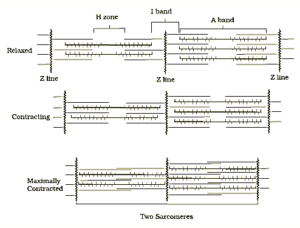
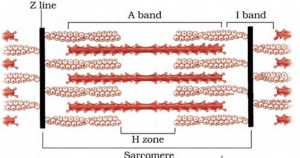
1. Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions.
Solution:
The diagram below shows the sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions:
2. Define sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Solution:
Sliding filament theory states that the muscle fibre contraction occurs due to the sliding of the thin filaments over thick filaments.
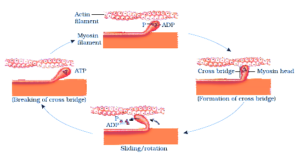
3. Describe the important steps in muscle contraction.
Solution:
The mechanism of muscle contraction is explained well by the sliding filament theory which states that the muscle fibre contraction occurs due to the sliding of the thin filaments over the thick filaments.