About Godavari River
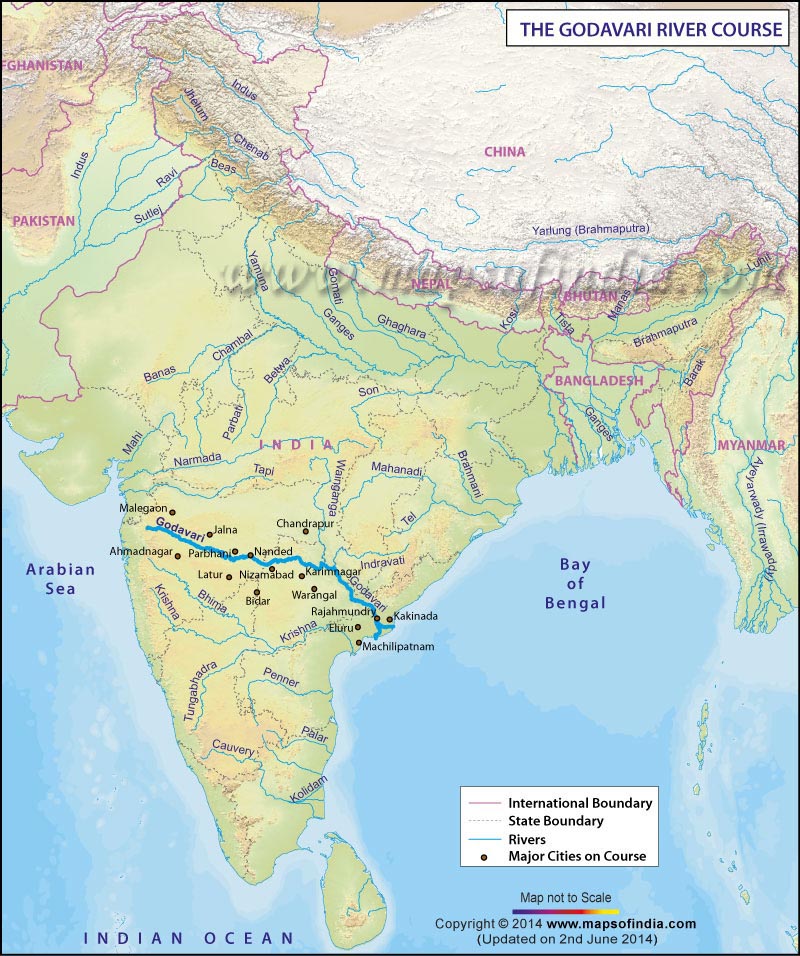
The source of the Godavari River is situated near Trimbak in Nashik District of Maharashtra. After setting off, the river runs towards the east, traversing the Deccan Plateau. In the end, the river empties into the Bay of Bengal at Narasapuram in West Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh.
Itinerary of Godavari River
The river is an important stream in central India, rising in the Western Ghats Mountain Range. The name of the origin is Trimbakeshwar and it is situated in the Nashik District or Subdivision in the state of Maharashtra and runs towards the east over the Deccan terrain through the Maharashtra state. The river is also named as Southern Ganges or Dakshin Ganga. The river moves into Andhra Pradesh at Kandhakurthi in Nizamabad district of Andhra Pradesh, moves past the Deccan terrain and subsequently bends to run according to a southeasterly course till it pours into the Bay of Bengal via two mouths. An important place of attraction on the riverbanks is Basara in Adilabad District. It houses a popular place of worship for Goddess Saraswati. It is also the second oldest temple for the deity in India.
The biggest city on the riverbanks of the Godavari is Rajahmundry. In this place, the river has the maximum breadth (about 5 km from Rajahmundry to the other bank at Kovvur.
The Sri Ram Sagar Dam was built across this river (1964-1969) and it satisfies the irrigation requirements of districts like Nizamabad, Adilabad, Warangal, and Karimnagar in Andhra Pradesh.
A popular temple township in Andhra Pradesh is the Dharmapuri and there is a holy place of worship devoted to Lord Sri Laxmi Narashimha Swamy. The place draws religious devotees from across Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. According to Dr. Sanganabhatla Narsaiah, a famous Telugu writer and academic of Desi Chandas in Telugu and Principal of SLNSA College - Dharmapuri, the river was also named as 'Telivaha' in this territory, which was assumed to have thrust the word 'Telugu' to the dialect.
In spite of the fact that the river originates just 80 km from the Arabian Sea, the river runs a length of 1,465 km or 910 miles to pour into the Bay of Bengal. Only over Rajahmundry, a barrage is located that supplies water for cultivation purposes. Beneath Rajahmundry, the river splits into two torrents that broaden into a big river delta, which has a widespread passable irrigation channel arrangement, Dowleswaram Barrage that connects the area to the Krishna River delta to the southwest.
Drainage basin of Godavari River
The catchment basin of the river is 342,812 km2 and it comprises more than one state, which is almost 1/10th of India and is bigger than the territories of Ireland and England combined. The Indravati, Pravara, Wardha, Wainganga, Kanhan, Pench, and Penuganga rivers flow a huge quantity of water into the Godavari River System . Major tributaries of the river are as follows:
- Manjira River
- Indravati
- Sabari River
- Bindusara River
Religious importance
The Godavari River is regarded as holy by Hindus and there are various religious spots on the riverbanks. The river has been revered as a particular site of pilgrimage for a considerable period of time. A number of eminent individuals, including Baladeva (5000 years back) and lately Chaitanya Mahaprabhu (500 years back) have dipped in her waters to offer prayers.
Godavari is also regarded as Dhakshin Kashi (Rajahmundry) or Dakshin or Southern Ganges. The Pushkaram Fair is organized on the riverbanks. Countless people have a sacred bath in the holy waters of the river to wash themselves off of any misdeeds.
It has been mentioned in the myth that the famous mentor Gautama stayed on the Brahmagiri Hills, located at Trayambakeshwar with his wife Ahalya. The sage kept the store of rice in a granary. At one time, a cow came into the granary and consumed the rice. Once the sage attempted to drive the cow out with Durbha grass, it died. The sage wished to save himself of the wrongdoing of "Gohatya". He offered prayers to Lord Shiva and urged him to fetch the Ganges to cleanse his abode. Lord Shiva was satisfied with the sage and emerged as Triambaka and fetched the Ganges River. As the Ganges River was taken down by Sage Gautama to Triambakeshwar, the river is named here as Gautami. The river is also called as Godavari since the river assisted Sage Gautama to wash away his misdeeds.
Environmental importance
The delta of the Godavari River is home to the Coringa mangrove forests and they are the second biggest mangrove development in India. A portion of this has been acknowledged as the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary, which is famous for its reptiles. The sanctuary is also home to a broad range of crustaceans and fishes. These jungles also function as impediments for windstorms, cyclones, and surges and waves hence safeguarding the villages close by.
The Krishna Godavari catchment area is one of the principal nesting locations of the imperiled Olive Ridley Turtle. The Godavari ranks as the second biggest river in India following the Ganges.
Important cities and towns on the riverbanks
Listed below are the important cities and towns located on the riverbanks of Godavari:
In Andhra Pradesh:
- Nirmal, Adilabad (Nirmal Toys)
- Basara, Adilabad (Gnana Saraswati Temple)
- Battapur, Nizamabad (Armoor Toys)
- Tadpakala, Nizamabad (Armoor Toys)
- Dharmapuri, Karimnagar (Narasimha Swamy Temple)
- Goodem Gutta, Adilabad (Temple)
- Manthani, Karimnagar (Sri Rama, Gautameshwara Swami(Siva) Temple, Sarswathi Temples)
- Kaleshwaram, Karimnagar (Siva or Kaleswara Mukhteswara Swamy Temple)
- Godavarikhani, Karimnagar
- Mancherial, Adilabad
- Bhadrachalam, Khammam
- EturiNagaram, Warangal
- Yanam
- Rajamundry
- Tallapudi
- Kovvur
- Antarvedi
- Narsapur
- Tadipudi
In Maharashtra:
- Trimbakeshwar (10th Jyotirliga of Lord Shiva)
- Nashik (Popular sacred city and Kumbhamela spot)
- Paithan (Old capital of Satvahan empire, Sacred Place)
- Kopargaon
- Nanded (Known for Sachkhand Gurudwara)
- Gangakhed
- Gevrai in District Beed
- Sironcha (Town located close to the meeting point of Pranahita and Godavari rivers)
Bridges and dams on the river
Given below are the important bridges and Dams on the Godavari River:
Havelock Bridge
The construction of Havelock Bridge began in 1876. It is a railway bridge, which was named after the erstwhile Governor of Madras. Construction was completed in 1897 and the oldest bridge on Godavari linked East Godavari with West Godavari. The entire construction work was overseen by F.T. Granville Walton who had built the Dufferin Bridge on the Ganges and Granville Mills, British engineers. Extending for 3 kms, built with concrete stonework and steel beams, the bridge facilitated the trains traveling from Chennai to Howrah. With growing movement in cargo and travelers, a rail-cum-road bridge was also constructed 25 years ago over the downstream of the river. As the first railbridge survived its purpose by functioning for more than a century, train services on this bridge were postponed in 1997 with the construction of the third Godavari Bridge. At present, the first bridge still is placed as a testimonial of human enterprise and skill.
Rail-cum-road Bridge
The bridge has been built to serve both as a rail bridge and a street between the East and West Godavari Districts.
New Railway Bridge
The construction work began in 1997 over the upstream of the river.
Places of interest on Godavari riverbanks
Similar to any other important rivers in India, there are several pilgrimage sites and tourist spots on the banks of this river such as the following:
- Nashik - One of the four Sinhastha Kumbh Mela and also a Hindu religious site.
- Trimbakeshwar - One of the 12 Jyotirlingas and old place of worship for Lord Shiva.
- Nanded - Home to Takht Sri Hazur Sahib, one of the five holiest sites in Sikhism.
- Paithan - Home to Saint Eknath's dwelling area, popular Jayakwadi dam, and a picturesque garden called as Sant Dnyneshwar Udyan.
- Dharmapuri, Andhra Pradesh - The area is famous for the Lord Narasimha temple (religious spot for Hindus). Godavari runs from north to south in Dharmapuri, therefore the river is named as "Dakshina Vahini" (running towards the south).
- Basar (formerly, Vyasara) - Sri Gyana Saraswati temple is located on the banks of the river in Adilabad, Andhra Pradesh. The distance from Hyderabad, capital of Andhra Pradesh is 210 km. You can reach there by road and rail (closest important station is Nizamabad, though Basar station is still there). It is assumed that the sage Vyasa authored the Mahabharata on the riverbanks of Godavari at this site, and hence the spot has been named as Vyasara.
- Bhadrachalam - Houses Hindu temple of Lord Rama.
- Kaleshwaram - Sri Kaleswara Mukhteswara Swamy Temple is located here on the riverbanks of Triveni sangamam of Pranahita and Godavari rivers (boundary of Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh). The place is 115 km from Warangal city and 125 km from Karimnagar.
- Pattiseema - It is a village where a Hindu temple is located on a tiny hill on an isle in the river.
- Rajahmundry - It is the hub for Telugu Literature. Rajahmundry is an urban settlement that represents Telugu traditions. It is home to Aadikavi Nannaya, one of the authors of Kavitrayam. Known for the Godavari Pushkaralu - an occasion that takes place once in every 12 years, observed with splendor and grandeur and visited by lakhs of people coming from different places of the world. A dip in Godavari during the Pushkaram Fair is assumed to be as good as dipping in the sacred River Ganges.
- Antarvedi - Home to Laxmi Narasimha Swamy temple.
Last Updated on : February 19, 2026