I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following documents are not required for obtaining an export license?
(a) IEC number
(b) Letter of credit
(c) Registration cum membership certificate id) Bank account number
Question 2. Which of the following documents is not required in connection with an import transaction?
(a) Bill of lading (b) Shipping bill
(c) Certificate of origin (d) Shipment advice
Question 3. Which of the following do not form part of duty drawback scheme?
(a) Refund of excise duties
(b) Refund of customs duties
(c) Refund of export duties
(d) Refund of income dock charges at the port of shipment
Question 4. Which one of the following is not a document related to fulfill the customs formalities?
(a) Shipping bill (6) Export license
(c) Letter of insurance (d) Performa invoice
Question 5. Which one of the following is not a part of export documents?
(a) Commercial invoice (b) Certificate of origin
(c) Bill of entry (d) Mate’s receipt
Question 6. A receipt issued by the commanding officer of the ship when the cargo is loaded on the ship is known as:
(a) Shipping receipt (b) Mate receipt
(c) Cargo receipt (d) Charter receipt
Question 7. Which of the following document is prepared by the exporter and includes details of the cargo in terms of the shippers name, the number of packages, the shipping bill, port of destination, name of the vehicle carrying the cargo?
(a) Shipping bill (b) Packaging list
(c) Mate’s receipt (d) Bill of exchange
Question 8. The document containing the guarantee of a bank to honour drafts drawn on it by an exporter is
(a) Letter of hypothetication (b) Letter of credit
(c) Bill of lading (d) Bill of exchange
Question 9. Which of the following does not belong to the World Bank group?
(a) IBRD (6) IDA
(c) MIGA (d) IMF
Question 10. TRIP is one of the WTO agreements that deal with:
(a) Trade in agriculture (b) Trade in services
(c) Trade related investment measures (d) None of these
Answers:
1. (b) 2. (a) 3. (d) 4. (d) 5. (c)
6. (b) 7. (a) 8. (b) 9. (d) 10. (d)
II. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Discuss the formalities involved in getting an export license.
Answer:Before exporting goods, it is mandatory for exporters and export firms to fulfill the legal formalities, including securing an export license. The following are the formalities to obtain an export license.
1. Bank account number:An exporter must open an account in a bank authorised by the Reserve Bank of India and get an account number.
2. IEC code:An export firm must obtain an IEC (Importer Exporter Code) from the Directorate General for Foreign Trade (DGFT) or the Regional Import Export Licensing Authority by submitting documents such as the exporter’s profile, prescribed certificates, two attested photographs and details of non-resident interest.
3. Registration-cum-membership certificate:An export firm should get itself registered with the appropriate Export Promotion Council, such as the Engineering
Export Promotion Council (EEPC) and the Apparel Export Promotion Council (AEPC), and obtain a Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC).
4. Registration with ECGC:An export firm must also get itself registered with the ECGC (Export Credit and Guarantee Corporation) in order to protect itself from any uncertainties in payments brought upon by political or commercial risks.
Question 2. Why is it necessary to get registered with an Export Promotion Council?
Answer: If a firm wants to export goods, then it must first obtain an export license. In order to obtain an export license, the firm is required to register itself with the Appropriate Export Promotion Council, such as the Engineering Export Promotion Council (EEPC) and the Apparel Export Promotion Council (AEPC). Such councils are set up by the government for promoting the export of various goods falling under their purview. O ice the registration is complete, the firm obtains the Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate (RCMC). This in turn enables it to take advantage of the benefits made available to export firms by the government. Thus, it is necessary for export firms to register themselves with an Export Promotion Council.
Question 3. What is IEC number?
Answer: An TEC number refers to the ‘Importer Exporter Code number. It is a 10-digit number granted by the Directorate General for Foreign Trade (DGFT) to an import/export firm depending upon the firm’s credibility. It is essential for an importer/ exporter to obtain this number as it is to be provided in various import/export documents. In order to obtain this number, an export or import firm submits an application to the DGFT or the Regional Import Export Licensing Authority along with documents and information such as the profile of the importer/exporter, fee receipt from a bank, non-resident’s interest details, certificate from the banker on the prescribed form, two photographs attested by the banker and a declaration about the applicant’s non-association with firms placed in the caution list. Once the final submission is done and authenticated, the DGFT or the Regional Import Export Licensing Authority issues an IEC number to the importer/exporter, which helps the firm concerned in availing itself of benefits granted by the DGFT to importers/exporters.
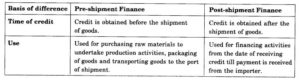
Question 4. What is pre-shipment finance?
Answer: As soon as order is confirmed and letter of credit is received, the exporter approaches the bank to receive pre-shipment finance which he needs to buy raw materials and other inputs to produce good to be exported. Firms require finance for various activities such as purchase of raw material and manufacture of goods. In the case of exporters, this finance is obtained from banks in the form of advances known as pre-shipment finance. These advances are called pre-shipment finance as they are used in operations completed before the final shipment of goods takes place. This type of credit is obtained by an exporter from his or her banker after the order has been confirmed and the letter of credit has been received from the importer. Once the bank extends credit, the exporter uses the funds to purchase raw materials to undertake production. Preshipment finance is also used for processing and packaging goods and transporting them to ports for shipment.
Question 5. Why is it necessary for an export firm to go in for pre-shipment inspection?
Answer: Pre-shipment inspection refers to the inspection of goods before their final shipment in order to ensure that only quality goods are exported. The Government has initiated measures such as compulsory inspection of certain goods by promulgating the Export Quality and Inspection Act, 1963, and designating various agencies to undertake inspection. Exporters are required to contact the Export Inspection Agency (EIA) or another designated agency and obtain an inspection certificate after getting the goods checked. However, in the case of goods exported by star trading houses, export houses, 100 per cent export-oriented units and industrial units set up in Export Processing Zones (EPZs) or Special Economic Zones (SEZs), no such inspection is required.
Question 6. Discuss the procedure related to excise clearance of goods.
Answer:Excise duty is the amount payable on raw materials used in the manufacture of goods.
Exporters are required to pay excise duty and get excise clearance. In order to get excise clearance, a manufacturer must first submit an invoice to the Regional Excise Commissioner. The Excise Commissioner then examines the invoice and, if satisfied, issues the excise clearance to the manufacturer. However, in many cases, the government may either exempt a manufacturer from payment of excise duty or refund it after payment in case the manufactured goods are meant for export. The basic objective of such exemptions is to promote the export of goods and provide a competitive market for Indian exports in the world market.
Question 7. Explain briefly the process of customs clearance of export goods.
Answer:Before the final loading of goods for export, it is necessary for the exporter to get the goods cleared by customs. This is known as Securing Customs Clearance. In this regard, an exporter first requires to submit the following documents to the customs appraiser at the Customs House:
1. Shipping bill
2. Export order
3. Letter of credit
4. Commercial invoice
5. Certificate of origin
6. Certificate of inspection, if necessary
7. Marine insurance policy.
After the submission of the documents, a carting order is obtained from the superintendent of the port concerned. The carting order acts as a gate pass for the cargo to enter the dock as it gives the necessary instructions to the staff. The physical movement of cargo then takes place from the dock to the port area and finally the goods are stored in an appropriate storage. It may not be possible for the exporter to be present at all times for performing these formalities, and therefore the task is assigned to a Clearing and Forwarding (C and F) agent.
Question 8. What is Bill of Lading? How does it differ from bill of entry?
Answer:Bill of Lading is an essential document required at the time of an export transaction. It is issued by the shipping company as a token of acceptance that the goods have been put on board in its vessel. A Bill of Lading is an undertaking from the shipping company to transfer the goods to the port of destination. Bills of Lading are freely transferable.
In contrast, a Bill of Entry is required at the time of an import transaction. It is a form supplied by the customs office and filled by the importer once the goods are received. A Bill of Entry is submitted at the customs office with information such as the name and address of the importer, name of the ship in which the goods were transported, number of packages, marks on the package, description of imported goods, quantity and value of the imported goods, name and address of the exporter, port of destination and customs duty payable.
Question 9. What is Shipping Bill?
Answer:Shipping Bill contains information about the goods that are exported. That is, it contains particulars such as’the name of the vessel, port at which the goods are to be discharged, country of final destination and exporter’s name and address. A Shipping Bill is essential for an export transaction as it is on the basis of this document that the customs grants clearance to the export.
Question 10. Explain the meaning of Mate’s Receipt.
Answer:Mate’s Receipt is issued by the captain or commanding officer of a ship to an exporter. This receipt acts as evidence that the exporter’s cargo has been loaded on the ship. It contains information such as the name of the vessel, berth, date of shipment, condition of the cargo when it was loaded, description of the packages of the cargo, number of packages and marks on the packages. Once the port dues are received, the port superintendent gives the Mate’s Receipt to the C and F agent concerned. It is only after the Mate’s Receipt has been obtained that the shipping company will issue the bill of lading.
Question 11. What is a Letter of Credit? Why does an exporter need this document?
Answer:Letter of Credit is issued by the bank of an importer guaranteeing to honour a draft of a certain amount drawn on it by the exporter. It is an important document because, in international transactions, there is always a risk of the importer defaulting on payment once the goods are received. Thus, to minimise the risk of such defaults, the exporter often demands a letter of credit. A letter of credit enables the exporter to assess the credit worthiness of the importer. It is the most appropriate and secure method of payment for settling an international transaction.
Question 12. Discuss the process involved in securing for exports.
Answer:Once the goods for export are shipped, the importer is informed about the shipment by the exporter. However, to claim the title of the goods, the importer is required to submit various documents, such as a copy of the invoice, bill of lading, packaging list, insurance policy, certificate of origin and letter of credit. These documents are sent by the exporter and provided by the exporter’s bank only when the bill of exchange has been signed and accepted by the importer. The bill of exchange states the amount that the importer must pay to the bearer of the bill. Once the bill is received and accepted, the importer’s bank is instructed by the importer to transfer money to the exporter’s bank account.
In case the exporter wants immediate payment from his or her bank even if the payment has not been released by the importer, then he or she can secure payment by signing a letter of indemnity. This letter acts as an undertaking that the exporter will indemnify the bank, along with the accrued interest, in case of non-payment by the importer.
Last, when the exporter receives the payment from the bank, he or she obtains a bank certificate of payment. This certificate states that the necessary documents along with the bill of exchange have been presented to the importer for payment and that the payment has been received in accordance with the exchange control regulations.
Question 13. Differentiate between the following:
1. Sight and issuance drafts,
2. Bill of lading and airway bill,
3. Pre-shipment and post-shipment finance.
Answer:
1. Sight and Issuance Draft

2. Bill of Lading and Airway Bill
![]()
3. Pre-shipment Finance and Post-Shipment Finance