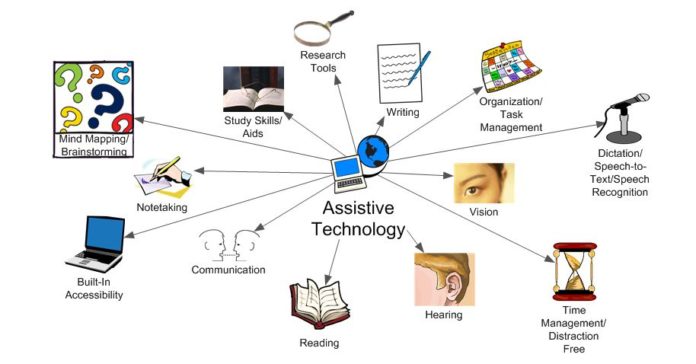
Often, people with special abilities are not given due importance, whether it’s an event where they are restricted to anything due to disabilities. In order to help them in day-to-day activities, assistive technology plays a vital role where its equipment, products and systems improve learning, working processes for them. It is any item, piece of equipment, software program or product system undertaken to raise, maintain and enhance the functional capabilities of persons with disabilities. It helps people who have difficulty typing, speaking, writing, remembering, pointing, seeing, hearing, learning, walking, and other activities. Different disabilities require different assistive technologies.
Assistive technology can be low-tech such as communication boards consisting of cardboard or fuzzy felt, or high-tech like special-purpose computers. It could be hardware, namely mounting systems, prosthetics and positioning devices. Assistive technology includes computer hardware such as special switches, keyboards, and pointing devices for helping them out. Others comprise computer software like screen readers and communication courses. These are inclusive or mainly focused on learning different theories, materials and curriculum aids. These can be specialised curricular software, electronic devices, educational software, wheelchairs, walkers, braces, power lifts, pencil holders, eye-gaze, head trackers, etc.
How to know the right Assistive Technology?
The right decision to make is by creating a team of professionals and consultants instructed to match particular assistive technologies for specific needs. An AT team may comprise regular and special education teachers, family doctors, speech-language pathologists, rehabilitation engineers, occupational therapists and other specialists who consult representatives from companies that manufacture assistive technology.
Some of the issues raised by teachers, parents and children about the use of AT comprise the cost of procuring several software titles, shifting from one application to another and the lack of a link between the applications suggested and those used by the school. Companies such as Microsoft and Apple have answered these concerns and have attached various unique AT tools to their products.
Who pays for Assistive technology?
a) School systems pay for general, special education understanding content as well as technology specified in an IEP
b) Government schemes such as social security, veteran’s benefits, or state Medicaid agencies pay for assistive technology if a doctor recommends it as an essential medical device
c) Private health insurance pays for assistive technology if a doctor prescribes it as a vital rehabilitative device.
d) Rehabilitation and job training programmes, whether funded by government or private agencies, could pay for assistive technology and training to assist people in getting jobs.
e) Employers may pay for assistive technology that is a reasonable option to enable an employee to practice crucial job tasks
Examples of Assistive Technology for the student with a learning disability
a) The use of multimedia and electronic information permits students with reading disabilities to enhance their understanding of a topic or idea without relying on their reading capabilities.
b) Computers and word processors can lower the pressure of editing and re-writing assignments, enabling the writing process to swifter and allowing students to work more independently
c) A photo shot with any device that contains a camera may be used instead of a replica of details from a whiteboard. This information can be stored online and, in some cases, converted to text.
d) An MP3 recorder on any device can record innovations and assist tackle short term memory issues.
In upper primary and secondary school, the use of AT could lead to assistive technology to accommodate the difficulties that the student may be sustaining. Software such as Text to Speech allows for better enhancement of information and independent learning, while software to back the writing process can help with the high demand on writing in some years of school. Further, technology to support the organisations, study skills, time management and memory can be set up at any stage in this.