The Ravi River is one of the most important rivers in South Asia, yet it often does not get the attention it deserves. After starting in the Himalayas, it travels across India and Pakistan before joining the Chenab River. The water from the Ravi is largely responsible for the establishment of cities like Lahore, one of Pakistan's largest. Many farms in the region depend on its waters to grow crops such as wheat and rice. The river also plays a key role in shaping local cultures, inspiring stories, traditions, and even religious practices over centuries. History shows how the Ravi helped advance civilizations. Ancient trade routes crossed its banks, and many towns grew around its flow. Over time, governments built large dams and irrigation projects on the river. These projects aimed to control water flow and support agriculture. But they also caused tensions, as countries argue over how much water each should get. Melting glaciers in the Himalayas threaten to reduce their flow, and pollution from cities and farms harms the water quality.
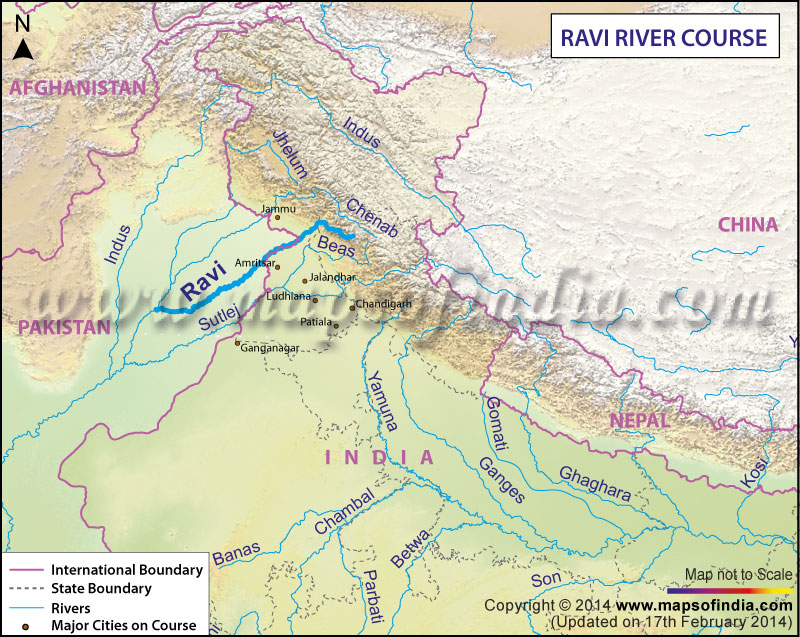
Origin and Course of the Ravi River
The Ravi River starts high in the Indian Himalayas, particularly in the Chamba District of Himachal Pradesh. It rushes southwest, dropping from the mountains into the plains. After traveling through Himachal Pradesh, it enters Punjab, where it broadens before crossing into Pakistan. Along its route, the river receives water from several smaller streams and tributaries, such as the Uj, Bias, and Chenab rivers. These contributions make Ravi a vital part of the region’s water system.
Hydrology and Water Flow Data
The Ravi River typically carries an average discharge of about 4,500 cubic meters of water every second. The amount of water flowing through the river at any particular time is shown by this measurement. This volume does not, however, remain constant throughout the year. Depending on the season, it might vary greatly. The river's flow significantly increases throughout the summer. This happens in part because snow from the mountains melts and feeds the river, adding more water. The rainy season, called the monsoon, also floods the area with heavy rains, causing the river to swell. In contrast, during winter, the flow slows down significantly. Cooler temperatures mean less snow melts and fewer rains, so the river’s water levels drop. These seasonal changes have a big impact on people living near the river. Farmers depend on its water for their vegetables. Industries also depend on the river for various needs. When the river flows strongly, farming becomes easier and more productive. When flows reduce, farmers struggle to irrigate their fields. Flooding in the monsoon season can destroy crops or homes, while droughts in winter can leave communities without enough water. Climate evolution has made these practices more irregular. Instead of predictable seasons, there are more frequent floods and dry spells. This causes great problems for communities that depend on the river. Floods can wipe out entire villages or flood farmland, destroying livelihoods. Droughts can last longer and become more severe, leaving people short of water. These changes threaten the health and economy of the areas near the Ravi River. As the weather becomes more unpredictable, communities find it harder to plan for the future. The increase in extreme weather events puts more strain on local resources. This ongoing shift is a serious concern for everyone who relies on the river’s flow for their daily life and work.
Geographical Significance
The Ravi River has carved deep valleys and lush green lands along its course. Its riverbanks support diverse ecosystems, offering a home to numerous plants and animals. The river also helps shape local landscapes, creating fertile plains that are perfect for farming. Such geographical features made the Ravi flow a natural route for ancient travelers and settlers.
Historical and Cultural Significance of the Ravi River
Ancient Civilizations and Historical Sites
Long before modern borders, the Ravi River was part of the great Indus Valley civilization. Archaeologists have found relics of ancient cities along its banks, showing its importance in early trade and settlement. Towns like Multan in Pakistan, located near the river, flourished as trading hubs centuries ago. Religious sites along the Ravi, including temples and mosques, reflect its spiritual importance to local communities.
Cultural Practices and Traditions
The river plays a big role in local festivals and rituals. Many communities celebrate the river during the spring festival of Baisakhi, especially in Punjab. Folk stories and legends also link the river to gods and mythological figures, making it a symbol of life and renewal. For many, the Ravi isn’t just a waterway-it’s part of their identity and daily life.
Socio-Economic Impact of the Ravi River
Agriculture and Irrigation
The Ravi supplies water for millions of farmers in India and Pakistan. Its riverbanks produce crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane. Large irrigation systems, including canals and dams, boost productivity but sometimes cause overuse and water shortages. Still, fertile plains along the river make farming one of the region’s most important economic activities.
Hydroelectric Power and Infrastructure
Dams built along the Ravi River, such as the Ranjit Sagar Dam, play a crucial role in generating clean and renewable energy for surrounding towns, cities, and industries. These structures also help in water storage, irrigation, and flood control, contributing to regional development and agricultural productivity. Additionally, reduced downstream flow can harm aquatic ecosystems, affect agricultural lands, and threaten the livelihoods of those who depend on the river. Balancing development with environmental and social responsibility is essential to ensure the long-term sustainability of hydroelectric projects on the Ravi.
Cross-border Water Management
The 1960 Ravi River Treaty between India and Pakistan helps divide water fairly. Despite this agreement, disagreements and tensions often emerge about water sharing. Improving cooperation and finding new solutions remain crucial for peace and the sustainable use of this shared resource.
Contemporary Issues and Future Outlook
Water Disputes and Cooperation
India and Pakistan sometimes face disputes over water rights. Diplomatic efforts aim to resolve conflicts, but political tensions can complicate these talks. Creative fixes like cooperative basin management and rainwater collection could reduce conflict and foster collaboration.
Sustainable Development and River Management
Sustainable practices are vital for Ravi’s future. This includes reducing pollution, encouraging eco-friendly farming, and protecting wildlife. Community participation and strict policies play a critical role in balancing growth with conservation.
Future Prospects
The Ravi River offers great potential for eco-tourism and cultural preservation. Developing responsible tourism can boost local economies while fostering appreciation for the river’s heritage. Advanced water management technologies can help monitor and conserve this historic waterway for future generations.
Conclusion
The Ravi River is more than just a body of water; its rich history, ecological significance, and importance to local communities make it a vital resource. Sustainable protection and management are essential to preserving its legacy. From government bodies to individual citizens, everyone must work together to safeguard its health and future. While the past highlights its value, the future depends on the actions we take today.
Last Updated on : July 01, 2025