- The variance of flora and fauna in a certain habitat is considered biodiversity.
- The primary components of biodiversity are species evenness and species richness.
- India is noted for its diverse biodiversity, with forests and trees covering around 24.46% of its geographical area.
- The phrase "biodiversity hotspots," coined by Norman Myers, refers to areas noted for their high biodiversity richness and endemic species.
Two main qualifying criteria for biodiversity hotspots
- To qualify as a hotspot, a location must meet the following two requirements, according to Conservation International:
- It is recommended that the location contains at least 1500 species of vascular plants, indicating a high level of endemism.
- It must include 30% (or less) of its native habitat, indicating that it is endangered.
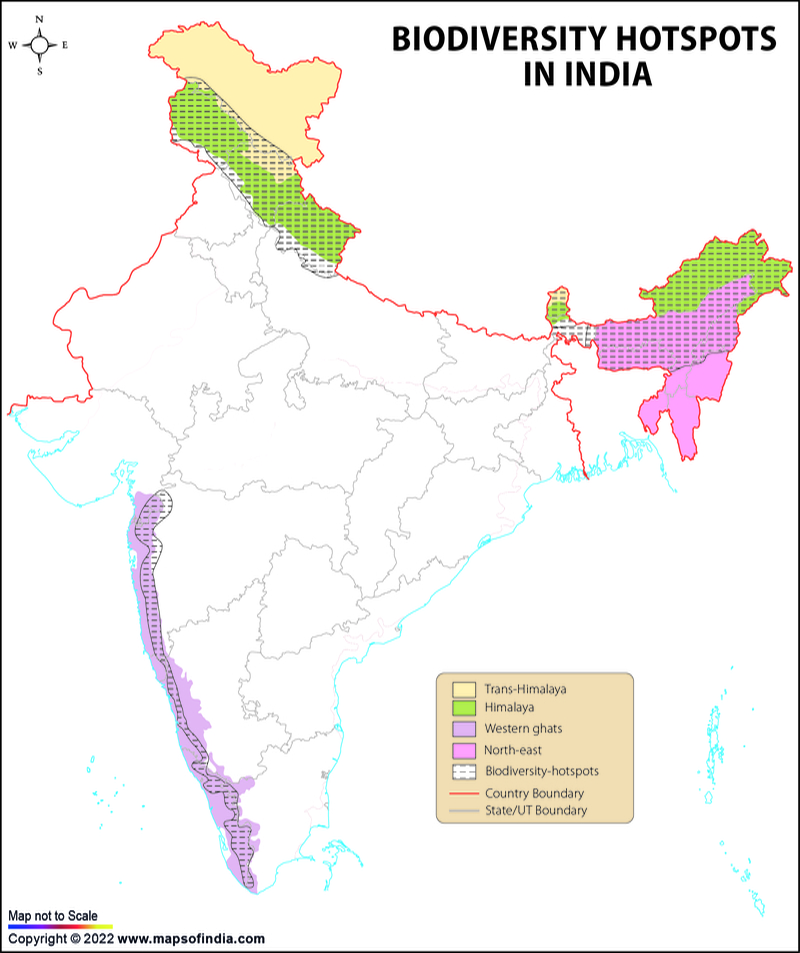
- India has four significant biodiversity hotspots that meet the criteria for being designated a biodiversity hotspot:
- The Indo-Burma region
- Himalayan Region
- Sundaland region
- Western
Region of Indo-Burma
- The Indo-Burma Region covers a total area of 2,373,000 km2.
- Six big animal species have been identified in this region in the last 12 years: the Large-antlered Muntjac, the Annamite Striped Rabbit, the Grey-shanked Douc, the Leaf Deer, the Annamite Muntjac, and the Saola.
- It is particularly noteworthy for its endemic freshwater turtle species, the majority of which are at risk of extinction due to overfishing and habitat destruction.
- There are also 1,300 bird types, including the critically endangered, Orange-necked Partridge, White-eared Night-heron, and Grey-crowned Crocias.
The Himalayan Mountains
- The Himalayas (overall) encompass North-East India, Central and Eastern Nepal, and Bhutan and are considered the tallest in the world.
- This region (NE Himalayas) is home to 163 endangered species, including the Wild Asian Water Buffalo and the One-horned Rhino, as well as 10,000 plant species, 3160 of which are indigenous.
- This mountain range encompasses almost 750,000 square kilometres.
Sundaland
- Sundaland is a South-East Asian hotspot that includes Thailand, Indonesia, Brunei, Singapore, and Malaysia.
- Sundaland was designated a World Biosphere Reserve by the United Nations in 2013.
- This region is well-known for its diverse terrestrial and marine ecosystems.
- Sundaland is one of the world's ecologically richest regions, with 25,000 species of vascular flora, 15,000 of which are unique to this region.
The Western Ghats
- A large portion of the deciduous and rain forests in peninsular India are found in the Western Ghats, which run across the western edge of the peninsula.
- In addition to its flora and fauna species, it is also home to an estimated 325 species of globally endangered fish, amphibians, reptiles, and amphibians, according to UNESCO.
- Originally covering 190,000 km2, the flora in this region has been degraded to 43,000 km2.
Last Updated on : January 14, 2026