1. What are macromolecules? Give examples.
Solution:
Macromolecules are the biomolecules that are formed by the polymerization of a huge number of micromolecules possessing higher molecular weight. Micromolecules are found in the colloidal state in the intercellular fluid due to their insoluble nature. Protein is a macromolecule.
2. Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phospho-diester bond.
Solution:
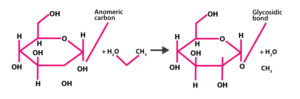
Glycosidic bond – The bond between the individual monosaccharides is called a glycosidic linkage. This bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharide units.
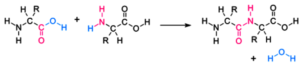
Peptide bond – It is a covalent bond. The amino acids in proteins are linked to one another through peptide bonds. It is formed between when the carboxyl group (-COOH) of one amino acid interacts with amino group (-NH2 ) of the adjacent amino acid when condensed.
Formation of Peptide bond – Example
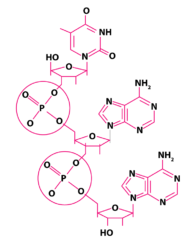
Phospho-diester bond – that joins successive sugar molecules in a polynucleotide. It is a strong covalent bond formed between two adjacent sugar groups and phosphate. These are the bonds that form the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic acids
3. What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins?
Solution:
It is a structure that forms when the secondary coiled polypeptides are folded to produce a hollow, wollen ball-like structure. It is folded such that the functional side groups appear on the surface while the inactive side groups are found inside.
4. Find and write down structures of 10 interesting small molecular weight biomolecules. Find if there is any industry which manufactures the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers.
Solution:
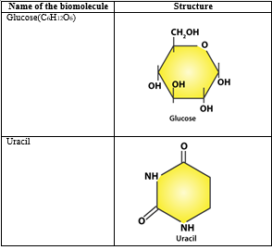
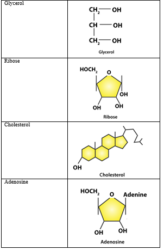
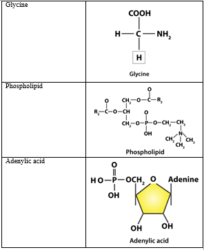
Compound
Manufacturer
Buyer
Starch
Premier starch products private limited
Research institutes and laundries
Liquid Glucose
Imperial liquid glucose
Used in making flavored drink and in research
Enzymes like amylase, protease, and cellulase
Planet Biotech India
Used in research
5. Proteins have primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to purity or homogeneity of a protein?
Solution:
Positional information of a protein is called the primary structure of the protein. The first amino acid in a protein is called N-terminal amino acid, and the last amino acid in a protein is called the C-terminal amino acid.
Yes, we can connect this information to check the purity or homogeneity of a protein. On the basis of carboxyl and amino groups, amino acids can be acidic, basic and neutral. Proteins can be acidic, basic and neutral.
6. Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., Cosmetics etc.)
Solution:
Following are the list of proteins used as therapeutic agents.
Insulin, Oxytocin, Immunoglobin, Antidiuretic Hormone( ADH), Thrombin, Fibrinogen, Renin and streptokinases.
Some other applications are:
Are used as artificial sweeteners. Thaumatin is a low-calorie sweetener.
Proteins are used as dietary supplements to maintain health
They are used in creams and shampoos
7. Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Solution:
When glycerol combines with three fatty acids on each of the OH groups through ester bonds, it is known as triglyceride.

All the three fatty acids of triglyceride in pure fat are similar while in mixed fat, they are dissimilar.
8. Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yoghurt, from your understanding of proteins
Solution:
During fermentation, milk protein such as casein is denatured which transforms globular proteins into fibrous proteins. This change is responsible for the production of curd or yoghurt.
9. Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models).
Solution:
Yes, Biomolecules can be represented by ball and stick model. Here bonds which hold the molecule are
indicated by sticks while the atoms are represented by balls.
The figure below is a model of D-glucose where atoms of hydrogen are indicated by green balls, oxygen atoms are represented by pink balls and carbon atoms are represented by grey balls.
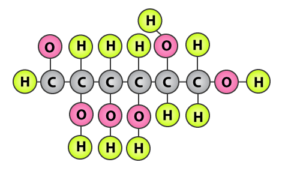
10. Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating
(ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Solution:
The pH of the amino acid is recorded, and the weak base is slowly supplemented to the amino acids while continuously noting the pH. The number of changes recorded indicates the number of ionisable functional groups –COOH in the acidic range and –NH2in the alkaline range.
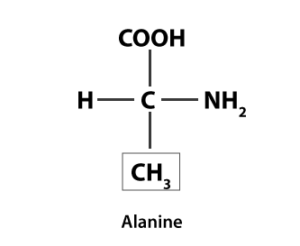
11. Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
Solution:
The structure of Alanine is as follows: