Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. State the need for the preparation of bank reconciliation statement?
Solution:
The need and importance of the bank reconciliation statement are as follows:
It ensures accuracy of the balances and records shown by the pass book and cash book.
It detects the errors which might have occurred in a cash book in connection with bank transactions and helps in rectifying those errors.
Regular preparation of bank reconciliation statement helps in prevention of frauds.
It detects any undue delay caused during the recording of transactions or collection of cheques.
This helps in taking appropriate action to prevent any further delay.
It keeps a check on the accuracy of entries made in both the books.
It helps in updating the cash book as per the pass book.
Q2. What is a bank overdraft?
Solution:
When a firm or an account holder withdraws excess amount over the available bank balance, the account, then, runs a negative bank balance. The negative balance is called a bank overdraft. In other words, bank overdraft is the excess of withdrawals over deposits and is considered a liability to an account holder.
Q3. Briefly explain the statement ‘wrongly debited by the bank’ with the help of an example.
Solution:
The statement ‘Wrongly debited by the bank’ is alleged when the bank wrongly debits the customer’s account. A wrong debit reduces the account balance of the customer. Wrong debits occur when a transaction is wrongly recorded or when incorrect amount is debited from an account. Such errors can occur in the following two cases:
A person has more than one account in a bank: A cheque of Rs.4,000 issued from his/her savings account was wrongly paid through his/her current account.
Amounts of cheques are wrongly recorded: A cheque payment of Rs.60,000 was wrongly debited in the pass book as Rs.6,000.
Q4. State the causes of difference occurred due to time lag.
Solution:
The causes of difference which occur because of time lag are given below:
1. Cheques issued but not presented for payment at the bank.
The firm/customer issues cheques to its suppliers or creditors. But not all these cheques are presented to the bank. The entry in the cash book is made immediately on issue of the cheque but the bank will not pass an entry until the cheque is presented for payment.
2. Cheques paid or deposited but not collected and credited by the bank.
Entry is passed by the firm in the cash book when it receives cheques from its debtors which increase the balance as per the cash book. But the bank credits the firm’s account only when they have received the payment from the customer’s bank or in other words, once the cheque is collected by the bank.
Q5. Briefly explain the term favourable balance as per cash book.
Solution:
Favourable balance is the excess of total of debit side over total of credit side in a bank column of a cash book. It is also known as debit balance as per the cash book. In other words, favourable balance means excess of deposits over withdrawals.
Q6. Enumerate the steps to ascertain the correct cash book balance.
Solution:
Most of the transaction items which normally cause differences between the balances appear only in the pass book. Such items are first recorded in the cash book to find the adjusted balance of the cash book and then the bank reconciliation statement is prepared. The below given steps are involved in the preparation of adjusted cash book.
Step 1:The bank balance as per the cash book is noted.
Step 2:All the errors committed in the cash book are to be recorded and rectified.
Step 3:Transaction present only on the credit side of the pass book needs to be recorded on the debit side of the cash book.
Step 4:Transaction present only on the debit side of the pass book needs to be recorded on the credit side of the cash book.
Step 5:Total the cash book and find the balancing figure. This balancing figure is used for preparing the bank reconciliation statement.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. What is a bank reconciliation statement? Why is it prepared?
Solution:
Business organisations maintain the cash book for recording cash and bank transactions. It shows the balance of both the accounts at the end of an accounting period.
Similarly, the bank also maintains an account for each customer in its book. All deposits made by the customer are recorded on the credit side of the account and all withdrawals are recorded on the debit side of the account.
A copy of this is sent to the customer by the bank. This is called pass book or bank statement. This statement is used by the firm to tally its bank transactions as recorded by the bank with the cash book. The balance of the cash book must tally with that of the pass book.
But as both the books are maintained by two different parties, the bank balances as shown by the cash book and that shown by the pass book do not always match. The entries in both the books are, thus, compared and the items because of which the difference has occurred are determined and rectified. Thus, to reconcile the balances of the cash book and the pass book, a statement is prepared. This statement is called the bank reconciliation statement.
Specimen of Bank Reconciliation Statement:
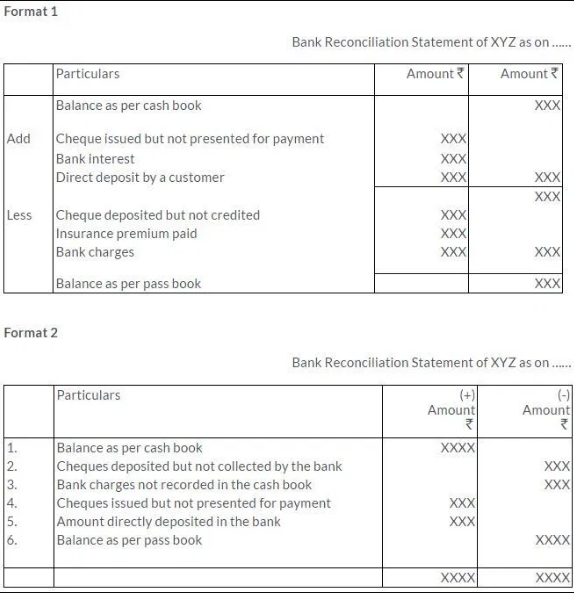
Q2.Explain the reasons where the balance shown by the bank passbook does not agree with the balance as shown by the bank column of the cash book.
Solution:
The reason for the error in balance between the cash book and pass book can be stated as follows:
Timing difference on recording of the transactions
While comparing the balances of both the accounts, transactions found usually appear only in the cash book or only in the pass book. Such differences are caused by the time gap in recording the transactions in the books relating to either receipts or payments.
Transactions which appear in the cash book but not in the pass book:
1. Cheques issued but not presented for payment at the bank
The firm/customer issues cheques to its suppliers and creditors, but not all these cheques are presented to the bank. The entry in the cash book is made immediately on issue of the cheque but the bank will not pass an entry until the cheque is presented for payment.
2. Cheques paid or deposited but not collected and credited by the bank
Entry is passed by the firm in the cash book when it receives cheques from its debtors which increase the balance as per the cash book. But the bank credits the firm’s account only when they receive the payment from the customer’s bank or in other words, once the cheque is collected by the bank.
Transactions which appear in the pass book but not in the cash book:
1. Direct bank charges, commission and interest debited by the bank
Bank provides us various services for which it levies some charges which is directly debited from the firm’s account. The firm will know of these charges only after she/he verifies the entries with the bank statement.
Example: Interest on overdraft, unpaid cheques and cheque collection charges
2. Expenses directly paid by the bank on behalf of the customers
Depending upon the standing instruction of the customer, the bank makes regular payment on behalf of the customer. The bank debits the customer’s account when the payment is made but the firm will pass the entry in his book only after he receives the bank statement. Thus, the balance as per the pass book will be less than the balance in the cash book.
Example: Insurance premium, telephone bills and rent
3. Amounts directly deposited in the customer’s account
There are times when the firm’s debtors deposit money or make payments directly into the firm’s bank account. This results in an increase in the balance of the bank account. As no intimation is received by the firm, there will be no record of the same in the cash book.
4. Incomes directly collected by the bank on behalf of customer but not recorded in cash book
As per the agreement between the customer and the bank, the bank directly accepts payments such as dividends and rents and credits the same into the customer’s account. This increases the balance as per the pass book and causes a decrease in the balance in the pass book.
5. Cheques deposited dishonoured or bills discounted dishonoured
The bank sometimes allows the facility of discounting the bills of the customers. If such a bill is dishonoured on its date of maturity, the same is debited to customers account. As this information is not available to the firm, there will be no entry in the cash book. Similarly, when a cheque deposited by the firm in the bank is dishonoured, the same is debited to the customer’s account. As a result, there is a difference between the balances of the cash book and the pass book.
Errors in recording transactions by the firm or by the bank
Errors such as wrong recordings relating to cheques deposited/issued, wrong totaling or omission can be committed by the bank or the firm which can cause a difference between the cash book and the pass book balance.
Example: Wrong recording can be passed by the bank because of the similarity in names of its customers or some error caused by the clerk of the bank.
Cheques received by the firm are sent to the bank without passing an entry in the cash book or cheques received from the customers are omitted to be sent to the bank but an entry has been passed in the cash book.
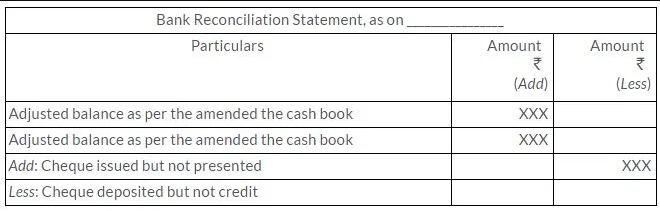
Q3. Explain the process of preparing bank reconciliation statement with amended cash balance.
Solution:
The below given steps are involved in the preparation of adjusted cash book.
Step 1:The bank balance as per the cash book is noted.
Step 2:All the errors committed in the cash book to be recorded are rectified.
Step 3:Transaction present only on the credit side of the pass book needs to be recorded on the debit side of the cash book.
Step 4:Transaction present only on the debit side of the pass book needs to be recorded on the credit side of the cash book.
Step 5:Total the cash book and find the balancing figure. This balancing figure is used for preparing the bank reconciliation statement.
The proforma of the bank reconciliation statement through amended balance is given below: