1.What to produce?
(a) What to produce refers to a problem in which decision regarding which goods and services should be produced is to be taken.
(b) Since its resources are limited, every economy has to decide what commodities are to be produced and in what quantities.
(c) ‘The guiding principle for an economy here is to allocate resources in such a way that gives maximum aggregate utility to the society.
2.How to produce?
(a) How to produce refers to a problem in which decision regarding which technique of production should be used is made.
(b) Goods and services can be produced in two ways: by using labour intensive techniques, and by using capital-intensive techniques.
(c) The guiding principle for an economy in such a case has to decide about the techniques of production on the basis of cost of production. Those techniques of production should be used which lead to the least possible cost per unit of commodity or service.
3.For whom to produce?
(a) For whom to produce refers to a problem in which decision regarding which category of people are going to consume a good, i.e., economically poor or rich.
(b) As we know, goods and services are produced for those who can purchase them or have the capacity to buy them.
(c) Capacity to buy depends upon how income is distributed among the factors of production. The higher the income, the higher will be the capacity to buy and vice versa. So, this is a problem of distribution.
(d) The guiding principle is that the economy must see here that important and urgent wants of its citizens are being satisfied for the maximum possible extent or not.
Question 2. What do you mean by the production possibilities of an economy?
Answer: Production possibilities of an economy refer to different combinations of goods and services which an economy can produce from a given amount of resources and a given stock of technology.
Question 3. What is a production possibility frontier?
Answer: Production possibility frontier is a curve which depicts all the possible combinations of two goods which can be produced with given resources and technology in an economy.
Question 4. Discuss the subject matter of economics.
Answer:
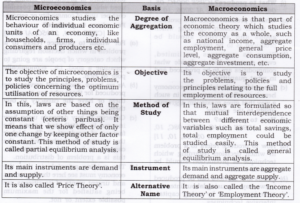
1. The subject matter of economics includes microeconomics and macroeconomics.
2. Microeconomics, studies the behaviour of individual economic units of an economy, like households, firms, individual consumers and producers etc. It does not study the economy as a whole.
3. Macroeconomics is the part of economic theory that studies the economy as a whole, such as national income, aggregate employment, general price level, aggregate consumption, aggregate investment, etc.
Question 5.Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics.
l. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is meant by economy?
Answer: Economy is a system which provides people with the means to work and earn living
Question 2. What is economics?
Answer: Economics is about studying economic problems arising due to limited means (having alternative uses) in relation to unlimited wants.
Question 3. Why does an economic problem arise?
Or
What gives rise to an economic problem?
Why does the problem of choice arise?
Answer: If we are not able to satisfy unlimited wants out of limited resources then the economic problem arises.
Question 4. State two features of resources that give rise to an economic problem.
Answer: The two features of resources that give rise to an economic problem are:
1. Resources are limited.
2. They have alternative uses.
Question 5. Which type of science is economics?
Answer: Economics is a social science.
Question 6. What is the basic reason for economic problem in all economies?
Answer: It is scarcity of resources.
Question 7. What is meant by economising of resources?
Answer: Economising of resources means that resources are to be used in such a manner that maximum output is realised per unit of input. It also means optimum utilisation of resources.
Question 8. What is meant by central problem of an economy?
Answer: The problem of making a choice among alternative uses of resources is known as basic or central problem of an economy.
Question 9. What does a rightward shift of production possibility curve indicate?
Answer: It indicates growth of resources.
Question 10. Give two examples of growth of resources.
Answer:
1. Supply of skilled labour (like IT engineers) has increased in India causing a rightward shift in the production of IT software.
2. Discovery of oil reserves in the gulf countries has caused a substantial shift to the right in the PPC of these countries.
Question 11. Give two examples of underutilisation of resources.
Answer:
1. Related to less developed countries: Labour is underutilised as indicated by mass unemployment in countries like India.
2. Related to developed countries: Capital is underutilised during depression when production is decreased owing to lack of demand.
Question 12. Define Opportunity Cost.
Or
Give the meaning of ‘Opportunity Cost’.
Answer: Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best alternative.
Question 13. Define Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT).
Answer: Marginal rate of transformation is the ratio of a number of units of a good sacrificed to produce an additional unit of another commodity.
Question 14. Why PPC is concave to the point of origin?
Answer: Because of increasing marginal opportunity cost.
Question 15. Define microeconomics.
Or
Give the meaning of microeconomics.
Answer: Microeconomics studies the behaviour of individual economic units of an economy, like households, firms, individual consumers and producers etc.
Question 16. Give one/two examples of microeconomics study
Or
Name any three variables of micro-economics.
Answer:
1. Individual demand;
2. Individual supply; and
3. Individual income.
Question 17. Name any three variables of macroeconomics.
Answer:
1. Aggregate demand;
2. Aggregate supply; and
3. National income.
Question 18. State any two central problems under ‘problem of allocation of resources’.
Answer:
1. What to produce and in what quantity?
2. How to Produce?
ll. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Why does an economic problem arise?
State any two causes of economic problem.
State two characteristics of the economic resources which give rise to economic problem.Or
Why does problem of choice arise?
Explain three factors that lead to an economic problem.
Answer: Economic problem arises because of scarcity of resources in relation to demand for them.
1. Wants are unlimited:
(a)This is a basic fact of human life. Human wants are unlimited.
(b)They are not only unlimited but also grow and multiply very fast.
2. Resources are limited:
(a)The resources to produce goods and services to satisfy human wants are available in limited quantities. Land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship are the basic scarce resources.
(b)These resources are available in limited quantities in every economy, big or small, developed or underdeveloped, rich or poor. Some economies may have more of one or two resources but not all the resources.
(c)For example, Indian economy has relatively more labour but less capital and land. The U.S. economy has relatively more land but less labour. No economy in the world is comfortable in all the resources.
3. Resources have alternative uses:
(a)Generally a resource has many alternative uses.
(b)A worker can be employed in a factoiy, in a school, in a government office, self employed and so on.
(c) Like this, nearly all resources have alternative uses. But the problem is that which resource should be put to which use.
Question 2. Give reasons for the following statements:
1. Every economy has to make the decision relating to what to produce.
2. Problem of choice arises because available resources have alternative uses.
Answer:
1. As, we know there is no economy in this world which possesses infinite resources to produce each and everything in infinite quantities.Therefore, if an economy decides to produce a quantity of one commodity, then they have to sacrifice the production of another commodity.
2. Resources in eveiy economy are always scarce. But the available resources can be put to alternative uses. Therefore, an economy will always prefer to make use of its resources in production of those goods and services that are most required and sacrifice the production of less- required goods and services.
Question 3. Why do all economies have similar central problems?
Answer: All economies whether developed or developing, have similar central problem because one or more of their resources (land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship) are limited and these resources can be put to alternative uses. The wants of the economies are unlimited. Therefore all economies have to face the basic economic problem of choice (what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce).
Question 4. State the central problems of an economy.
Answer: The central problems of an economy are:
1. What to produce and in what quantity?
2. How to produce?
3. For whom to produce?
Question 5. Define Production Possibility Curve and state its properties.
Answer: Production possibility curve is a curve which depicts all possible combinations of two goods which can be produced with given resources and technology in an economy. Properties of Production Possibility Curve
1. PPC is downward sloping: The downward slope of PPC means if the country wants to produce more of one good, it has to produce less quantity of the other goods.
2. PPC is concave to the point of origin: Concave shape of PPC implies that the slope of PPC increases. Slope of PPC is defined as the quantity of goods Y given up in exchange for additional unit of goods X.[Slope of Production Possibility Curve]
=ΔYΔX=AmountofGoodYlostAmountofGoodXgained
[Slope of PPC] = MRT = [Marginal Opportunity Cost]
Question 6. State any three assumptions on which a production possibilities curve is based.
Answer: The concept of PP curve is based on the following assumptions:
1. First, the amount of resources in the economy is fixed.
2. Second, the technology is given and unchanged.
3. Third, the resources are efficient and fully employed.
Using the figure given below answer the following (Q.9 & Q.10).
Question 7. Does production take place only on PPC?
Answer: Both Yes and No.
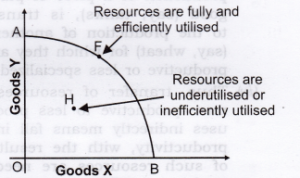
Yes, production will take place on PPC, if the given resources are fully and efficiently utilised. In such case, production will take place at any point on the curve AB, like point F. No, production will take place on PPC, if the resources are either underutilised or inefficiently utilised or both. In such case, production will take place on any point below the curve AB, like point H. Any point below the PP curve, thus highlights the problem of unemployment and inefficiency in the economy.
Question 8. “An economy always produces on but not inside PPC. Defend or refute.
Answer: The given statement is refuted. An economy operates on PPC, only when resources are fully and efficiently utilised. It means, if there is unemployment or inefficient use of resources, the economy may operate inside PPC. So, the economy may operate at point ‘H’ (Figure), in addition to the points on the curve AB on PPC.
Question 9. Why is Production Possibilities Curve concave? Explain.
Answer:
1. PPC is concave because of increasing marginal opportunity cost (MOC).
2. This behavior of the MOC is based on the assumption that all resources are not equally efficient in production of all goods.
3. Rise in opportunity cost occurs when factors (resources) which are specialized or more adopted for production of a piece of particular good (say, tanks), is transferred to the production of another good (say, wheat) for which they are less productive or less specialized.
4. Thus, transfer of resources from more productive to less productive uses indirectly means fall in their productivity, with the result more of such resources are needed to produce an additional unit of the other commodity. Thus marginal opportunity cost goes on increasing making the PP curve concave in shape.
Question 10. Give reasons for the following statements:
1. A Production Possibility Frontier is always a downward sloping concave curve.
2. An efficient economy would always produce a combination of goods
that lies on the given Production Possibility Frontier.
3. Growth of an economy is represented in the form of a rightward shift of a Production Possibility Frontier.
Answer:
1. A PPF slopes downward to indicate if an economy chooses to produce more of one commodity, then it would have to reduce the production of another commodity.
The concave shape of PPF is due to Increase in Marginal Opportunity Cost.
2. Any point on a given PPF presents a production possibility wherein all the available resources in an economy get fully utilized.
Any combination located below the given PPF shows an under utilization of available resources. Likewise, any point to the right of the PPF is beyond the available resources.
3. By economic growth, we mean that an economy has developed greater capacity to produce larger quantity of goods by acquiring more resources. Graphically, this would be represented by a rightward shift of PPF.
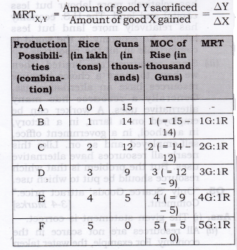
Question 11. Explain the meaning of opportunity cost with the help of production possibility schedule.
Answer: Opportunity cost of any commodity is the amount of other good which has been given up in order to produce that commodity. Alternatively opportunity cost of a given activity is the value of the next best activity.
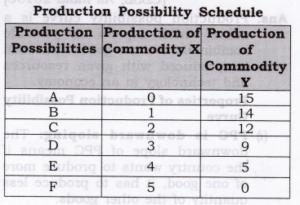
Initially at combination B, in order to produce one unit of X, the economy has to sacrifice one unit of Y. So, at combination B, opportunity cost is 1 unit. At combination C, for producing additional unit of commodity X, the economy has to sacrifice 2 units of commodity Y. So, at combination C, opportunity cost is 2 units. Similarly, at combination D, for producing additional unit of commodity X, the economy has to sacrifice 3 units of commodity Y. So, at combination C, opportunity cost is 3 units and so on.
Question 12. Define Marginal Opportunity Cost. Explain the concept with a hypothetical numerical example.
Answer:
1. Marginal opportunity cost is an addition to a cost in terms of a number of units of a commodity sacrificed to produce one additional unit of another commodity.
2. Marginal opportunity cost can also be termed marginal rate of transformation, Marginal rate of transformation is the ratio of number of units of a good sacrificed to produce one additional unit of another commodity.
lll. True Or False
Question 1. An economy always manages to meet all the needs of the people living in the country.
Answer: False: An economy always tries to provide means of living to all the people. It may be successful (as in most of the developed countries), or it may not be successful (as in many developing countries) to achieve its objective.
Question 2. In the context of an economy when we talk about ‘scarcity’, we refer to short supply of land.
Answer: False: Scarcity refers to limited availability of all types of goods and services in relation to their requirements. The concept of scarcity, thus, is not limited to land alone.
Question 3. Economic problem arises due to plenty of resources.
Answer: False: Economic problem arises due to scarcity of resources and alternative uses of various means.
Question 4. Because of destruction caused by war, a country’s PPF will shift to the left.
Answer: True: Country’s PPF will shift to the left; this will be due to the fact that the country’s capacity to produce will get reduced.
Question 5. A job guarantee scheme will lead to a rightward shift of PPF.
Answer: False: A job guarantee scheme does not add anything new to a country’s resources. This will only ensure that available unutilised or unemployed resources are productively employed.
Question 6. If a PPF shifts to the right, the new PPF will be parallel to the original.
Answer: False: A new PPF need not be parallel to the old one. It can take any possible shape.
Question 7. A ‘Production Possibility Frontier’ (PPF) is always represented as a upward sloping curve.
Answer: False: A PPF represents different combinations of two commodities that can be produced with the help of available resources in an economy. If an economy decides to produce a larger quantity of one commodity, it would be left with lesser resources to produce another commodity. A downward sloping curve represents this relationship.
Question 8. If the economy operates inside PPC, it shows full utilisation of resources.
Answer: False: If economy operates inside PPC, it shows underutilsation of resources.
Question 9. Growth of resources shifts PPC towards left.
Answer: False: Growth of resources increases the capacity of economy to produce more. It shifts PPC towards right and not left.
Question 10. PPC is concave shaped as production of one good can be increased only by reducing quantity of another good.
Answer: False: PPC is concave shaped due to increasing marginal opportunity cost.
Question 11. Economy can never operate outside PPC with the given resources and technology.
Answer: True: Economy can never operate outside PPC with the given resources and technology as all points outside PPC are unattainable.
Question 12. Economy always operates on PPC.
Answer: False: Economy operates on PPC only when resources are fully and efficiently utilised. If resources are not fully and efficiently utilized, economy operates at any point inside PPC.
Note: As per CBSE guidelines, no marks will be given if reason to the answer is not explained.
lV. Higher Order Thinking Skills Questions
Question 1. Define Marginal Opportunity Cost.
Answer: Marginal opportunity cost is an addition to the cost in terms of a number of units of a commodity sacrificed to produce an additional unit of another commodity.
Question 2. How does Maruti Udyog Ltd. fix the prices of its cars, is it studied in macroeconomics?
Answer: False: Macroeconomics is the study of aggregates e.g., determination of general price level in an economy. The principles underlying the pricing of a single good by a single firm or single industry are studied in microeconomics.
Question 3. Whether the cotton textile industry is an example of micro or macroeconomics?
Answer: Microeconomics.
Question 4. “Scarcity and choice go all together”. Defend or refute.
Answer:
1. We defend this statement because scarcity arises as resources are limited. The resources to produce goods and services to satisfy human wants are available in limited quantities. Land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship are the basic scarce resources.
2. These resources are available in limited quantities in eveiy economy, big or small, developed or underdeveloped, rich or poor. Some economies may have more of one or two resources but not all resources.
3. For example, the Indian economy has relatively more labour but less capital and land. The U.S. economy has relatively more land but less labour. No economy in the world is comfortable in all the resources.
4. Since resources are limited, then we have to make a choice because resources have an alternative use. Generally a resource has many alternative uses. A worker can be employed on a farm, in a factory, in a school, in a government office, self-employed and so on. Like this nearly all resources have alternative uses. But the problem is that which resource should be put to which use.
Question 5. “Only ‘Scarce Goods’ attract price.” Comment.
Answer:
1. The given statement is correct.
2. All resources are not scarce in the economy. For example, the water taken
from river or air we breathe is abundant in relation to wants. Such goods are available free of cost. These goods are known as Non-Economic Goods.
3. On the other hand, some goods are scarce in relation to their wants. For example, diamonds, petrol, electricity, etc. are scarce in relation to wants. These goods command price and are known as Economic Goods.
Question 6. A lot of people died and many factories were destroyed in an earthquake. How will it affect the PPC of the economy?
Answer: PPC of the economy will shift to the left from PP to P,Pr It happens because the number of possible combinations available with the economy has decreased due to destruction of resources in the economy.
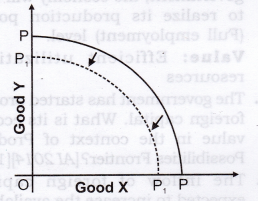
Question 7. Massive unemployment will shift PPC to the left. Defend or refute.
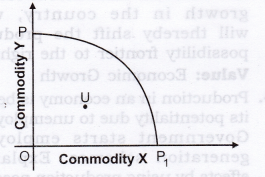
Answer: The given statement is refuted. Massive unemployment does not decrease the capacity of economy to produce. So, there will be no shift of PPC. However, due to unutilisation of human resources, economy will operate at some point inside PPC as shown in the adjacent figure at point U.