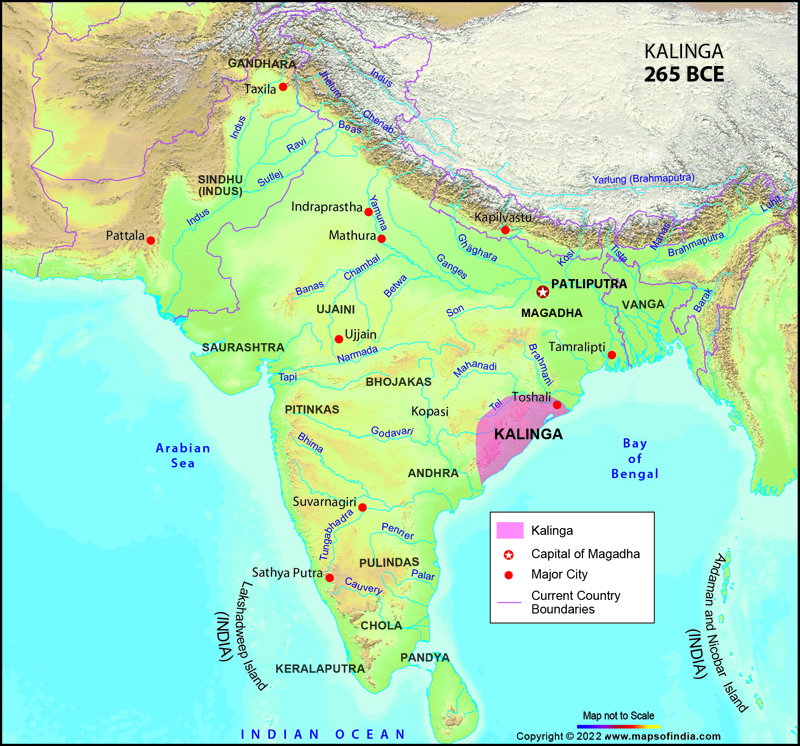
The ancient territorial subdivision of east-central India, Kalinga corresponded to various states which were: the present day northern Andhra Pradesh, almost the whole of Orissa
and also a little portion of Madhya Pradesh
. Kalinga strictly stretched not even a little farther than the south of the Godavari River thereby excluding the territory of Andhra which lied between Godavari and Krishna, then known as Vengi.
Semi-Hindu tribes were the inhabitants of the hinterland of Kalinga which was led through the thickly forested and mountaneous country of the central India and the Indo-Gangetic Plain's. Kalinga was the host to a rich seaborne trade with Myanmar (then Burma) and also with farther south and east areas. This rich sea trade was possible due to the ports of Kakinada, Vishakhapatnam, Chicacole, and Ganjam and the important cities of Rajahmundry and Vizianagaram.
It was first conquered by the founder of the Nanda Dynasty (c.343 - c.321BCE), Mahapadma of Magadha. Later the Magadhan Empire succeeded Kalinga a little later after the fall of the Nanda dynasty. But no later the Mauryan king Ashoka recaptured and took over Kalinga's throne in the 3rd century BCE. Ashoka conquered Kalinga after the unpopular Kalinga war which is believed to be a terrible war and which saw a lot of bloodshed and chaos. It is said that it was after this war that King Ashoka converted to Buddhism after witnessing so much of bloodshed and destruction.
It was in 261BCE when the historical Kailnga war was fought which proved to be a turning point for the Mauryan emperor Asoka and made him embrace non-violence and the teachings of Buddha. This war had witnessed the maximum bloodshed and furious kiling. The military campaign of Ashoka against Kalinga was one of the bloodiest in Mauryan history. On account of his army's unexpected bravery, Emperor Asoka issued two edicts specifically calling for a just and benign administration in Kalinga. However the south of Orissa remained unconquered by this Mauryan Emperor. Eventually it was Ashoka who began spreading Buddhism and Buddhist philosophy all over Asia.
Eventually the coastal parts were ruled by the Somavamshis of southern Kosala, who controlled the strategic town of Chakrakotta (in the former Bastar state). Out of all the rulers of Kalinga, the most famous ones were the Eastern Gangas (Ganga Dynasty). Their dynasty began ruling in the mid-11th century ce. They sometimes competed and allied themselves with the Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi.
The following century saw the renowned Anantavarman Chodnagagadeva, who built the temple of Jagannath at Puri. This temple was later protected and looked after by the Eastern Gangas (Ganga Dynasty), and like typical Indian belief the God was treated as their landlord.
Then in the 13th century the famous sun temple at Konarak was built by Narasimha I. From 1238 to 1305 the Eastern Gangas successfully ruled and withstood the Muslim infiltration, which happened in the north. But the downfall of the dynasty started in 1324 when the sultan of Delhi invaded south Kalinga.
Last Updated on: November 13, 2025
Ancient Kalinga |
|
||||||||
 | ||||||||
|
|
*Map showing the Ancient Kalinga in India.
Disclaimer: All efforts have been made to make this image accurate. However Mapping Digiworld Pvt Ltd and its directors do not own any responsibility for the correctness or authencity of the same.
Disclaimer: All efforts have been made to make this image accurate. However Mapping Digiworld Pvt Ltd and its directors do not own any responsibility for the correctness or authencity of the same.