Chapter 12 – Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Questions and Answers: NCERT Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids for Class 12 Chemistry
Class 12 Chemistry chapter 12 - Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
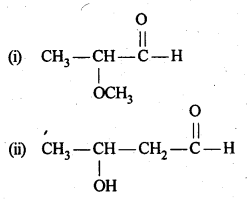
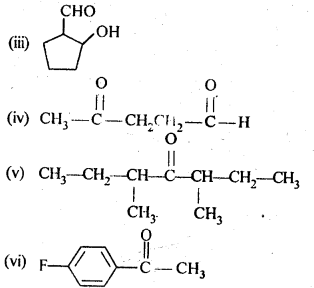
12.1. Write the structures of the following compounds:
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-OxopentanaI
(v) Di-sec.butylketone
(vi) 4-fluoroaeetophenone
Ans:
12.2. Write the structures of the products of the following reactions:
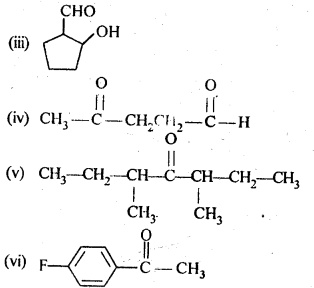
12.1. Write the structures of the following compounds:
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-OxopentanaI
(v) Di-sec.butylketone
(vi) 4-fluoroaeetophenone
Ans:

12.2. Write the structures of the products of the following reactions:
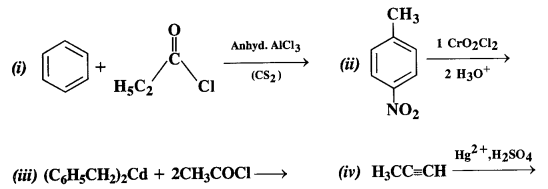
Ans:
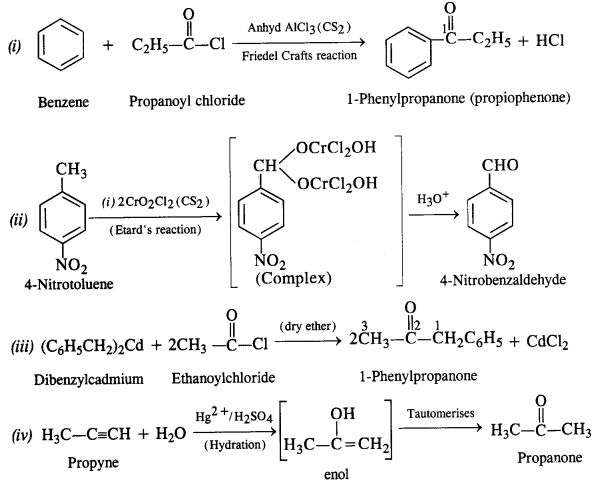
12.3. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH2CH3
Ans: The order is : CH3CH2CH3 < CH3OCH3 < CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH
All these compounds have comparable molecular masses CH3CH2OH undergoes extensive intermolecular Il-bonding and thus its b.pt. is the highest. CH3CHO is more pdlar than CH3OCH3 so that dipole-dipoie interactions in CH3CHO are greater than in CH3OCH3. Thus, b.pt. of CH3CHO > CH3OCH3. CH3CH2CH3 has only weak van der waals forces between its molecules and hence has the lowest b.pt.
12.4. Arrange the following carbonyl compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions :
(a) Ethanal, propanal, propanone, butanone
(b) Benzaldehyde, p-tolualdehyde, p-nitrobenzaldehyde, acetophenone
Ans: (a) The increasing order of reactivity of the carbonyl compounds towards nucleophilic addition reactions is :
butanone < propanone < propanal < ethanal
The reactivity is based upon two factors. These are: steric factors and electronic factors.
(b) The increasing order of reactivity is :
acetophenone < p-tolualdehyde < benzaldehyde < p-nitrobenzaldehyde
Explanation: Acetophenone being a ketone is the least reactive towards nucleophilic addition. All others are aldehydes. Among them, p-tolualdehyde is less reactive than benzaldehyde because CH3 group present at the para position w.r.t. -CHO group will increase the electron density on the carbonyl carbon atom due to hyper conjugation effect. As a result, the nucleophile attack occurs to lesser extent as compared to benzaldehyde.
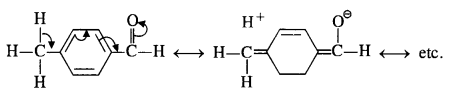
In p-nitrobenzaldehyde, the nitro group has an opposing effect. It is electron withdrawing in nature due to -I effect as well as -R effect. The electron density on the carbonyl carbon atom decreases and this favours the nucleophile attack.
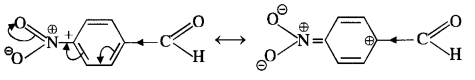
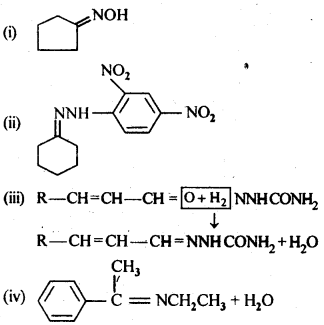
12.5. Predict the products of the following reactions:
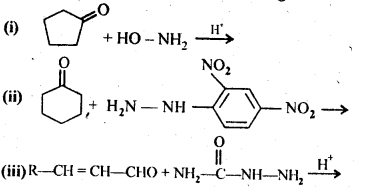
Ans:
12.6. Give the 1UPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) PhCH2CH2COOH
(ii) (CH3)2 C=CHCOOH
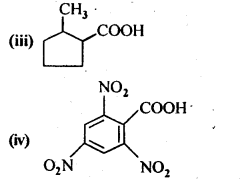
Ans: (i) 3 – Phenylpropanoic acid
(ii) 3 – Methylbut-2-enoic acid
(iii) 2-Methylcyclohexanecarboxylic acid
(iv) 2,4,6 – Trinitrobenzoic acid
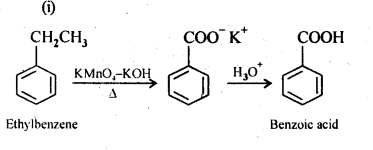
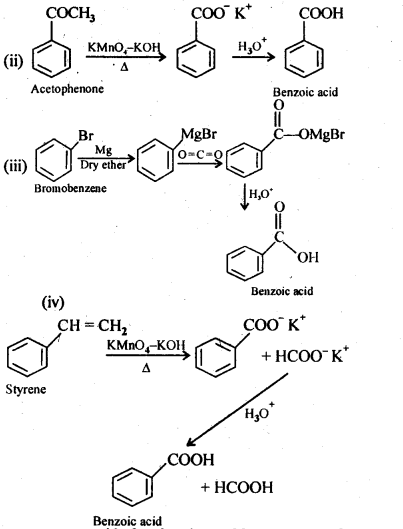
12.7. Show how each of the following compounds can be converted into benzoic acid.
(i) Ethylbenzene
(ii) Acetophenone
(iii) Bromobenzene
(iv) Phenylethene (styrene)
Ans:
12.8. Which acid from each of the following pairs would you expect to be a stronger acid?
(i) CH3COOH or CH2FCOOH
(ii) CH2FCOOH or CH2ClCOOH
(iii) CH2FCH2CH2COOH or CH3CHFCH2COOH
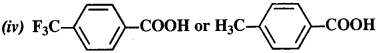
Ans:
Explanation: CH3 group with +I effect increases the electron density on the oxygen atom in O – H bond in the carboxyl group and cleavage of bond becomes diffcult. It therefore, decreases the acidic strength. The F atom has very strong -I effect, i.e., electron withdrawing influence. It decreases the electron density on the oxygen atom and cleavage of bond becomes easy. The acidic character therefore, increases. It is further related to the
1. No. of F atoms present in the molecule.
2. Relative position of the F atom in the carbon atom chain.
In the light of the above discussion.
(i) CH2FCOOH is a stronger acid.
(ii) CH2FCOOH is a stronger acid.
(iii) CH3CHFCH2COOH is a stronger acid.
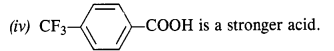
Last Updated on: January 14, 2026
