Chapter 7 – Excess Demand and Deficient Demand Questions and Answers: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics
Class 12 Economics (Macro Economics) Chapter 7: Excess Demand and Deficient Demand - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
I.Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is meant by excess demand in macroeconomics?
Answer: When in an economy aggregate demand exceeds “aggregate supply at full employment level”, the demand is said to be an excess demand.
Question 2. Define inflationary gap.
Answer: When in an economy aggregate demand exceeds “aggregate supply at full employment level”, the demand is said to be an excess demand and the gap is called inflationary gap.
Question 3. Give the meaning of deficient demand.
Answer: When in an economy aggregate demand falls short of aggregate supply at full employment level, the demand is said to be as deficient demand.
Question 4. Define deflationary gap.
OR
Give the meaning of deflationary gap.
Answer:” When in an economy aggregate demand falls short of aggregate supply at full employment level, the demand is said to be deficient demand and the gap is called deflationary gap.
Question 5. State two measures by which a central bank can attempt to reduce the inflationary gap.
Answer:
1. Increase in cash reserve ratio.
2. Increase in marginal requirement.
Question 6. What is the impact of increase in margin requirements?
Answer: Increase in margin requirements discourages borrowings and decreases the aggregate demand.
Question 7. Give the meaning of full employment.
Answer: Full employment equilibrium refers to the situation where aggregate demand = aggregate supply and all those who are able to work and willing to work (at the existing wage rate) are getting work.
Question 8. Give the meaning of involuntary unemployment.
Answer: Involuntary unemployment refers to a situation in which all able and willing persons to work at existing wage-rate do not find work. They are rendered unemployed against their wish. Hence, it is termed as involuntary unemployment.
Question 9. Is it necessary that equality between AD and AS is established at the full employment level?
Answer: No, it is not necessary that full employment occurs when AD = AS. Equilibrium can be achieved at full employment level, under employment level or at over full employment level.
Question 10. What is meant by full employment equilibrium?
Answer: Full employment equilibrium refers to a situation when equilibrium is attained i.e., aggregate demand is equal to aggregate supply at full employment level.
Question 11. What is underemployment equilibrium?
Answer: Underemployment equilibrium refers to a situation when equilibrium is attained i.e., aggregate demand is equal to aggregate supply below full employment level or when resources are not fully employed.
Question 12. What is the meaning of over full employment equilibrium?
Answer: Over full employment level refers to a situation when equilibrium is attained, i.e., aggregate demand is equal to aggregate supply beyond the full employment level.
II. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are the reasons or causes for excess demand?
Answer: The main reasons for excess demand are apparently the increase in the following components of aggregate demand:
1. Increase in household consumption demand due to rise in propensity to consume.
2. Increase in private investment demand because of rise in credit facilities.
3. Increase in public (government) expenditure.
4. Increase in export demand.
5. Increase in money supply or increase in disposable income.
Question 2. What are impacts or effects of excess demand on price, output, employment?
Answer:
1. Effect on General Price Level: Excess demand gives a rise to general price level because it arises when aggregate demand is more than aggregate supply at a full employment level. There is inflation in economy showing inflationary gap.
2. Effect on Output: Excess demand has no effect on the level of output. Economy is at full employment level and there is no idle capacity in the economy. Hence output can’t increase.
3. Effect on Employment: There will be no change in the level of employment also. The economy is already operating at full employment equilibrium, and hence there is no unemployment.
Question 3. What are the reasons or causes for deficient demand?
Answer: The main reasons for deficient demand are apparently the decrease in four components of aggregate demand:
1. Decrease in household consumption demand due to fall in propensity to consume.
2. Decrease in private investment demand because of fall in credit facilities.
3. Decrease in public (government) expenditure.
4. Decrease in export demand.
5. Decrease in money supply or decrease in disposable income.
Question 4. What are the impacts or effects of deficient demand on price (output) employment?
Answer:
1. Effect on General Price Level: Deficient demand causes the general price level to fall because it arises when aggregate demand is less than aggregate supply at full employment level. There is deflation in an economy showing deflationary gap.
2. Effect on Employment: Due to deficient demand, investment level is reduced, which causes involuntary unemployment in the economy due to fall in the planned output.
3. Effect on Output: Low level of investment and employment implies low level of output.
Question 5. Explain the role of Government expenditure and Open Market Operation in reducing AD/excess demand.
Answer: (a) Government Expenditure:
1. Government has to invest huge amount on public works like roads, buildings, irrigation works, etc.
2. During inflation, government should curtail (reduce) its expenditure on public works like roads, buildings, irrigation works thereby reducing the money income of the people and their demand for goods and services.
(b) Open Market Operation:
1. It consists of buying and selling of government securities and bonds in the open market by central bank.
2. In a situation of excess demand leading to inflation, central bank sells government securities and bonds to commercial bank. With the sale of these securities, the power of commercial bank of giving loans decreases, which will control excess demand.
Question 6. Differentiate between full employment and underemployment equilibrium.
Answer:
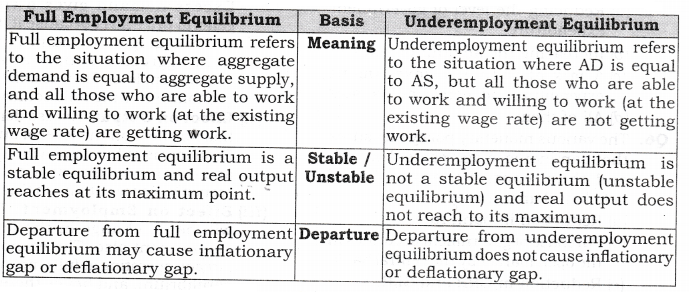
Question 7. What is meant by Margin Requirement? How does the Central Bank use this measure to control deflationary conditions in an economy?
Answer:
1. Business and traders get credit from commercial bank against the security of their goods. Bank never gives credit equal to the full value of the security. It always pays less value than the security.
2. So, the difference between the value of security and value of loan is called marginal requirement.
3. In a situation of deficient demand leading to deflation, central bank decreases marginal requirements. This encourages borrowing because it makes people get more credit against their securities.
lll. True Or False
Question 1. To control deflation the central bank should increase the bank rate.
Answer: False. The central bank should decrease the bank rate in order to control deflation.
Question 2. Purchase of government securities by the central bank in the open market is an appropriate policy to check depression in the economy.
Answer: True. To check depression the central bank should purchase government securities from the open market, so as to increase the availability of credit in the economy.
Question 3. To correct the deflationary gap, availability of credit should be increased.
Answer: True. Availability of credit should be increased to raise the level of aggregate demand.
Question 4. Fiscal policy has a direct effect on producing sector of the economy.
Answer: False. Fiscal policy has a direct effect on all the sectors of the economy.
Question 5. Equilibrium below full employment level does not lead to fall in output level.
Answer: False. Equilibrium below the full employment level leads to deflation, which causes low level of investment and employment implies low level of output.
Last Updated on: January 14, 2026
