1. Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Solution:
Glomerular Filtration rate (GFR) is the amount of filtrate formed by both the kidneys (nephrons) every minute. The GFR of a healthy person is approximately 125ml per minute. The GFR consists majorly of water and other constituents such as amino acids, glucose, potassium, sodium, urea, uric acid and ketone bodies.
2. Explain the autoregulatory mechanism of GFR.
Solution:
Kidneys regulate the glomerular filtration rate through the mechanism which is auto regulatory. It involves the action of juxtaglomerular apparatus, which is a microscopic structure present between the returning distal convoluted tubule and vascular pole of the renal corpuscle of the same nephron. It regulates the glomerular filtration rate and renal blood flow. When the glomerular filtration rate declines, the juxtaglomerular cells are activated for the release of renin. This triggers the glomerular blood flow causing the GFR to revert to normal. Renin causes GFR to revert to normalcy by activating the renin-angiotensin mechanism.
3. Indicate whether the following statements are true or false:
(a) Micturition is carried out by a reflex.
(b) ADH helps in water elimination, making the urine hypotonic.
(c) Protein-free fluid is filtered from blood plasma into the Bowman’s capsule.
(d) Henle’s loop plays an important role in concentrating the urine.
(e) Glucose is actively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Solution:
(a) Micturition is carried out by a reflex – True
(b) ADH helps in water elimination, making the urine hypotonic – False
ADH helps in reabsorption of water causing the urine to be hypotonic.
(c) Protein-free fluid is filtered from blood plasma into the Bowman’s capsule – True
(d) Henle’s loop plays an important role in concentrating the urine – True
(e) Glucose is actively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule – True
4. Give a brief account of the counter current mechanism.
Solution:
The chief adaptation for the conservation of water is the counter current mechanism that is functional inside the kidney. In the kidney there are two counter current mechanisms, namely:
1. Henle’s loop
2. Vasa rectae
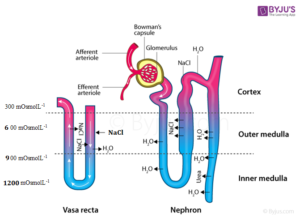
Henle’s loop is a U-shaped part of the nephron. The flow of blood in the two branches of the tube is in the opposite direction which gives rise to the counter currents.
Vasa recta, on the other hand is an efferent arteriole that forms a capillary network around the tubules in the renal medulla which tracks parallel to the Henle’s loop. Vasa recta is also U-shaped. The flow of blood is in opposite directions in the two limbs of vasa recta. Hence, the blood that enters the renal medulla in the descending limb comes in close proximity with the outgoing blood in the ascending limb
Through the counter current mechanism, the osmolarity increases in the cortex from 300 mOsmolL-1 to about 1200 mOsmolL-1in the inner medulla which helps in sustaining the concentration gradient. This in turn aids in the easy movement of water from the collecting tubules. The concentration gradient is due to the movement of urea and NaCl.
5. Describe the role of liver, lungs and skin in excretion.
Solution:
The role of liver, lungs and skin in the process of excretion is as follows:
Liver:
It is the chief site for the removal of inactivated products of steroid hormones, cholesterol, drugs and vitamins.
Dead erythrocytes possess haemoglobin. This haemoglobin is also disintegrated into bile pigments – biliverdin and bilirubin which are treated wastes.
Bile carries substances to the intestine which along with the wastes are eliminated
Lungs:
Carbon dioxide is expelled out of the body by the lungs
Approximately, it eliminates 200ml of carbon dioxide every minute
Water in the form of water vapor is also eliminated
Loss of water increases in colder conditions and declines in humid, hot conditions
During the process of expiration, several volatile material are also ejected
Skin:
It is chiefly responsible for thermoregulation(cooling) of the body
Sweat is excreted by the skin. It contains nitrogenous wastes. Sweat is excreted only when necessary, such as to cool the body
Sweat is excreted by the sweat glands, constitutes of urea, NaCl and lactic acid
Through the sebum, the sebaceous glands removes hydrocarbons, sterols and waxes
A protective oily covering is provided to the skin by the sebum
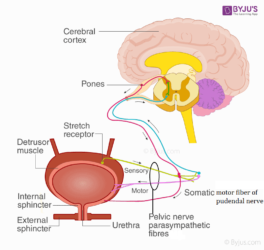
6. Explain micturition.
Solution:
Micturition is the process of releasing urine. Micturition is caused by a neural mechanism known as micturition reflex