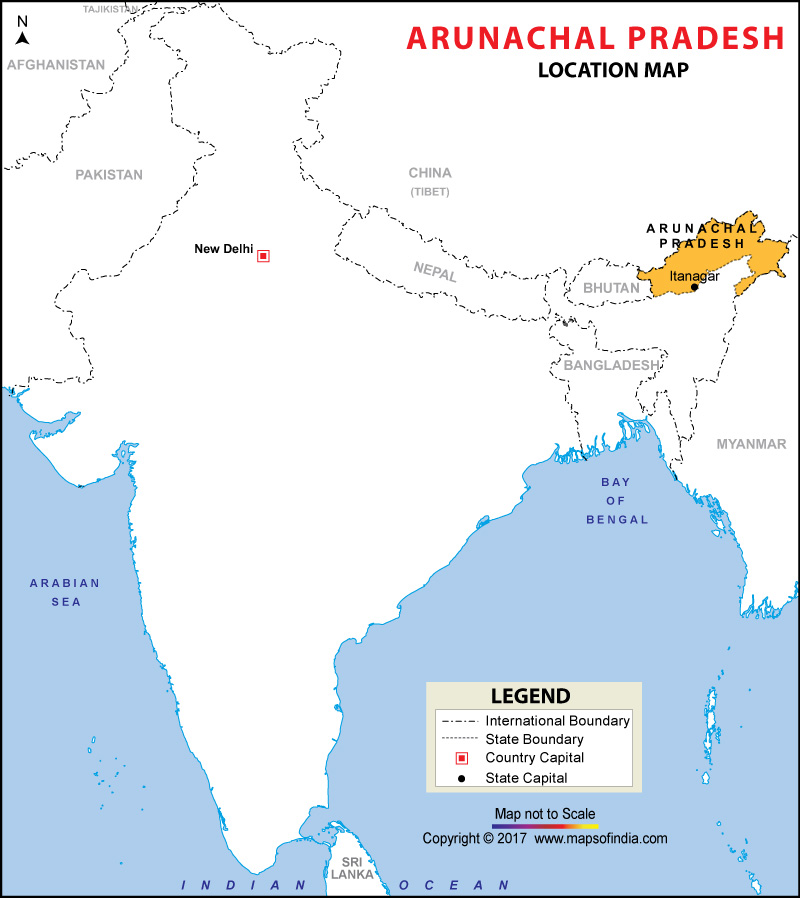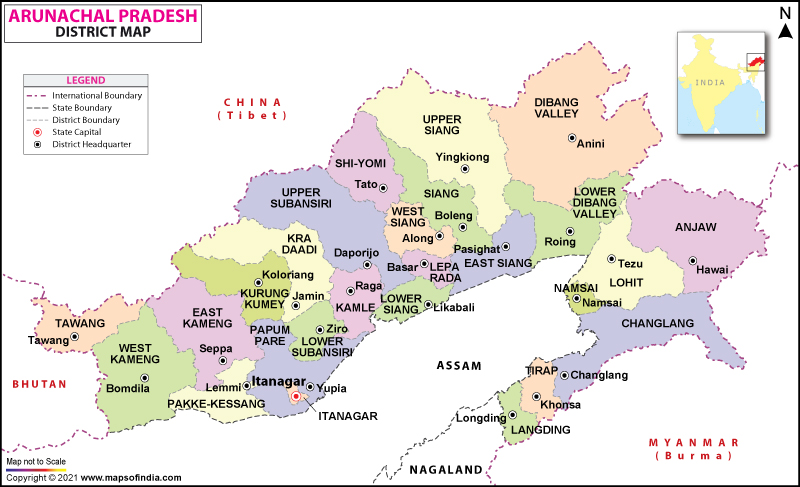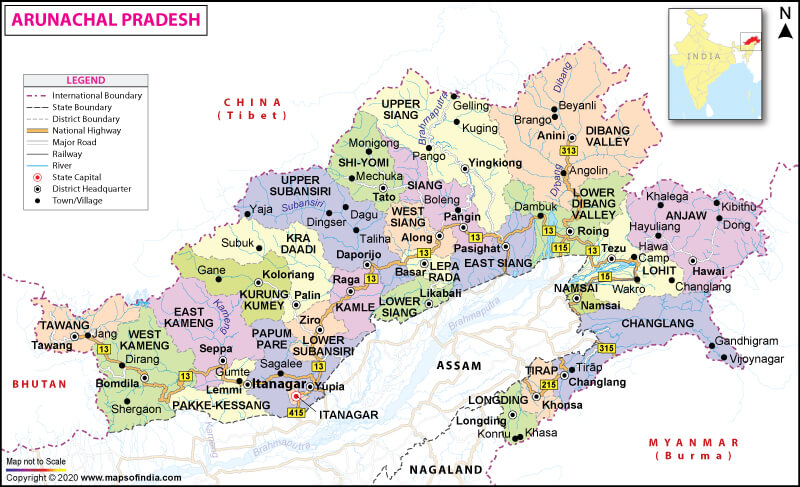

Where is Arunachal Pradesh?
Arunachal Pradesh is in the extreme northeast of India. It shares its borders with other Indian states such as Nagaland and Assam to the south. Arunachal Pradesh shares its borders with other countries such as Myanmar (440 km or 260 mi) to the east, Bhutan (160 km or 99 mi) to the west, and China (1,030 km or 640 mi) to the north. The McMahon Line is considered as the international border between Arunachal Pradesh and China.
What is the Geography of Arunachal Pradesh?
Arunachal Pradesh is the largest state among the seven states of northeast India. This state is spread across a total area of 83,743 sq. km (32,333 sq. mi).
Geographically, there are multiple natural regions in the state. Arunachal Pradesh’s first two regions are formed by the western parts of Kameng District and Tirap District. The foothills and upper, middle and the lower belts of the state form the other 3 topographical regions.
The state’s topography mainly consists of mountainous ranges as well as sub-mountainous terrains, which are located in the northern parts. A broad valley (a major characteristic feature of Arunachal Pradesh) has been created by the rivers that flow through these mountains.
Shivalik ranges encompass the state. The lofty slopes (starting from the eastern Himalayas’ snow-capped mountains and continuing to the mountainous regions in the state’s extreme north-eastern region) are an indelible part of Arunachal Pradesh’s land area. Many rivers flow through the undulating hilly terrain of Arunachal Pradesh. Some of these major rivers include Dibang, Siyum, Siang, Noa-Dihing, Lohit, Subansiri, Kamplang, Kameng, Kamla and Tirap.
Patkai hills are mainly found in the region encompassed by Lohit district, Changlang, and Tirap district. The highest Himalayan peaks found in Arunachal Pradesh are the Eastern Gorichen peak, the main Gorichen peak, Nyegi Kangsang, and Kangto.
Five river valleys divide Arunachal Pradesh, and they are the Tirap, the Lohit, the Siang, the Subansiri, and the Kameng. Siang is the most prominent river here. Kangto or Kanggardo Rize at 7,060 m (23,163 ft) (an Eastern Himalayan mountain) is the highest elevation point in Arunachal Pradesh. It is in the state’s West Kameng district along the border with the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. Major peaks present in the state are Sela Peak, Komdi Mountain, Lulupo, etc.
The eastern part of Arunachal Pradesh is separated from Tibet by the Himalayan ranges. Densely forested regions (consisting of semi-evergreen trees, broadleaf, semi-alpine forests and Alpine shrubs) can be found in the lowest elevations.
These Himalayan ranges run toward Nagaland, forming the border between India and Myanmar in the Tirap and Changlang districts. Patkai Bum Hills (lower elevation mountains than the Greater Himalayas) form the natural barrier along the border.
Read More: Geography of Arunachal Pradesh
What is the Climate of Arunachal Pradesh?
Arunachal Pradesh’s climatic condition changes in accordance with the topography as well as elevation. A hot and humid climate is found in the subtropical foothill zone. The average temperature of the place starts decreasing as elevation increases.
The temperature during summer (June-August) in the lower valleys hovers around mid-30s ˚C (mid-90s ˚F) and during winter (December-February) hover around 13 °C (mid-50s ˚F).
The extent of the annual rainfall level is around 3,300 mm (130 inches). Most of the rainfall takes place during the wet southwest monsoon, ranging from April to September. The central part of Arunachal Pradesh gets an annual rainfall level of around 4,100 mm (160 inches) or sometimes higher.
What is the Economy of Arunachal Pradesh?
The nominal GSDP of Arunachal Pradesh was INR 20,171 crore (US$ 2,815,882) at current prices in 2017-18. The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) grew at a rate of 14.06% between 2011-12 and 2017-18 to INR 243.53 billion (US$ 3.78 billion).
The state’s economy is still based on agriculture and the main crops cultivated are maize, wheat, millet, ginger, cereals, oilseeds, pulses, potato, sugarcane, and pineapple. Arunachal Pradesh has considerable mineral reserves. Over 116.55 MW hydropower generation capacity (out of the estimated potential of 50,328 MW capacities) is present in the state, as of May 2019.
The major industries present in the state are mining and mineral products (including cement), tourism, agro-based industries, plantation crops (tea, rubber, and many more), and tissue culture and floriculture. Textiles and handicrafts of this state are in high demand in the neighbouring countries. Immense international trade opportunities (especially with South Asian countries such as China, Bhutan, and Myanmar) are there in Arunachal Pradesh because of its unique location.
What is the Transportation System of Arunachal Pradesh?
The roadway is the main transport system in Arunachal Pradesh. Over 1,293 km (803 mi) long National Highway 13 (a Trans-Arunachal Highway) is the main highway in the state, which originates in Tawang and travels all along the state’s width to the south into Assam and ultimately ending at Wakro. The daily bus service is run by the Arunachal Pradesh State Transport Department.
Private bus services are also available. The nearest airport is 76 km (47 mi) away. It is the Lilabari Airport or North Lakhimpur Airport in Assam’s Lakhimpur district. Regular flights are available from Kolkata and Delhi to both Guwahati and Mohanbari.
Helicopter services connect Guwahati with Tawang and Anini. Other places with Air services are Naharlagun, Along, Yingkiong, Daporijo, Ziro, Namsai, Tezu, Changlang, Khonsa, Roing, and Pasighat.
Harmuti-to-Naharlagun, using the main Rangpara North Murkongselak railway line, is the first railway line in the state. It was opened up in late-2013. The first New Delhi-to-Naharlagun through-train was flagged off on 20 February 2015.
What are the Popular Tourist Attractions in Arunachal Pradesh?
The must-visit tourist spots in the state are Ziro Valley, Sela Pass, Namdapha National Park, Pasighat, Itanagar, Nuranang Falls, Dirang, Gorichen Peak, Bhalukpong, Tezu, etc.
Read More: Places to Visit in Arunachal Pradesh