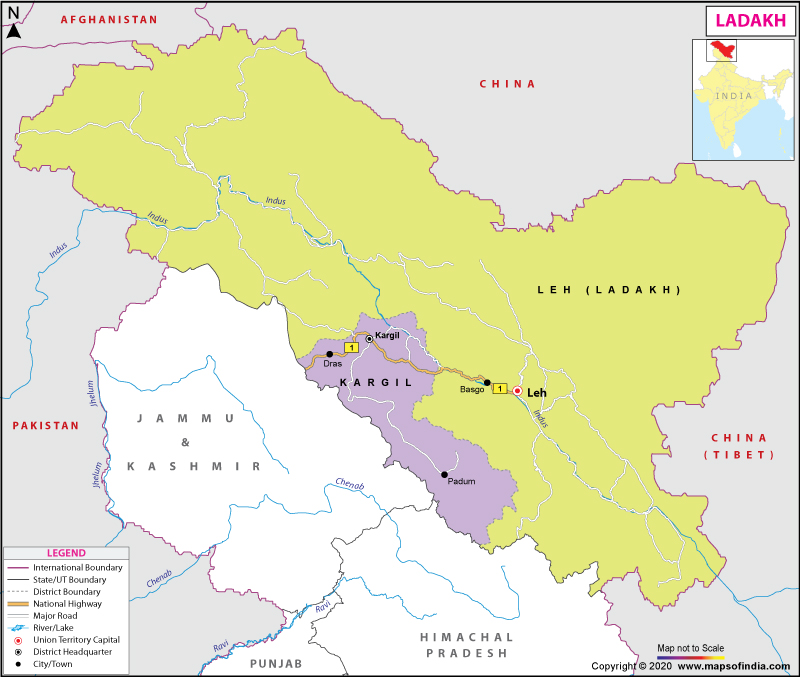

Where is Ladakh?
Ladakh is a region in the northern part of India. India administers it as a union territory. This region is subject to dispute between Pakistan (northwest), India (southeast), as part of Ladakh union territory until October 31, 2019, part of Jammu and Kashmir state; adding in, China presides over northeastern Ladakh. As Ladakh is a part of the strategically significant Kashmir region, the Indian military perpetuates a strong presence in the area. The largest town is Leh, which comprises Indus, Shyok, and Nubra river, followed by Kargil, which includes Suru, Dras, and Zanskar river valleys. Ladakh is dominated by the non-muslim population, unlike its neighbour Jammu and Kashmir. Further, the main religious groups in the region are 46% Muslims, 40% Tibetan Buddhists, 12% Hindus, 2% (others).
What is the Geography of Ladakh?
In one of the highest regions of the world, Ladakh envelopes 59,146 sq. km (45,000 sq. miles) and encompasses the Ladakh range, which is the southeastern extension of the Karakoram Range, and the Upper Indus River valley. The natural attributes of Ladakh are mainly deep valleys and high plains. High plains that are prevalent in the east subsides towards the west. It is adjoined with Tibet in the east, Lahaul, and Spiti in south, Jammu & Kashmir in the west, and the trans-Kunlun territory of Xinjiang in the north. The mountain here was formed over 45 million years by the embossing of the Indian plate into the more static Eurasian Plate. The Indus River in Ladakh sites some essential towns close to its banks.
On the other hand, The Siachen Glacier, which is 70 km long, is located in the eastern Karakoram range of the Himalaya Mountains along the altercated India-Pakistan border. It is not only the largest glacier in the Karakoram but also the second-longest in the world’s non-polar areas. The altitude of this glacier is 18,8745 feet (7537 meters), which further covers parts of both India and China. Ladakh’s highest peak is at an elevation of 25,171 feet (7672 meters).
What is the Climate of Ladakh?
Ladakh’s climate is cold and dry, with an average annual precipitation of roughly 3 inches. Sometimes, the region also witnesses beautiful, dry, and flaked snow. In Ladakh, summer commences from May to the end of August. Usually, the temperature here remains chilly and sometimes goes up to 33° C. For a trip to Ladakh, summers are the ideal since one can witness clear skies, which further offers panoramic views of the mountains. While summers are comparatively pleasant, winters in this part are harsh. Winters occur from October to May. In winters, old frost bites and snowfall are common here. During winters, Mercury level declines to very well below 0° C, and the whole area is smothered with snow. In peak winters, the temperature of Ladakh goes down to – 30° C, and the minus temperature remains for almost three months i.e., December to February.
What is the Economy of Ladakh?
The Union Territory has a system for irrigation, where it uses a network of channels which water from the ice and snow of the mountains. The principal crops here are barley and wheat. Rice has become a cheap staple now after it was subsidized by the government, earlier it was opulence in the Ladakhi diet. The traditional crop of the Union Territory is naked barley, the growth of which varies from its altitude.
Apart from agriculture, a minority of Ladakhi people are also employed as merchants and caravan traders who trade in textiles, carpets, dyestuffs, and narcotics between Punjab and Xinjiang. However, international trade completely stopped due to disputes. Ladakh is bestowed with vast hydropower from the Indus river.
What is the Transportation System of Ladakh?
In Ladakh, there is about 1,800 km (1,100 mi) of roads, of which about 800 km (500mi) are surfaced. Ladakh has an airport in Leh called Kushok Bakula Rimpochee Airport from which a daily flight to Delhi and a weekly flight to Srinagar and Jammu operates. Further, there are two airstrips as well at Daulat Beg Oldie and Fukche for military transport. For civilian flights, there was an airport called Kargil Airport, which is now used by the Indian Army.
What are the Popular Tourist Attractions of Ladakh?
Some of the popular tourist attractions in Ladakh are Pangong Lake, Zanskar Valley, Khardung La, Magnetic Hill, Leh Palace, Chadar Trek, Tso Moriri, Nubra Valley, Shanti Stupa Ladakh, Phugtal Monastery, Hemis National Park, Hemis Monastery, Spituk Monastery, Stok Palace, Alchi Monastery, Namgyal Tsemo Monastery, Chemrey Monastery, Tso Kar, Likir Monastery, Lamayuru, Sankar Gompa, Dha Hanu, Sindhu Darshan Festival, Nyoma, Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary, Hall of Fame Ladakh, Bactrian Camel Safari in Nubra Valley, Panamik Village, Yarab Tso Lake, MoonLand Lamayuru, Darcha Padum Trek, Maitreya Buddha, Samstanling Monastery, Wanla Monastery, Lamayuru Monastery.
Related Map: