Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Name any two types of commonly used negotiable instruments.
Solution:
Cheques and Bills of exchange are the commonly used negotiable instruments.
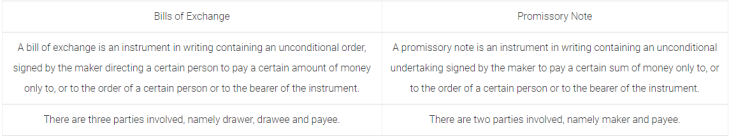
Q2. Write two points of distinction between bills of exchange and promissory note.
Solution:
Q3. State any four essential features of bill of exchange.
Solution:
Essential features of bills of exchange are as follows:
1. A bill of exchange is a written order to make payment.
2. It is an unconditional order to make payment by a person i.e. drawee.
3. The amount of bill of exchange and the date of payment are certain.
4. It is signed by the drawer of the bill.
5. It is accepted by the drawee by signing on it.
6. The amount specified in the bill of exchange is payable either on demand or on the expiry of a fixed period.
7. The amount specified in the bill is payable either to a certain person or to his order or to the bearer of the bill.
8. It is stamped as per legal requirements.
Q4. State the three parties involved in a bill of exchange.
Solution:
There are three parties in a bill of exchange:
1. Drawer is the person who makes the bill of exchange. She/he is a person who has granted credit to the person on whom the bill of exchange is drawn. The drawer is entitled to receive money from the drawee (acceptor).
2. Drawee is the person on whom the bill of exchange is drawn for acceptance and to whom credit has been granted by the drawer. He/she is liable to pay money to the creditor/drawer.
3. Payee is the person who receives the payment from the drawee. Usually the drawer and the payee are the same person.
Q5. What is meant by maturity of a bill of exchange?
Solution:
The date calculated after adding 3 days of grace to the due date of a bill is called the date of maturity of a bill. It is to be noted that when a bill is to be payable on demand/at sight, then days of grace is not applicable. When the period of a bill is mentioned in days, the maturity of bill is calculated in days. Similarly, when the period of a bill is mentioned in months, the maturity of bill is calculated in months. In certain cases, when the maturity date of any bill falls on a public holiday, then the maturity date of the bill will be the previous business day.
Q6. What is meant by dishonour of a bill of exchange?
Solution:
When the drawee of the bill fails to make the payment on the maturity date of the bill, then the bill is said to have been dishonoured. Hence, liability of the acceptor is restored. Entries made for recording dishonour of the bill of exchange are as follows:
In the books of drawer

Q7. Name the parties to a promissory note
Solution:
There are two parties to a promissory note:
1. Maker- The person who makes the note and undertakes to pay the amount.
2. Payee- The person who receives the payment.
Q8. What is meant by acceptance of a bill of exchange?
Solution:
A bill of exchange is a written instrument which contains an unconditional order directing a person to pay a certain amount on an agreed date. In other words, it is drawn by the creditor on her/his debtors to make a payment of a certain amount on the mentioned date. Such a bill comes into existence after the consent of both the parties. A bill cannot come into existence without the acceptance of a debtor. Hence, the debtor of the bill has to accept the terms of the bill, sign the same and make it a legal document.
Q9. What is noting of a bill of exchange?
Solution:
When the drawee of the bill fails to make the payment on the maturity date of the bill, then the bill is said to have been dishonoured. To have a legal proof of the dishonour, the bill gets noted by the notary public who is approved by the central/state government. The notary public charges fees called the noting charges for noting and protesting the bill of exchange of its dishonour.
Q10. What is meant by renewal of a bill of exchange?
Solution:
When the drawee does not have enough funds to make the payment, he may approach the drawer and ask for an extension of time for the payment. If the drawer agrees, then a new bill is drawn which is known as renewal of bill. The new bill may include interest for the extended period.
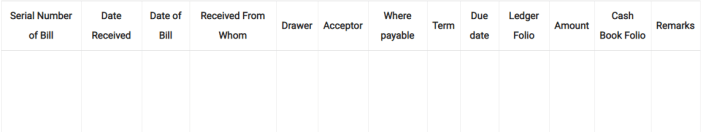
Q11. Give the performa of a Bills Receivable Book.
Solution:
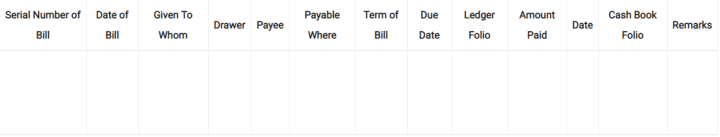
Q12. Give the performa of a Bills Payable Book.
Solution:
Q13. What is retirement of a bill of exchange?
Solution:
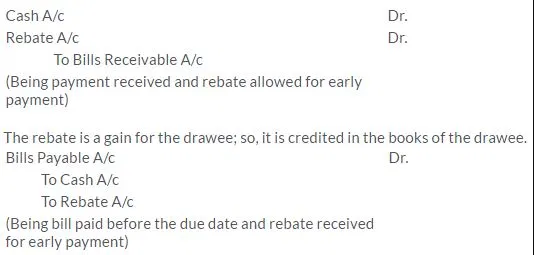
When the drawee of the bill pays off the amount of the bill before the maturity of the bill it is called retirement of the bill. Holder of the bill may give discount for such earlier payment which is called as ‘rebate’.
Entry in the books of the holder of the bill

Q14. Give the meaning of rebate.
Solution:
If the drawee wishes to pay the bill before the due date of the bill to the holder and the holder accepts such request, then due to the early payment, the holder may give some discount to the drawee. Such a discount is termed as rebate.
Q15. Give the performa of a Bill of Exchange.
Solution:
Performa of a Bill of exchange is given below.

Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. A bill of exchange must contain “an unconditional promise to pay”. Do you agree with a statement?
Solution:
According to Negotiable Instrument Act, 1981, “A bill of exchange is defined as an instrument in writing, containing an unconditional order, signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to, or to the order of, a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument.”
As the definition mentions the bill is an unconditional order to pay i.e. no conditions should be applicable with respect to the payment and the drawee of the bill is obliged to pay the maker of the bill. This is one of the main features of a bill of exchange. All the conditions with respect to the bill, for example; the amount, the date of payment, the parties involved needs to be specified with clarity.
Q2. Briefly explain the effects of dishonour and noting of a bill of exchange.
Solution:
On the maturity of the bill, when the acceptor of the bill fails to make the payment, it is said that the bill is dishonoured. This restores the liability of the acceptor.
Entry in the books of drawer:

Noting charges is the fee paid to the notary public for noting and protesting the bill of exchange of its dishonour.
Effect of Noting charges in the books of the drawer:

Q3. Explain briefly the procedure of calculating the date of maturity of a bill of exchange? Give example.
Solution:
The procedure to calculate the date of maturity of a bill of exchange is given below.
1. Determine the date on which the bill will be due.
2. Add three days of grace to the due date of the bill. It is standard process to add days of grace.
3. The date obtained after adding the three days to the due date is called the maturity date of the bill.
However, the application of the days of grace depend on the following situations:
1. Days of grace are not applicable when a bill is payable ‘at sight’ or on demand.
2. When the period of the bill is mentioned in months, the calculation of the maturity date will be in the terms of calendar month.
3. When the period of the bill is mentioned in days, the calculation of the maturity date is also calculated in days including the date of payment but excluding the date of transaction.
4. If the bill matures on a national holiday or Sunday, then the preceding business day becomes the maturity date of the bill.
5. For example, if the maturity date of a bill is calculated as on 15th August, 2015 then the preceding day that is 14th August, 2015 will be considered as the maturity date.
6. If the maturity day happens to be an emergency holiday declared under the Negotiable
7. Instruments Act, 1881, then the next working day is to be considered as the maturity date.
Q4. Distinguish between bill of exchange and promissory note.
Solution:

Q5. Briefly explain the purpose and benefits of retiring a bill of exchange to the debtor and the creditor.
Solution:
When the drawee of the bill pays off the amount of the bill before the maturity of the bill it is called retirement of the bill. Holder of the bill may give discount for such earlier payment which is called as ‘rebate’.
As the holder of the bill provides the rebate, it is a loss for the holder of the bill and hence it is debited in the books of the holder when payment is received.