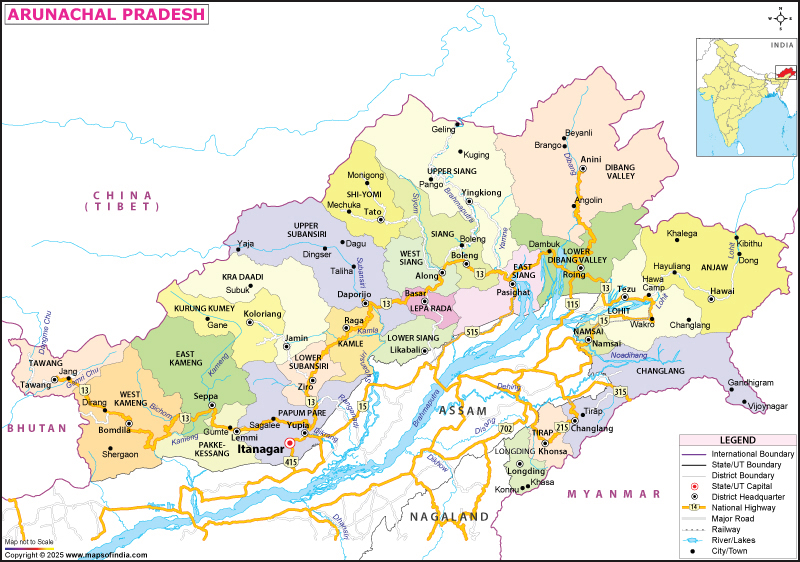
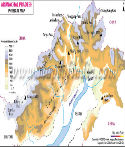
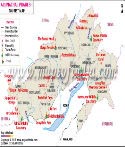
As of Feb 2024, it comprises 28 districts. The state is called "Land of the Rising Sun" The literary meaning of the "Land of the Rising Sun" is "the land of the dawn-lit mountains." It receives the first rays of the sun in the country. The state has its capital in Itanagar, which is also its largest city.
The state is famous for its natural beauty and a stable agricultural economy. Major crops of Arunachal Pradesh: pulses, sugarcane, rice, wheat, maize being its main crops. It has a considerable amount of forest cover, which ensures that the forest products also contribute to its economy.
The tourism sector of the state has not been fully utilized. The state government is in the process of reviving tourism in Arunachal Pradesh, which was affected due to the novel coronavirus pandemic and nationwide lockdown.
Geography of Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh covers an area of 83,743 km2 (32,333 sq mi). It ranks 14th in terms of the total area in the country. The state extends from the snow-covered Himalayas to the Brahmaputra plains. It falls between 26° 30' and 29° 30' North latitude and 91° 30' and 97° 30' East longitude.
The state has some parallel hill ranges, deep gorges and fast-flowing rivers. Internationally, it borders Bhutan on the west; China (Tibet Autonomous Region) on the north and northeast; and Myanmar on the east. Internally, it shares borders with the Indian states of Assam and Nagaland to the south.
Arunachal Pradesh Climate
The presence of Himalayas has affected the climate of Arunachal Pradesh to a large extent. The climate of Arunachal Pradesh, depends on its elevation. The upper regions of the state experience alpine or tundra climate, while the middle Himalayan portions have a temperate climate. Humid conditions prevail in the lower regions of the state.
In the high-altitude area of the North, such as the peaks of Kangto and Gorichen, which are both above 7000, the weather is cold all year round and there are significant amounts of snow in the winter months. This area fits into the alpine or tundra climate category, which is characterized by long, cold winters and short summers. The flora in these high elevation areas is limited to hardy shrubs and grasses with an absence of trees.
The central belt of the state, belonging to the middle Himalaya slope, encompasses warm and temperate climates. The summer is hot and the winter can be cold in the winter, however it is not as cold as the alpine zone. This zone has a variety of flora and fauna often containing dense forests of pine, oak and rhododendron.
The southern zone of Arunachal Pradesh including the foothills and plains has a hot and humid subtropical climate. This area receives large amounts of rainfall especially in May-September during the southwest monsoon. The annual rainfall in some areas exceeds 3000 mm. The hot weather and high humidity allow for tropical and subtropical forests to thrive in Arunachal Pradesh. The flora of these areas is particularly rich in species and diversity and makes the area an important agricultural area in Arunachal Pradesh.
Economy
Arunachal Pradesh has an economy based on its natural resources, established practices, and developing growth sectors. The economy of Arunachal Pradesh is predominantly agrarian and utilises diverse ecosystems, forests, and dimensions of horticulture and cottage industries. In spite of the relatively rugged land and metrics in development, Arunachal Pradesh is moving toward economic diversity and development.
Arunachal Pradesh is primarily an agricultural state. The main crops here are rice, pulses, sugarcane, wheat, millets, oilseeds, and ginger. The farmers employ various devices to increase their agricultural yield- Jhum farming and terrace farming are two of these methods. In Jhum cultivation, the farmers prepare the land by setting it on fire or cutting down the unwanted cultivation. Terrace farming involves the shaping of hilly agricultural lands into multiple terraces in a bid to check soil erosion.
Rice is the staple food and the most growing crop, particularly in the plains and low valleys. The Jhum, or shifting cultivation is an age-old established practice by tribal communities living in the hills. Jhum has been criticized for its environmental impacts; however, it is closely associated with the cultural and social lives of the indigenous tribes. Terrace farming is common in the more settled areas that have moderate slopes where sustainable agriculture and water management can be practiced more efficiently.
The forest cover of Arunachal Pradesh is fairly well exploited. The state boasts of several rice mills, fruit preservation departments, and horticulture units. In 2018-19 the state's horticulture jumped to 213.87 thousand metric tonnes (MT). Many fruits, like oranges, apples, pineapples, and kiwis, are cultivated along with medicinal plants and spices. Horticulture has been promoted heavily by the government under various schemes, as it has potential for improving farmers’ incomes and supporting agro-industrial development.
Similarly, the industry in Arunachal Pradesh is only just emerging, but it holds significant potential because of the immense mineral and forest resources found throughout the state. The state is replete with several key industries including art and crafts, handlooms, cane and bamboo, power, and mineral-based industry. Traditional industries like handicrafts and handlooms are important to provide local employment and reflect Arunachal's cultural identity. Each of Arunachal's tribal communities has its distinct artistic expression through weaving, carving, pottery making, and cane and bamboo designs, etc.
Arunachal Pradesh has plentiful bamboo and cane, allowing small-scale units that produce baskets, mats, furniture, and a number of other handcrafted products. These items are being marketed both nationally and internationally. Baskets are being acknowledged for their low environmental impact and cultural significance. Handloom weaving, particularly women's handloom weaving, is producing colourful and emblematic textiles that exhibit the tribal heritage and are even starting to be marketed as high-value artisanal products.
In addition, the power sector is a crucial development. Arunachal Pradesh has mountains and fast-flowing rivers. Together with lots of potential for Hydroelectric generation, a number of large and small hydropower projects are underway to exploit this energy. Part of this effort is to maintain needed power in the region while also creating extra power for the regional grids. The state has mineral deposits too, such as coal, limestone, and dolomite, which are now being developed for industrial purposes.
Arunachal Pradesh Demography
Based on the latest census data from 2023, Arunachal Pradesh's estimated population is approximately 1.56 million (15.62 lakh), accounting for around 0.11% of India's total population.
Arunachal Pradesh has a very diverse population, with ethnic diversity with approximately over 26 major tribes and over 100 sub-tribes. The major tribes include Nyishi, Adi, Apatani, Tagin, Mishmi, Monpa, and Wancho, each tribe with their languages, customs, and culture. Indigenous languages are the main languages of communication between tribes. However, Hindi, Assamese, and English are used as bridging languages of communication between tribes and communities.
The sex ratio has improved in the state in gender distribution. The sex ratio is approximately 949 females in a 1,000 males. It's better than the national average of 930. This remarkable trend can be attributed to the interventions of programs such as Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao without a doubt. There are also 5 districts in the state: Shi Yomi, East Kameng, Kamle, Upper Siang, and Tawang sex ratios greater than 1000 females per 1,000 males.
Arunachal Pradesh Rivers
Arunachal Pradesh is primarily an agricultural state. The main crops here are rice, pulses, sugarcane, wheat, millets, oilseeds and gThe major rivers flowing through the state are Brahmaputra, Subansiri, Lohit, Kameng, and Tirap. These rivers are snow-fed, originating from the Himalayas and splitting the state into five river valleys: the Kameng, the Subansiri, the Siang, the Lohit, and the Tirap
Tourism Sector of Arunachal Pradesh and Important Tourist Destinations
The snow-capped mountains and the beautiful valleys of the state add to the scenic beauty of Arunachal Pradesh. These features can serve as major tourist draws if tourism is explored. However, there are some places in the state which entice tourists:
Tawang:It is located at a height of 2,669 m (8,757 ft) feet above sea level. The hill station with some high altitude but inaccessible lakes is a major draw for adventure lovers.
Itanagar:the largest city of Arunachal Pradesh, has places like Jawaharlal Nehru State Museum, Ganga Lake (Gyakar Siny), and the Ita Fort, which are worth visiting. Apart from these, there are several wildlife sanctuaries and four National parks in the state.
WildLife Sanctuaries in Arunachal Pradesh
Dr. D. Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary
Itanagar Wildlife Sanctuary
Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary
National Parks of Arunachal Pradesh
Mouling National Park in Jengging
Namdhapa National Park in Miao
Arunachal Pradesh State Information | |
|---|---|
| Capital | Itanagar |
| Date of formation | February 20,1987 |
| Governor | Kaiwalya Trivikram Parnaik |
| Chief Minister | Pema Khandu |
| Tourist attractions | Twang Hompa, Dirang, Bomdila |
| Festivals | Losar, Si-Donyi, Reh, Mopin and Solung |
| Major dance and music forms | Lion and Peacock dance, Ponung, Roppi, Wancho dance |
| Arts and crafts | Monpas are especially good wood carvers, women in AP are expert weavers. |
| Languages | Monpa, Mild, Aka, Sherdukpen, Apatani, Adi, Hill Miri |
| Size | 83,743 sq. km |
| Population (Census 2011) | 1.56 million (approx.) |
| Rivers | Siang, Lohit, Kameg, Dikrong, Tirap, Dibang, Subansiri, Noa-Dihing, Kamlang |
| Forests and wildlife sanctuaries | Namdapha NP, Monling NP |
| State animal | Mithun |
| State bird | Great Indian hornbill |
| State flower | Rhynchostylis retusa |
| State tree | Dipterocarpus retusus |
| Major crops | Jhum |
| Factoids | The mithun is considered a unit of wealth and is allowed to roam free till it is sacrificed and eaten on special occasions. |
| Monpas, who are Buddhists, live in the mountains of western Arunachal Pradesh | |
| No. of District | 28 |
Maps in Other Regional Languages
Last Updated on: November 13, 2025
|
|