Question 1. Explain why the demand curve facing a firm under monopolistic competition is negatively sloped?
Answer:
1. The demand curve of a firm under monopolistic competition is negatively sloped because of product differentiation.
2. The product of the sellers are differentiated but close substitutes of one another.
3. Each seller has some degree of monopoly power of ‘Making’ the price. But since there are many close substitutes available, the result is downward sloping and elastic demand curve.
Question 2. What is the reason for the long run equilibrium of a firm in monopolistic competition to be associated with zero profit?
Answer:
1. The reason why firm in monopolistic competition earns zero profit in the long run is free entry and exit of firm.
2. If firm earns super-normal profits in the short run then new entry will take place in the long run. If the firm is incurring losses in the short run, firm will leave in the long run.
3. The result is zero abnormal profits in the long run.
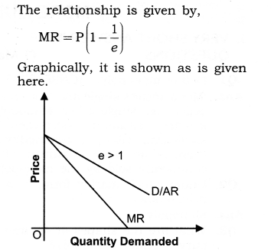
Question 3. What is the value of MR when the demand curve is elastic?
Answer: When demand curve is elastic (e > 1), MR is positive.
Question 4. List the three different ways in which oligopoly firms may behave.
Answer: Oligopoly firm may—:
1. cooperate with each other and formally have a contract or written document of their policies.
2. cooperate with each other but have tacit (informal) understanding.
3. not cooperate with each other.
Question 5. What is meant by prices being rigid? How can oligopoly behaviour lead to such an outcome?
Answer:
1. Price rigidity refers to a situation in which whether there is change in demand and supply, the price tends to stay fixed.
2. In an oligopolistic market firms . are in a position to influence the prices.
3. However, they stick to their prices in order to avoid a price war. If a firm tries to reduce the price the rivals will also react by reducing their prices. So, it will be of no benefit.
4. Likewise, if a firm tries to raise the price other firms will not do so. As a result, the firm which intended to raise the price will lose its customers. So, oligopoly behaviour leads to price rigidity in an oligopolistic market.
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Define monopoly.
Answer: ‘Mono’ means single and ‘poly’ means seller, i.e., single seller. Monopoly is a market situation where there is a single firm selling the commodity and there is no close substitute of the commodity sold by the monopolist.
Question 2. Under which market form, firm is a price-maker?
Answer: Monopoly.
Question 3. What are the shapes of AR and MR curves under monopoly?
Answer: Both AR and MR curves slope downward s. ‘
Question 4. How many firms are there in a monopoly market?
Answer: One firm.
Question 5. What is a price-maker firm?
Answer: A price maker firm is one to fix the price itself because of its monopoly power.
Question 6. What does Monopolistic Competition mean?
Answer: It refers to a market situation in which there are many firms which sell closely related but differentiated products.
Question 7. Why is the demand curve under monopoly less elastic as compared to the demand curve under monopolistic competition?
Answer: Demand curve under monopoly is less elastic as compared to the demand curve under monopolistic competition due to absence of close substitutes in monopoly.
Question 8. Define product differentiation.
Answer: Product differentiation refers to differentiating the products on the : basis of brand, size, colour, shape, etc.
Question 9. In which form of market there is product differentiation?
Answer: Monopolistic competition.
Question 10. Give the meaning of ‘Oligopoly’.
Answer: Oligopoly is a market situation in which an industry has only a few firms (or few large firms producing most of its output) mutually dependent for taking decisions about price and output.
II. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. A monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price. Give reasons with true or false.
Answer: False: A monopolist cannot sell any quantity he likes at a price.
1. A monopolist faces a downward sloping demand curve because of price discrimination which means that a monopolist can sell more quantity only by lowering the price.
2. A monopolist controls only the supply of the product and not the demand of the product.
Question 2. Why AR curve (demand curve) under monopolistic competition is more elastic than AR curve under monopoly?
Answer:
1. AR curve under both the markets slope downwards.
2. However, AR curve under monopolistic competition is more elastic as compared to AR curve under monopoly because of presence of close substitutes.
3. AR curve is less elastic in monopoly because of no close substitutes.
Question 3. Explain the feature of few firms in an oligopoly market.
Answer:
1. The number of sellers in an oligopoly market is small—when there are two or more than two, but not many sellers.
2. What matters is that these few sellers account for most of the industry’s sales.
3. These “few” sellers consciously dominate the industry and indulge in intense competition. Each firm is aware of that it possesses a large degree of monopoly power.
4. For example, the market for mobile service provider in India is an oligopolist structure as there are only few producers of mobile service provider. There exists severe competition among different firms and each firm tries to manipulate both prices and volume of production to outsmart each other.
Question 4. Explain the main features of barriers to the entry of firms.
Answer:
1. The main reason why the number of firms is small is that there are barriers which prevent entry of firms into industiy.
2. Patents, large capital, control over the crucial raw material etc, prevent new firms from entering into industry.
3. Only those who are able to cross these barriers are able to enter.
Question 5. Give reasons for the following statements:
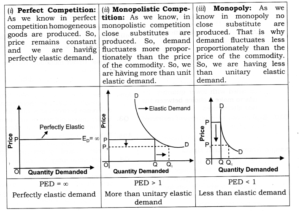
1. Demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is a horizontal straight line.
2. Demand curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm is a downward sloping curve.
3. Demand curve facing a monopoly firm is less elastic than that curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm.
Answer:
1. Under perfect competition, every firm is a price-taker firm. The price is set by industry demand and supply. Therefore, every firm faces a horizontal straight line demand curve indicating that it can sell any quantity at the given price.
2. A monopolistic competitive firm has to design its own pricing strategy. It can expect to sell larger quantity at a lower price, and vice-versa. Hence, its demand curve slopes downwards.
3. A monopolist is the only producer of a good which has no close substitutes. A monopolistic competitive firm, on the other hand, produces a good that has several close substitutes. Hence, the demand curve facing a monopolistic competitive firm is more elastic than that faced by a monopoly firm.
Question 6. Draw a demand curve in different market situation and also compare its elasticity of demand.
Answer: