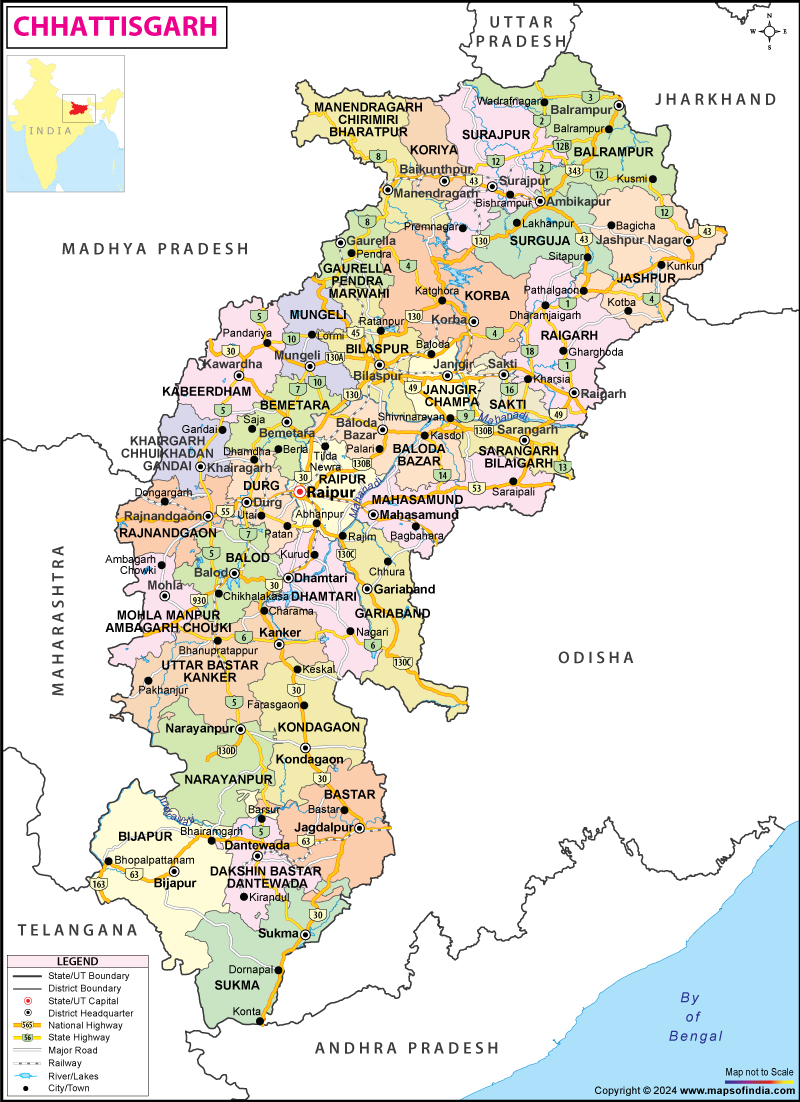
Chhattisgarh was a part of the state of Madhya Pradesh. It came to be recognized as a separate state in November 2000. Raipur is the capital of Chhattisgarh. The state is located in the central part of India.
The geographical location of Chhattisgarh is 17 degree 46 min north to 24 degree 5 min north latitude and from 80 degree 15 min east to 84 degree 20 min east longitude. Madhya Pradesh borders Chhattisgarh in the north western part. Maharashtra borders on the west and Andhra Pradesh lies in its south. Orissa is located in the eastern side. The state of Jharkhand borders Chhattisgarh in the north eastern part. Chhattisgarh Geography is diverse and thus is very interesting.
The total area of Chhattisgarh is 192,000 square km. The total population of the state according to 2001 census is 20,795,956. The population density of the state per square km is 108. The topography of Chhattisgarh can be divided into many physiographic divisions. The Indo-Gangetic plain in the state is very fertile. The Satpura Range, Vindhyachal Mountain Range and the Maikal Range form the hilly terrain of Chhattisgarh. The Chhota Nagpur Plateau is another important topographical division of Chhattisgarh.
The vegetation of Chhattisgarh includes the vast stretch of forests. About 44% of the total area of Chhattisgarh is covered by forest. The trees that are mostly found in the state are Sal, Bamboo, Teak, and trees of mixed deciduous variety. The soil of Chhattisgarh is rich and is known for its red color. The soil in the riverine plains is very fertile. The two most important rivers that flow through Chhattisgarh are Mahanadi and Indravati. There are numerous lakes in the state.
The Chhattisgarh Geography includes the climate of Chhattisgarh. The climate of the state is mainly dry and hot. In the summer months, the temperature is very high and the state is frequented by dust storms. In the months of winter, very cold wind blows over the state. Chhattisgarh receives a good amount of rainfall. The state receives rainfall mainly from the South West monsoon winds.
Chhattisgarh is located in the central part of India. Madhya Pradesh borders Chhattisgarh in the north western part. Maharashtra borders Chhattisgarh on the west and Andhra Pradesh lies in its south. Orissa is located in the eastern side.
Chhattisgarh is bordered by the state of Jharkhand in the north eastern part. The geographical location of Chhattisgarh is 17 degree 46 min north to 24 degree 5 min north latitude and from 80 degree 15 min east to 84 degree 20 min east longitude. The total Chhattisgarh Area is 192,000 square km. The total population of Chhattisgarh state is 20,795,956, according to the census of 2001. The density of population in the state is 108 per sq. km. About 44% of the total area of Chhattisgarh is occupied by forest.
Climate
The ideal time to visit Chhattisgarh, is when Chhattisgarh climate remains pleasant. Chhattisgarh state experiences a tropical type of climate. The state, formerly a part of Madhya Pradesh is situated in the central part of India. The city of Raipur is the state capital of Chhattisgarh. It is bordered by land on all sides. The geographical factors like distance from the sea and altitude of the state have influenced the Chhattisgarh climate. The climatic condition during summer is hot and gusts of dry wind blows over the state. During winter the temperature falls to some extent.
During the summer season in Chhattisgarh, the temperature varies from 40 degree to 42.5 degree Celsius. From the month of March, the temperature starts to rise in Chhattisgarh. The summer season prevails from April to middle of June. In summer very dry wind blows over most parts of the state. This influences the Chhattisgarh climate.
Topography
Chhattisgarh topography includes landforms of mountain ranges, plateau region and plain land areas. Chhattisgarh, a state of the Indian subcontinent, was recognized as a separate state in November 2000. The capital of Chhattisgarh is Raipur and the state is divided into sixteen districts.
The river basin situated in the central region of Chhattisgarh is divided into undulating Rimland and the the plain land of Chhattisgarh. The gradient of the Chhattisgarh Plain is generally flat. The elevation of the plain land varies from 250 meter to 330 meter. The loamy and clayey soil of this plain area is very fertile and suitable for agriculture.
Maikal range is a stretch of hilly region in the central part of India. Satpuda-Maikal landscape extends for a distance of about five hundred kilometer. To one side of this stretch of landscape, Achanakmar Wildlife Sanctuary of Chhattisgarh and on the other side lies the Melghat Tiger Reserve of Maharashtra. This stretch of land extends along with Satpuda and Maikal range in Chhattisgarh.
Satpura Range stretches through Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh state. The mountain range spans for about a distance of 900 km. Vindhya Range and Satpura Range lie parallel to each other. Satpura mountain range separates the Deccan plateau in the south from the Indo-Gangetic plain in the north. Rivers like Mahanadi, Tapti and Godavari drain through the hilly region in Chhattisgarh.
Rivers & Lakes
The Indian State of Chhattisgarh is blessed by the numerous water bodies. These comprise of several rivers and lakes of Chhattisgarh that provide the necessary water contributing much towards the fertile plains of the state. Agriculturally, the state of Chhattisgarh is one of the most productive areas in India.
Soil & Vegetation
Chhattisgarh Soil and Vegetation is both rich and diverse. The 26th state of India Chhattisgarh was formed on November 1,2000.
It is located between 80° 15' and 84° 20' East of Longitude and 17° 46' and 24° 5 North of Latitude. It encompasses a total area of 136 lakh hectares of total land, which consists of 58.81 lakh hectares of cultivable land area and 60.76 lakh hectares forest land area. The vegetation of Chhattisgarh comprises of numerous varieties of horticultural plants, trees, crops like paddy, maize, pulses and many more. Some of the main trees found in the forests of Chhattisgarh are Bija, Saja, Harra, Tendu, Teak, haura, Mahua etc.
Agriculture is the main occupation of the people of Chhattisgarh where nearly 80% of the population is engaged in cultivation. The major crop grown in Chhattisgarh is paddy especially in the central plains of the state, popularly known as rice bowl of central India. Apart from paddy other crops grown here are oilseeds, wheat, coarse grains, groundnut, maize and pulses. The soil of the state is suitable for the cultivation of horticultural plants guava, mango, banana etc. and a various types of vegetables.
Last Updated on: May 15,2020