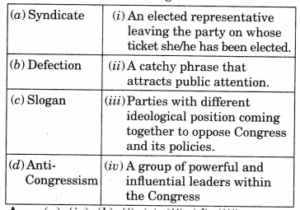
Chapter 5 – Challenges to and Restoration of Congress System Questions and Answers: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science (Politics In India Since Independence)
Class 12 Political Science (Politics In India Since Independence) NCERT book solutions for Chapter 5 - Challenges to and Restoration of Congress System Questions and Answers.