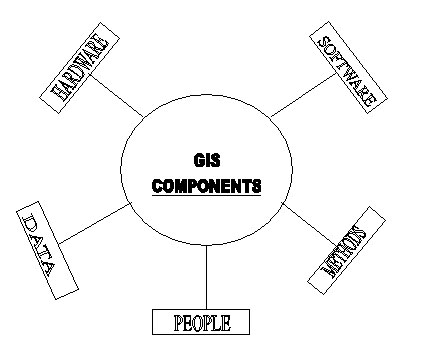
Geographical Information System has three important components: computer hardware set of application modules and a proper organization context.
A working GIS integrates five key components: -
Computer Hardware Module: The general hardware component of a geographical information system is the computer or central processing unit. It is linked to a disk drive storage unit, which provides space for storing data and programs. A digitizer, scanner and other device is used to convert data from maps and documents into digital form and send them to computer. A digitizer board is a flat board used for vectorisation of any map object. A plotter or other kind of display device is used to present the result of the data processing and a tape device is used for storing data or programs on magnetic tape.
Computer Software Module The GIS software includes the programs and the user interface for driving the hardware. GIS software is essential to generate, store, analyze, manipulate and display geographic information or data. A good GIS software requires user friendliness, functionalities, compatibilities, updatability, documentation, costeffectivness. The following is a list of GIS software producers and their main products.
- Environmental Systems Research Institute ( ESRI ): ArcInfo, ArcView.
- Autodesk: AutoCAD Map
- Clark Labs: IDRISI
- International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth Sciences: ILWIS
- Mapinfo Corporation: Mapinfo.
- Bentley Systems: Microstation.
- PCI Geomatics: PAMAP
- TYDAC Inc. : SPANS
Data Data is the most important component of a GIS. Geographic data and related tabular data can be collected in house, compiled to custom specifications and requirements, or purchased from a commercial data provider. A GIS can integrate spatial data with other existing data resources, often stored in a DBMS. The integration of spatial and tabular data stored in a DBMS is a key functionality afforded by GIS.
People GIS technology has limited value without the people who manage and develop plans for applying it to real world problems. GIS user range from technical specialists who design and maintain the system to those who use it to help them perform their everyday work. The identification of GIS specialist's vs. end users is often critical to the proper implementation of GIS technology. This is what called 'brain ware' which is equally important as the Hardware and software. Brain ware refers to the purpose and objectives, and provides the reason and justification, for using GIS.
Method A successful GIS operates according to a well designed implementation plan and business rules, which are the models and operating practices unique to each organization.
For many years, though GIS has been considered to be too difficult, expensive, and proprietary. The advent of graphical user interface (GUI), powerful and affordable hardware and software, and public digital data has broadened the range of GIS application and brought GIS to mainstream use.
|
|
|
|
Last Updated on 28 September 2012