The CBSE Class 12 term 2 Physics exam concluded today, with students coming out from centres and stating that it was moderately balanced.
It included concept-based questions. Some students said it was a little hard to solve. However, it was easier than term 1 exam.
While others believed that a few would be able to get 100% marks in Physics. It comprised questions from NCERT, and as per some students, it was scoring.
The paper was of 35 marks for 2 hours, containing 3 sections.
Physics (Class 12) Term 2 Question Paper 2022
SECTION A
1. Two crystals C1 and C2. made of pure silicon, arc doped with arsenic and aluminum respectively.
(i) Identify the extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
Ans. C1 – n-type semiconductor
C2 – p-type semiconductor
why is doping of intrinsic semiconductors necessary
Answer: Doping of intrinsic semiconductors is done to increase the concentration of the majority charge carrier so that it can be used as a p-type or n-type semiconductor in the diode.
(ii) Why is doping of intrinsic semiconductors necessary ?
2. Why a photo-diode is operated in reverse bias whereas current in the forward bias is much larger than that in the reverse bias ? Explain.
Mention its two uses.
Ans. A photodiode converts incident light to electric current more effectively in reverse bias conditions. Actually, in a forward bias, the depletion region between the PN junction is very thin because it allows current to flow. But in reverse bias the depletion region becomes thick. Now, The incident light creates electron-hole pairs in the depletion region. Greater the area of depletion region, more are the electron-hole pairs that can be created by the incident light which is directly proportional to the amount of current produced. That’s why photodiode is connected in reverse bias.
3. (a) What results do you expect if ok-particle scattering experiment is repeated using a thin sheet of hydrogen in place of a gold foil ? Explain. (Hydrogen is a solid at temperature below I4K)
Ans: In the alpha-particle scattering experiment, if a thin sheet of solid hydrogen is used in place of a gold foil, then the scattering angle would not be large enough. This is because the mass of hydrogen (1.67 × 10 −27 kg) is less than the mass of incident α−particles (6.64 × 10 −27 kg). Thus, the mass of the scattering particle is more than the target nucleus (hydrogen). As a result, the α−particles would not bounce back if solid hydrogen is used in the α-particle scattering experiment.
OR
(b) Why is the frequency and not the intensity of light source that determines whether emission of photoelectrons will occur or not ? Explain.
SECTION B
4. How will the interference pattern in Young’s double-slit experiment be affected if :
(i) The screen is moved away from the plane of the slits.
Ans. When the screen is moved away, ‘D’ increases, therefore the width of the fringes increases.
(ii) The source slit is moved away from the plane of the slits.
Ans. As the source slit width increases, the fringe pattern gets less and less sharp. When the source slit is so wide then the interference pattern disappears.
(iii) The phase difference between the light waves emanating from the two slits S1 and S2 changes from 0 to π and remains constant.
Ans. The central fringe will become dark, as the phase difference between the light waves from two slits is odd after changing to π
5. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference: Of 100 V. Calculate:
(i) The speed acquired by the alpha particle, and
(ii) The de-Broglie wavelength associated with it.
(Take mass of alpha particle = 6.4 x 1022 kg)
6. (a) (i) Define SI unit of power of a lens.
Ans. The power of a lens is its ability to converge or diverge the rays of light falling on it. The power of a lens is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length of the lens.SI unit of power is dioptre (D).
P=f1=1D. The power of the lens is the ability of a lens to converge the rays falling on it. One dioptre is the power of the lens whose focal length is 1m.
(ii) A plano convex lens is made of glass of refractive index 1.5 The radius of curvature of the convex Surface is 25 cm.
(ii.i) Calculate the focal length of the lens.
u= 1.5
The radius of curvature of the plane surface is infinity i.e. R1=∞
The radius of curvature of convex surface R2=−25 cm
1/f= (u-1) (1/R1- 1/R2)
Ans. 50cm
(ii.ii) If an object is placed 50 cm in front of the lens, find the nature and position of the image formed.
OR
(b) A slit of width 0.6 mm is illuminated by a beam of light consisting of two wavelengths 600 nm and 480 nm. The diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1.0 m from the slit. Find:
(i) The distance of the second bright fringe from the central maximum pertaining to light of 600 nm.
(ii) The least distance from the central maximum at which bright fringes due to both the wavelengths coincide.
7. (a) (i) Arrange the following electromagnetic radiation in the ascending order of their Frequencies.
X-rays, Microwaves, gamma rays, radio waves
Ans. Radiowaves< Microwaves< X rays< Gamma rays
(ii) write two uses of any two of these radiation.
Ans. X rays can be used in Medical Science, Security purposes, Astronomy etc. Infrared rays find use in Electrical heaters, cooking food etc like microwaves.
The other questions would soon be provided here with their solutions. Keep refreshing the page for the same.
OR
(b) With the help of a ray diagram explain the working of a reflecting telescope. Mention two advantages of a reflecting telescope over a refracting telescope.
8. A ray of light passes through a prism of refractive index √2 as shown in the figure. Find:
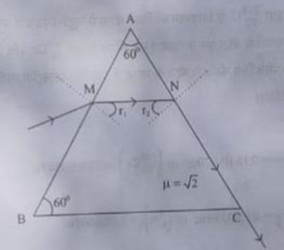
(i) The angle of incidence (√r2) at face AC.
(ii) The angle of minimum deviation for this prism.
9. (a) Use Bohr’s postulate to prove that the radius of nth orbit in a hydrogen atom is proportional to n2.
(b) How will the energy of a hydrogen atom change if n increases from 1 to ∞ ?
10. ( i) Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n union diode.
(ii) Differentiate between the threshold voltage and the breakdown voltage for a diode.
(iii) Write the property of a junction diode which makes it suitable for rectification of ac voltages.
11. In a fission event of 238/92 by fast moving neutrons, no neutrons are emitted and final products, after the beta decay of the primary fragments, 140/58ce and 99/44Ru Calculate Q for this process. Neglect the masses of electrons/positrons emitted during the intermediate steps.
SECTION C
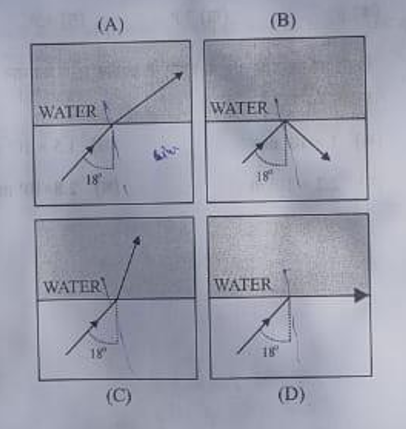
12. A ray of light travels from a denser to a rarer medium. After refraction, it bends away from the normal. When we keep increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction also increases till the refracted ray graze, along the interface of two media. The angle of incidence for which it happens is called critical angle. If the angle of Incidence is increased further the ray will not emerge and it will be reflected back in the denser medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection of light.
(i) A ray of light travels from a medium into water at an angle of incidence of 18′. The refractive index of the medium is more than that of water and the critical angle for the interface between the two media is 20′. Which one of the following figures best represents the correct path of the ray of light ?
(ii) A point source of light is placed at the bottom .11 1:toh tilled with water, of refractive index ton depth d. The area of the surface of water through which light from the source can emerge. is :
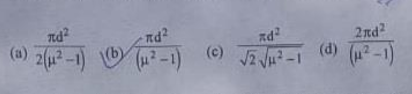
(iii) For which of the following media, with respect to air, the value or critical angle is maximum ?
(a) Crown glass (b) Flint glass (c) Water (d) Diamond
(iv) The critical angle for a pair of two media A and B of refractive indices 2.0 and 1.0 respectively is :
![]()
(v) The critical angle of pair of a medium and air is 30•. The speed of light in the medium is :





