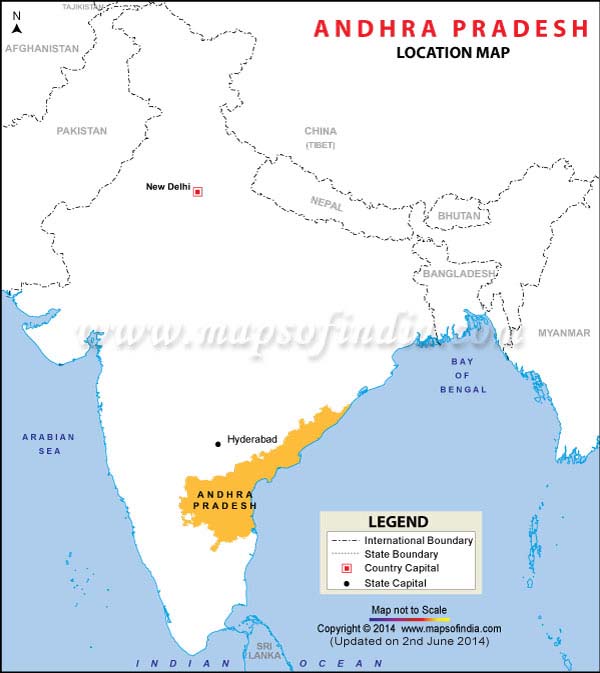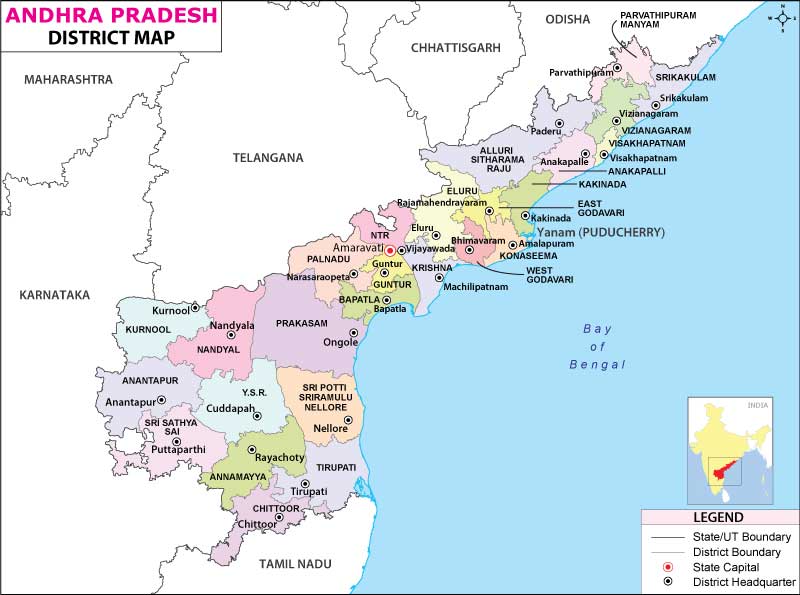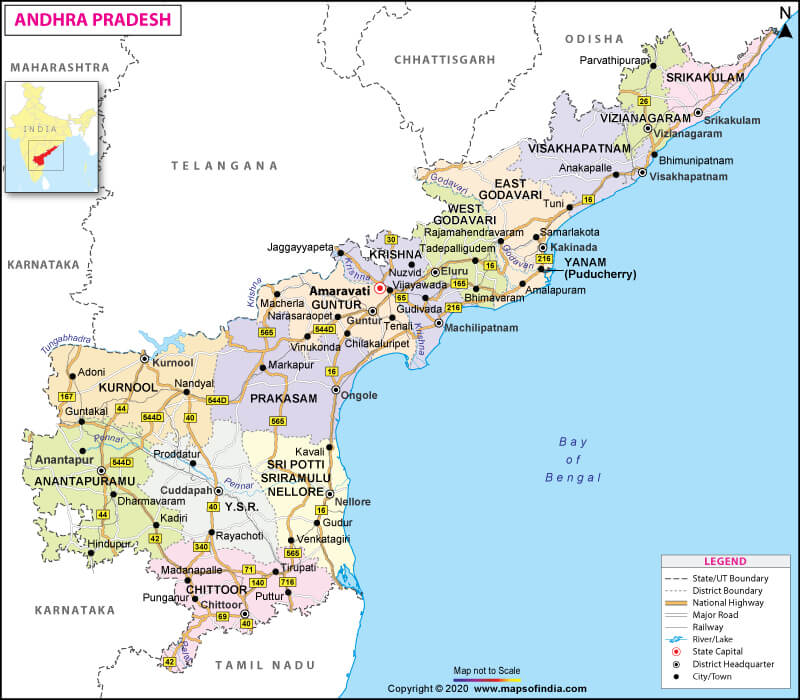

Where is Andhra Pradesh?
Andhra Pradesh is located in the southeastern part of India. It shares its border with Tamil Nadu in the south, Karnataka in the west, Odisha and Chhattisgarh in the north-east, and Telangana in the north-west. The Bay of Bengal is located to its east.
What is the Geography of Andhra Pradesh?
Andhra Pradesh is spread across a total area of 1,60,205 sq. km (61,855 sq. mi). There is around 15,000 sq. km (5,792 sq. mi) of territorial waters. The new state of Telangana was carved out of the northwestern portion of Andhra Pradesh on 2 June 2014.
Andhra Pradesh has the second-longest coastline (after Gujarat) among the states and Union Territories in India. The coast is 974 km (605 mi) long. There are two major geographical regions in the state: Rayalaseema (inland southwestern part) and Coastal Andhra (eastern and northeastern parts bordering the Bay of Bengal). Out of the total 13 districts, four districts are located in Rayalaseema and nine districts in Coastal Andhra.
Andhra Pradesh has a wide range of landforms, ranging from the hilly Eastern Ghats and Nallamala Hills to the Bay of Bengal shores. Arma Konda (also known as Jindhagada) is the highest elevation point in the state at 1,690 m (5,540 ft). It is also the tallest mountain peak in the entire Eastern Ghats.
Krishna and Godavari are the major rivers of the state. The central part of the plains (made up of fertile alluvial soil) is formed by the Krishna and Godavari deltas.
The vast coastal belt of Andhra Pradesh is spread along the Bay of Bengal, starting from Srikakulam to Nellore district. The plains form the Eastern coastal plains to the east of Eastern Ghats. The Godavari, Krishna, and Penner Rivers have created delta regions, forming the coastal plains.
The Eastern Ghats are a significant landform in Andhra Pradesh, forming the more extensive mountain system that extends from central India to the far south. They run parallel to the east coast. The mountains in the Eastern Ghats don’t form a continuous range, and on their flanks, they are highly porous.
Gneissic rock is found in the southwestern plateau region (which is generally known as Rayalaseema). The plateau has become an area of graded valleys after continued erosion. In the far southwestern parts of Andhra Pradesh, these form the highest elevations, exceeding 600 m (2,000 ft). They slope downward towards the northeast. The Penneru River creates the primary drainage system. The landscape here also has red sandy soil as well as isolated hills. In certain parts of the region, black soil is also found.
What is the Climate of Andhra Pradesh?
The month of summer starts in March and continues till June. The tropical rainy season extends from July-September and the winter season begins in October and continues till February.
During summer, the climate remains extremely hot and humid with average maximum temperature exceeding 35 °C (95 °F). In the central portion of Andhra Pradesh, the temperature surpasses 40 °C (104 °F). In the far southwest, the average minimum temperature reaches as low as 20 °C (70 °F) during night-time.
A somewhat cold temperature persists during the winter season with the minimum temperature averaging around 20 °C (70 °F) in the far southwest.
All parts of Andhra Pradesh, except the northeastern region, have the maximum temperature oscillating within 30-35 °C (86 and 95 °F). In the extreme northeastern part, the minimum temperature during winter can reach 15 °C (60 °F).
The annual rainfall level starts decreasing as you move towards the southwestern plateau area of Andhra Pradesh. While the regions in the coastal belt get around 1,000-1,200 mm (40-47 in) of annual rainfall, the western-most part of the plateau receives only half of the amount of this rain which is received by the coastal areas. The northeastern mountains receive more than 47 in (1,194 mm) of rainfall. It can sometimes receive as high as 55 in (1,400 mm) of rain.
Read More: Climate of Andhra Pradesh
What is the Economy of Andhra Pradesh?
The economy of Andhra Pradesh is one of the fastest-growing in India. The nominal gross state domestic product (at current prices) increased from Rs. 734,659 crore (around US$102,440,777) in 2017-18 to Rs. 847,056 crore (around US$9,326,239,030) in 2018-19.
The social, physical and industrial infrastructure of Andhra Pradesh is significantly developed, especially the virtual connectivity. The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade’s (DPIIT) data shows that the equity inflow of FDI was US$ 18.469 billion during April 2000-March 2019.
Currently, there are 19 operational SEZs in different sectors (IT, leather, pharma, food processing, apparel, footwear, etc.) present in the state. Andhra Pradesh (AP) boasts of being the first state in India to enact the Industrial Single Window Clearance. The World Bank has ranked AP as the topmost state in India in terms of ease of doing business.
The latest CMIE survey has found out that there is no unemployment rate among people having no education. However, 25.32% of the graduates (5,51,000 graduates) are unemployed. The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) Report 2017 shows that 21% of the 50 million population in Andhra Pradesh are living in multidimensional poverty.
What is the Transportation System of Andhra Pradesh?
Andhra Pradesh has a total 53,403 km (33,183 mi) of roadways, out of which 6,401 km (3,977 mi) are national highways, 14,722 km (9,148 mi) are state highways, and 32,280 km (20,060 mi) district roads. Over 3703.25 km (2,301 mi) long railway network (broad gauge) is present in the state.
Seven operational airports are there in Andhra Pradesh, out of which three are international, three regional/domestic, and one is private (Sri Sathya Sai Airport in Puttaparthi). Visakhapatnam, Vijayawada, and Tirupati are the international airports of the state. Visakhapatnam is the largest cargo-handling seaport in Andhra Pradesh.
What are the Popular Tourist Centers in Andhra Pradesh?
The most popular tourist destinations in the state are Vizag, Raku Valley, Tirumala’s Sri Venkateswara Temple, Borra Caves, Talakona Waterfalls, Belum Caves, Mantralayam, Gandikota, Rajahmundry, Amaravati, Srikalahasti, Ahobilam, Papikondalu, Srisailam, etc.
Read More: Tourist Places in Andhra Pradesh