Chapter 10 Internal Trade Questions and Answers: NCERT Solutions for Class 11th Business Studies
Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 10: Internal Trade - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
Question 1. What is meant by internal trade?
Answer: Internal trade refers to the buying and selling of goods and services within the domestic territory of a country. It is known as internal trade. In other words, the process of exchanging goods and services within the national boundaries of a country is called internal trade. Purchases of goods from a local shop, a mall or an exhibition are all examples of internal trade. The government does not levy customs or import duties on goods and services that are produced within the country for meeting the domestic demand.
Internal trade can be classified into the following two categories:
* Retail Trade: It refers to the buying and selling of goods in small quantities for final consumption.
* Wholesale Trade: It refers to the buying and selling of goods in bulk, i.e., the exchange of large quantities of goods meant for resale in local markets.
Question 2. Specify the characteristics of fixed shop retailers.
Answer: As the name suggests, fixed-shop retailers are retailers who have permanent establishments. It means that they sell goods and services from fixed shops and do not move from place to place to serve customers. For example, retailers functioning from fixed establishments in the local grocery market.
The following are some of the characteristics of fixed-shop retailers:
1. Fixed-shop retailers operate on a large scale and have huge resources at their disposal compared with itinerant traders. However, among fixed-shop retailers, there are retailers who operate on a small scale or a large scale.
2. They generally deal in more than one product—that is, their range of goods varies from consumer durable goods to non-durable goods.
3. Fixed-shop retailers provide services such as free home delivery and supply of goods on credit to their customers.
4. They have a greater credibility in the eyes of consumer as they can be traced if the product is found to be defective or there is any other problem.
Question 3. What purpose is served by wholesalers providing warehousing facilities?
Answer: Wholesalers purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers, store them and distribute them to retailers in small quantities for further resale. This bulk purchase of goods enables manufacturers to undertake production on a large scale without worrying about storage facilities. By offering warehouses close to the centres of distribution, wholesalers provide what is known as ‘place utility’. Wholesalers not only provide warehousing facilities such as collection, storage and protection of goods but also facilitate marketing and distribution, creating ‘time utility.
Question 4. How does market information provided by wholesalers benefit the manufacturers?
Answer: Wholesalers provide a variety of information to both manufacturers and customers. To manufacturers, they provide information about:
1. The tastes and preferences of customers
2. Conditions prevailing in the market
3. Level of competition in the market and
4. Types of goods and features demanded by consumers.
This information helps manufacturers to cater to the changing needs of consumers.
Question 5. How do the wholesalers help the manufacturer in availing the economies of scale?
Answer: Wholesalers often purchase goods in bulk quantities from manufacturers. Once a purchase is made, the wholesalers distribute the goods in small quantities to retailers for further resale. However, during this process, they provide manufacturers with a variety of warehousing facilities such as collection, storage, marketing and distribution of goods. These services reduce the burden on manufacturers by creating time and place utility, thus enabling them to produce goods on a large scale and benefit from the economies of scale.
Question 6. Distinguish between single line stores and specialty stores. Can you identify such stores in your locality?
Answer: Single-line stores are small shops that deal in only one product. For example, garments or shoes. However, single-line stores offer a wide variety of the product. For instance, a single-line store that deals in garments will have a wide variety of clothes in all sizes for men, women and children.On the other hand, specialty stores deal only in a particular type of product from a selected product line. For example, men’s clothing. Such stores generally sell all the brands of the product in which they specialise. For instance, if a store specialises in men’s clothing, then it will have all the brands of men’s garments. On the basis of these features, we can identify the different types of stores in a locality—whether they are single-line stores or specialty stores. Single line stores are more frequently found in local retail markets while specialty stores are found in wholesale markets.
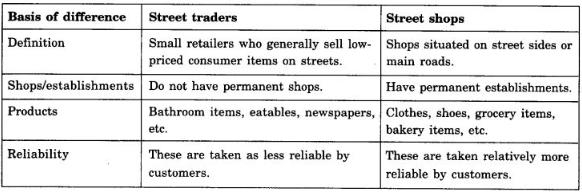
Question 7. How would you differentiate between street traders and street shops?
Answer:
Question 8. Explain the services offered by the wholesalers to the manufacturers.
Answer: Wholesalers offer a wide variety of services to manufacturers. The following are examples of such services:
1. They facilitate large-scale production: Wholesalers purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and sell them to retailers in small quantities for further resale. This bulk purchase made by wholesalers enables manufacturers to undertake production on a large scale without worrying about storage facilities. Thus, wholesalers facilitate large-scale production.
2. They provide storage facilities: When wholesalers purchase goods in bulk quantities from manufacturers, they store these goods in their god owns or warehouses, reducing manufacturers burden of finding proper storage .
3. They collect market information: Wholesalers provide different kinds of information to manufacturers, such as information about the tastes and preferences of customers, prevailing market conditions, level of competition in the market and type of goods demanded by consumers. This in turn helps manufacturers to produce goods according to the market needs.
Question 9. What are the services offered by retailers to wholesalers and consumers?
Answer: Retailers offer a variety of services to wholesalers and customers. Some of these services are listed below.
1. They provide information to customers: Retailers provide information to customers about the new products available in the market, their features, prices, etc. This information helps customers decide which product to buy.
2. They provide information to wholesalers: Retailers provide information to wholesalers, such as the tastes and preferences of customers, prevailing market conditions and level of competition in the market. Wholesalers pass on this information to manufacturers.
3. They store a wide variety of goods: Retailers generally store a wide variety of goods based on consumer tastes and preferences and thus allow customers to choose from the available range of products.
4. They facilitate distribution of goods: Retailers facilitate the distribution of goods to consumers for final consumption.
5. They help in promotion of goods: Since retailers are in direct touch with customers, they can promote the sale of goods through personal interaction. Thus, retailers help wholesalers and manufactures in promoting the sale of goods.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Itinerant traders have been an integral part of internal trade in India. Analyse the reasons for their survival in spite of competition from large scale retailers.
Answer: Itinerant traders are retailers who do not have a fixed place of operation. That is, they do not have a shop from where they sell their products. They are also known as mobile traders as they keep moving from place to place in order to sell their products. They are generally found on street sides, and they shift their place of operation in search of more customers. They usually sell low-priced and non-standard goods.The reasons that itinerant traders survive in spite of the tough competition from large-scale retailers can be attributed to the following factors:
1. It is very easy to set up a small scale retail shop. One person with limited funds himself can start business. He need not associate other persons and no formalities are necessary.
2. A small scale retail shop can be located anywhere. It can provide goods of daily use near the place of consumers. They are not required to travel to big markets.
3. The small scale retailer knows his customers. He can attend to them personally and cater to their individual tastes and needs. Such personalised service is not available in large scale retail stores.
4. Small scale retailers cater to the masses that have limited income and can afford to buy small quantity. In India majority of the population is poor.
5. It is easy to manage and control a small sale retail shop. The owner himself is the manager. He has direct motivation to work hard and increase the efficiency of business. He takes personal interest in his business organisations.
6. Small amount of capital is required to start a small retail shop. People with small amount of funds can start retail business on a small scale.
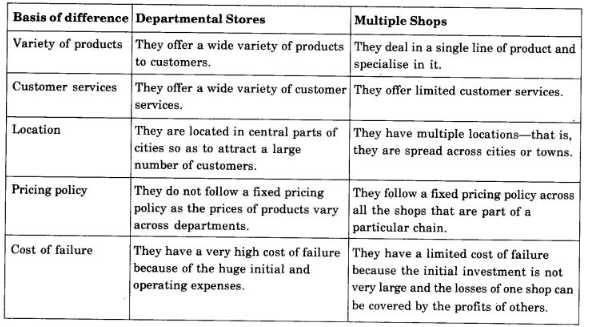
Question 2. Discuss the features of a departmental store. How are they different from multiple shops or chain stores?
Answer: Departmental stores are basically large, fixed establishments that deal in a wide variety of products. The following points highlight the features of a departmental store:
1. Central locations: Department stores are generally located in central areas so as to attract a large number of customers.
2. Defined hierarchy: The management in departmental stores follows the same hierarchy that is generally followed in any joint stock company. That is, the top management consists of a board of directors, with the managing director, the general manager and the department managers under it in that order.
3. Absence of middlemen: Departmental stores purchase goods directly from manufacturers and sell them to customers. Thus, they eliminate the role of middlemen.
4. Centralised purchase with decentralised sales: In a departmental store, the purchases from manufacturers are handled by a single division that follows a centralised purchase policy. On the other hand, the sales are handled by the respective sections of the departmental store, which follow a decentralised policy for sales.
Differences between Departmental stores and Multiple shops
Question 3. Why are consumers cooperative stores considered to be less expensive? What are its relative advantages over other large scale retailers?
Answer: Consumer cooperative stores are formed by groups of consumers to provide goods at reasonable prices to members of consumer societies. In such societies, the role of middlemen is eliminated as these societies purchase goods from manufacturers or wholesalers directly and sell them to society members at reasonable rates. As consumer cooperative stores do not aim at profit-making, the prices of goods offered by them are much lower than the prices of goods at retail shops. Compared with large-scale retailers, the capital requirement for starting a consumer cooperative society is very low. Thus, consumer cooperative stores do not require much investment, and the goods sold by them are priced lower.
The following are some advantages that consumer cooperative stores have over large- scale retailers:
1. Democratic management: Consumer cooperative stores are democratic organisations as they are managed and controlled by elected managing committees of consumer societies. The members of managing committees are elected by the members of consumer societies on the principle of ‘one member, one vote’.
2. Limited liability: The liability of the members of consumer cooperative societies is limited to the amount of shares held by them. Thus, in case a society’s liabilities increase beyond the assets, the members will not be liable to repay the debts using their personal assets.
3. Low price of goods: As the goods offered by consumer cooperatives are directly purchased from manufacturers and wholesalers, the role of middlemen is eliminated. Therefore, consumer societies are able to sell goods at lower prices.
Last Updated on: January 14, 2026
