1. State the location and function of different types of meristems.
Solution:
The location and function of different types of mersitems are as follows:
Meristem
Location
Function
1. Apical meristem
Root and shoot tips
Forms primary tissue and increases the length of the plant
2. Intercalary meristem
Above and below the stem nodes and leaf bases
Helps in growth of leaves and internodes
3. Secondary meristem
At the periphery of roots and stem
Helps in the increase of thickness of the plant
2. Cork cambium forms tissues that form the cork. Do you agree with this statement? Explain.
Solution:
Yes, cork cambium forms tissues that inturn form the cork. When the stem increases in girth, another meristematic tissue known as phellogen or cork cambium grows in the cortex region of the stem. This phellogen cuts off cells on both of the sides. The outer cells differentiate into the phellem or the cork while the inner cells differentiare into the phelloderm or secondary cortex. The cork is impermeable to water because of suberin, rendering protection to the tissues underneath.
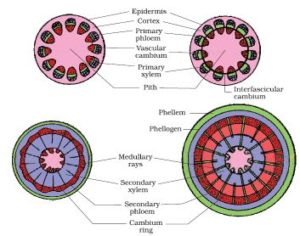
3. Explain the process of secondary growth in the stems of woody angiosperms with the help of schematic diagrams. What is its significance?
Solution:
The primary xylem and phloem exhibits the presence of a strip of cambium in woody dicot roots known as the interfascicular cambium which is formed from the cells of the medullary rays connecting the interfascicular cambium. Hence, the continuous cambium ring is formed. The cambium separates from the newly formed cells on either sides while the cells found towards the exterior differentiate into the secondary phloem. The cells detach towards the pith giving rise to the secondary xylem. The secondary xylem is synthesized in excess compared to the secondary phloem.
When there is secondary growth in plants, the girth of the plants increases, along with an increase in the water content and nutrients in order to assist the ever growing leaves, rendering support to the plants.
4. Draw illustrations to bring out the anatomical difference between
(a) Monocot root and Dicot root (b) Monocot stem and Dicot stem.
Solution:
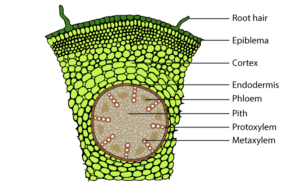
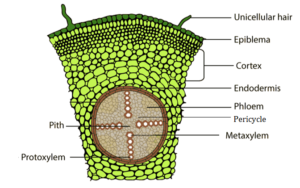
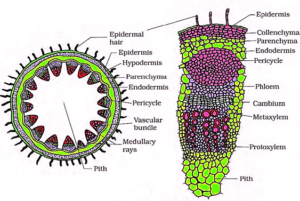
(a) Monocot root and Dicot root
Monocot root
Dicot root
(b) Monocot stem and Dicot stem
Monocot stem
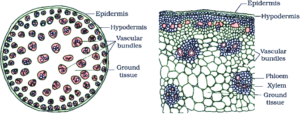
Dicot stem

5. Cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant from your school garden and observe it under the microscope. How would you ascertain whether it is a monocot stem or a dicot stem? Give reasons.
Solution:
The following characteristics can be used to distinguish if it is a monocot or a dicot stem:
Dicot stem
Monocot stem
Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring
Vascular bundles are scattered
Vascular bundles are open
Have closed Vascular bundles with a bundle sheath.
Presence of collateral, conjoint and open vascular bundles with a strip of cambium between the xylem and phloem
Presence of collateral, conjoint and closed vascular bundles, dispersed in the ground tissue that contains the parenchyma
Ground tissue can be differentiated into the parenchyma, collenchyma, endodermis, pith and pericycle. Medullary rays are found between the vascular bundles
Phloem parenchyma is absent, water-containing cavitites are present.
Monocot stem
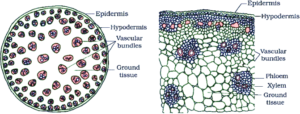
Dicot stem
6. The transverse section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features – (a) the vascular bundles are conjoint, scattered and surrounded by a sclerenchymatous bundle sheaths. (b) phloem parenchyma is absent. What will you identify it as?
Solution:
The traverse section is of Monocot stem. It is because the vascular bundles are dispersed in monocot stems. The phloem parenchyma is not found.
7. Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues?
Solution:
Xylem and Phloem are called complex tissues because they are made of more than one type of cells which work together as a unit to perform the function. Xylem transports water while phloem transports food.
8. What is stomatal apparatus? Explain the structure of stomata with a labelled diagram.
Solution:
Stomata are structures present in the epidermis of leaves. Stomata regulate the process of transpiration and gaseous exchange. Each stoma is composed of two bean-shaped cells known as guard cells which enclose stomatal pore.
Guard cells are dumbbell-shaped, where its outer wall is thin and inner wall is highly thickened. These structures possess chloroplasts and regulate the closing and opening of the stomata. The epidermal cells near the guard cells in some cases become specialized in their structure shape and size, they are referred to as subsidiary cells. The guard cells, the stomatal aperture and girdling subsidiary cells are collectively referred to as stomatal apparatus.
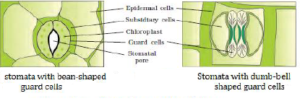
9. Name the three basic tissue systems in the flowering plants. Give the tissue names under each system.
Solution:
Following are the three basic tissue systems in the flowering plants.
Epidermal tissue system
Epidermal tissue system includes epidermis and epidermal appendages. Epidermis comprises of epidermal cells and guard cells while the epidermal appendages includes root hair, stem hair, stinging hair and glandular hair.
The ground tissue system
Ground tissue system is made up of simple tissues such as parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Vascular tissue system
Vascular tissue system consists of complex tissues such as Xylem, phloem and vascular cambium.
10. How is the study of plant anatomy useful to us?
Solution:
Study of plant anatomy useful to us in the following ways
To understand structural adaptations in plants to different climatic conditions
Helpful in identifying monocots, dicots and gymnosperms.
Physiological conditions can be studied, which helps in crop improvement.
Study of plant fibres such as flax, jute etc helps in their commercial exploitation as it enables to predict the strength of wood which can be utilized to its potential.
11. What is periderm? How does periderm formation take place in the dicot stems?
Solution:
Phellogen, phellem, and phelloderm are collectively known as periderm. While plants undergo secondary growth, the outer epidermal layer and the cortical layer are ripped due to cambium. In order to replace them, the cortex cells turn meristematic which produces the cork cambium or the phellogen which comprises of a thin-walled, narrow and rectangular cells.
The phellogen sheds cells on either sides. The cells which shed from the exterior gives rise to the cork or phellem. The suberin accumulates in its cell wall making it impermeable to water while the inner cells emerge to become the secondary cortex or phelloderm which is parenchymatous.
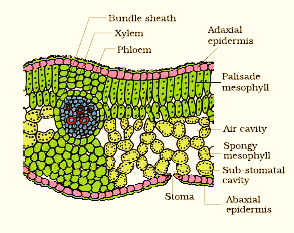
12. Describe the internal structure of a dorsiventral leaf with the help of labelled diagram.
Solution:
Dicots exhibit dorsiventral leaves. When examined, the vertical section of a dorsiventral leaf consists of three different parts, they are:
Epidermis – it is found on the adaxial epidermis (upper surface) and the abaxial epidermis (lower surface). On the outside, the epidermis is covered with a thick cuticle. Compared to the upper surface, the abaxial epidermis comprises of more stomata.
Mesophyll – it is a tissue found in between the abaxial and adaxial epidermises. This tissue is
differentiated into the palisade parenchyma and the spongy parenchyma. The palisade parenchyma is composed of tall, compactly-arranged cells while the spongy parenchyma comprises of round or oval, loosely-arranged cells possessing intercellular spaces. The mesophyll comprises of chloroplasts that carry out photosynthesis.
Vascular system – The vascular bundles that are found in leaves are closed and conjoint which are engirdled by thick layers of bundle-sheath cells