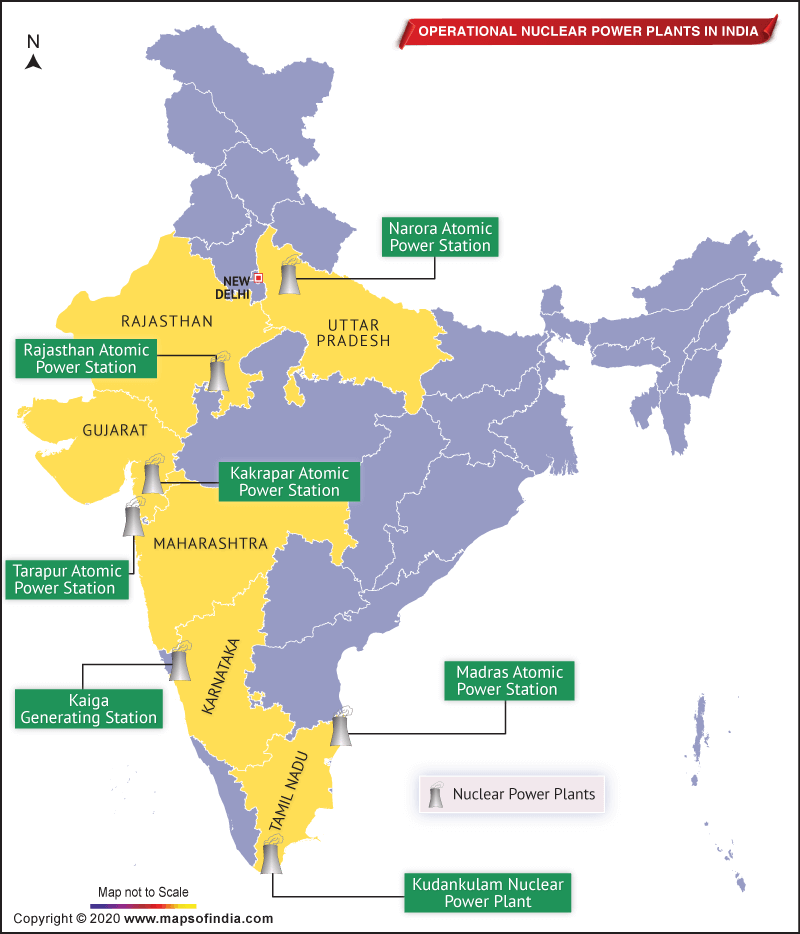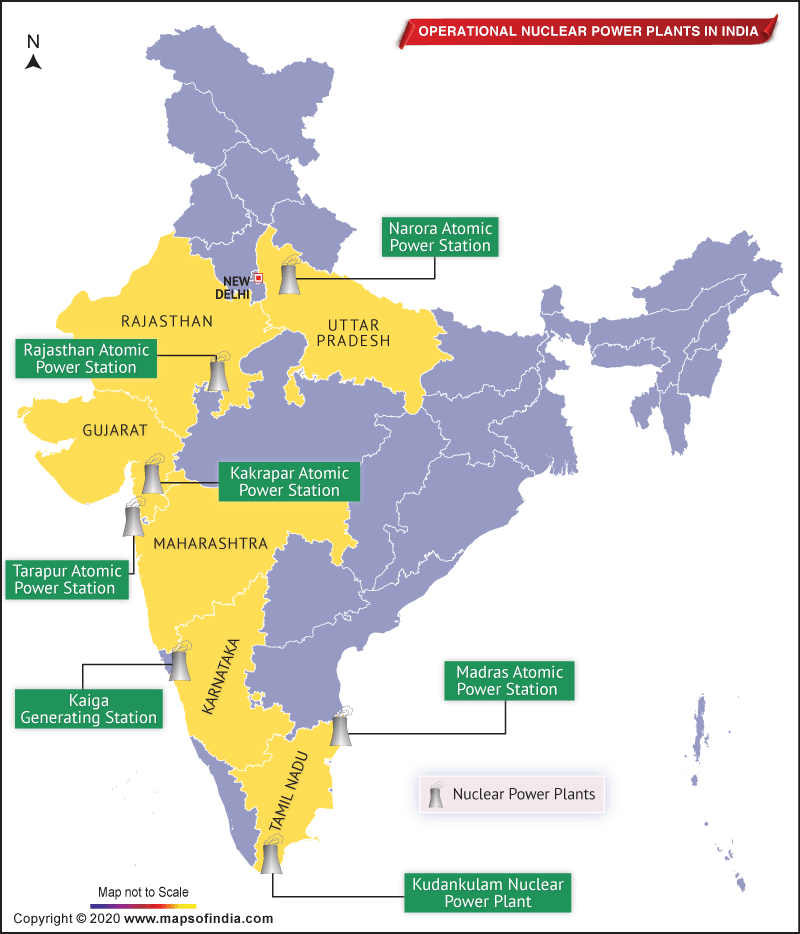
Nuclear power is the 5th largest source of electricity generation in India. In October 2010, India planned to generate 63 GW nuclear power capacity by 2032. Currently, it produces 35 TWh of energy, which is around 3.22% of total electricity supply of India. There are 22 operational nuclear reactors in 7 nuclear power plants across India. Their installed capacity is 6,780 MW, which is 3.5% of the total installed base.
Now, let’s check details of the 22 nuclear reactors in these 7 nuclear power plants:
| Sr. No. | Power Station Name | State | Operator Name | Nuclear Reactor Numbers | Commenced on | Nuclear Reactor Type | Total Capacity (in MW) |
| 1 | Kaiga Generating Station | Karnataka | NPCIL | 4 Reactors (All of them are Horizontal Pressure Tube models) of 220 MW capacity each | Nov 16, 2000; Mar 16, 2000; May 06, 2007; Jan 20, 2011 |
Pressurized Heavy-Water Reactor (PHWR) Design | 880 |
| 2 | Kakrapar Atomic Power Station | Gujarat | NPCIL | 2 Reactors (All of them are Horizontal Pressure Tube models) of 220 MW capacity each | – | Pressurized Heavy-Water Reactor (PHWR) Design | 440 |
| 3 | Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant | Tamil Nadu | NPCIL | 2 Reactors (All of them are VVER V-412 models) of 1,000 MW capacity each | – | Water-Water Energetic Reactor (WWER or VVER) Design | 2,000 |
| 4 | Madras Atomic Power Station (MAPS) at Kalpakkam | Tamil Nadu | NPCIL | 2 Reactors (All of them are Horizontal Pressure Tube models) of 220 MW capacity each | – | Pressurized Heavy-Water Reactor (PHWR) Design | 440 |
| 5 | Narora Atomic Power Station (NAPS) | Uttar Pradesh | NPCIL | 2 Reactors (All of them are Horizontal Pressure Tube models) of 220 MW capacity each | – | Pressurized Heavy-Water Reactor (PHWR) Design | 440 |
| 6 | Rajasthan Atomic Power Station | Rajasthan | NPCIL | – 1 Reactor (Horizontal Pressure Tube Model) of 100 MW – 1 Reactor (Horizontal Pressure Tube Model) of 200 MW – 4 Reactors (Horizontal Pressure Tube Model) of 220 MW |
– | Pressurized Heavy-Water Reactor (PHWR) Design | 1,180 |
| 7 | Tarapur Atomic Power Station (T.A.P.S.) | Maharashtra | NPCIL | – 2 Reactors (BWR-1, Mark 1 models) of 160 MW each – 2 Reactors (Horizontal Pressure Tube Models) of 540 MW each |
– | – Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) Design – Pressurized Heavy- Water Reactor (PHWR) Design |
1,400 |
| 7 Nuclear Power Stations | 22 Reactors | 6,780 MW |
Nuclear Power Stations and Nuclear Fuel Needs
Uranium reserves in India are extremely limited. That’s why the country has to import large quantities of uranium from countries such as Russia, Namibia, Argentina, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia. India has stressed upon exploration and discovery of newer uranium reserves. Large deposits of uranium have been discovered by Atomic Minerals Directorate for Exploration and Research (AMD) of India in Karnataka’s Tummalapalle belt and Bhima basin in Karnataka.
Availability of low-grade uranium in India is extremely limited. Just 92,000 tonnes of such domestic uranium are available. In comparison, India has large reserves of thorium. The current domestic Thorium reserve is estimated to be 518,000 tonnes. That’s why Indian scientists and political system have started giving more interest in thorium fuels and fuel cycles for nuclear power generation.