Question 1. What are the Characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
Answer:
1. Large number of buyers and sellers
2. Homogeneous product
3. Free entry and exit of firms
4. Perfect knowledge about the market
5. Perfect mobility of factors of production
6. Absence of transportation and selling cost
Question 2. What is price line under perfect competition?
Answer :
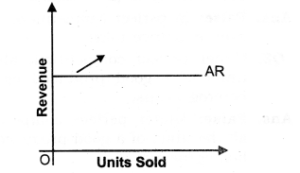
1. The price line shows the relationship between the market price and a competitive firm’s output level,
2. The vertical height of the price line is equal to the market price as shown in the given figure.
Question 3. What is the relation between market price and average revenue of a price taking firm (i.e. perfectly competitive firm)?
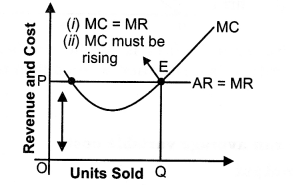
Answer: The average revenue (AR) of a firm is defined as total revenue per unit of output sold. Let a firm’s output be Q and the market price be P, then TR equals P x Q. Hence,
AR=TRQ=P×QP=P
In other words, for a price-taking firm, average revenue equals the market price.
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Define market for a good.
Answer: Market refers to a region where buyers and sellers of a commodity come in contact with each other to effect the transactions of purchase and sale of the commodity.
Question 2. What are the main forms of market?
Answer: (i) Perfect competition (ii) Imperfect competition.
Monopoly
Monopolistic competition
Oliopolgy.
Question 3. Define perfect competition.
Answer: It refers to a market situation in which buyers and sellers operate freely and a commodity sells at a uniform price.
Question 4. What do you mean by homogenous product?
Answer: Products sold in the market are homogeneous, i.e., they are identical in all respects like quality, colour, size, weight, design, etc.
Question 5. In which market forms are average revenue and marginal revenue of a firm always equal?
Answer: Perfect competition.
Question 6. In which market form does a firm face a perfectly elastic demand curve?
Answer: Perfectly competitive market.
Question 7. What induces new firms to enter an industry?
Answer: Abnormal profits, i.e., above normal profits.
Question 8. If the firms are earning abnormal profits how will the ‘number of firms in industry change?
Answer: The number of firms in the industry will increase.
Question 9. In which market form are goods sold at a uniform price?
Answer: Perfect competition.
Question 10. Why are selling costs not incurred in perfect competition?
Answer: Selling costs are not incurred in perfect competition as there exists perfect knowledge among the buyers and sellers.
Question 11. What is meant by the term ‘price – taker ‘ in the context of a firm?
Answer: A firm is said to be a price-taker if it has to accept the price, as determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
Question 12. Under which market form a firm is a price-taker?
Answer: Perfect competition.
Question 13. What is a price taker firm?
Answer: A price taker firm is one which has no option but to accept the price as determined by the industry as in perfect competition.
II. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain feature of homogeneous product. Or
Explain the implication of : homogeneous product.
Answer:
1. Products sold in the market are homogeneous, i.e., they are identical in all respects like quality, colour, size, weight, design, etc.
2. The products sold by different firms in the market are equal in the eyes of the buyers.
3. Since, a buyer cannot distinguish between the product of one firm and that of another, he becomes indifferent as to the firms from which he buys.
4. The implication of this feature is that since the buyers treat the products as identical they are not ready to pay a different price for the product of any one firm. They will pay the same price for the products of all the firms in the industry. On the other hand, any attempt by a firm to sell its product at a higher price will fail.
To sum up, the “homogeneous products” feature ensures a uniform price for the products of all the firms in the industry.
Question 2. “In perfect competition, industry is the price maker and firm is the price taker.” Discuss.
Answer: Yes, this statement is true.
1. As we know, in Perfect competition, homogeneous goods are produced. So, industry cannot charge different price from different firms.
2. So, industry will give that price to the firm where industry is in equilibrium, i.e., where Demand = Supply. Any movement from that point would be unstable.
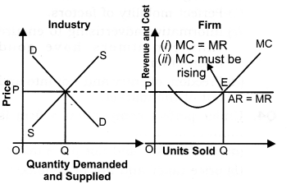
3. In the given diagram, price and revenue is measured on vertical axis and units of commodity on horizontal axis. Industry will give OP price or point E to the firm as at that point Demand = supply, i.e., industry is in equilibrium. The firms will follow the same price and charges same from the consumer.
Question 3. Explain features of perfect knowledge about the market.
Answer:
1. Perfect Knowledge means both buyers and sellers are fully informed about the market.
2. The firms have all the knowledge about the product market and the input markets. Buyers also have perfect knowledge about the product market.
3. Let us first take the product market. The implication of perfect knowledge about the product market is that any attempt by any firm to charge a price higher than the prevailing uniform price will fail. The buyers will not pay because they have perfect knowledge. A uniform price prevails in the market.
4. Regarding the knowledge about the input markets the implicit assumption is that each firm has an equal access to the technology and the inputs used in the technology.
5. No firm has any cost advantage. Cost structure of each firm is the same.
6. Since there is uniform price and uniform cost in case of all firms, and since profit equals revenue less cost, all the firms earn uniform profits.
Question 4. What is the relationship between TR, AR and MR under perfect competition?
Answer:
1. In the perfect competition, a firm is a price taker.
2. It has to sell its product at the same price as given (determined) by the industry. Consequently, price = AR = MR.
3. Hence, a firm’s AR and MR curve will be a horizontal straight line parallel to X axis.
4. Since price remains the same, i.e., MR is constant, therefore, TR increases at the Constant rate as increase in the output sold.
5. As the result of, TR curve facing a competitive firm is positively sloped straight line. Again, because at zero output Total Revenue is zero therefore, TR curve passes through the origin O as shown in the given figure.
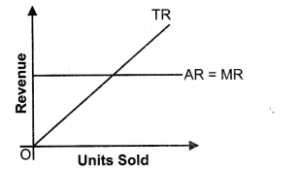
Question 5. Why is AR curve of a firm under perfect competition parallel to X-axis?
Answer:
1. AR curve of a firm under perfect competition is parallel to X-axis because in perfect competition homogeneous product are produced, that is why price remains constant and as we know AR = TR/Q = PX Q/Q = Price. So, AR remains constant.
2. As, AR is on Y-axis, that is why AR curve remains constant and parallel to X-axis.