Chapter 14 – Biomolecules Questions and Answers: NCERT Biomolecules for Class 12 Chemistry
Class 12 Chemistry chapter 14 - Biomolecules - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
14.1. Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane and benzene (simple six membred ring compounds) are insoluble in water Explain.
Ans: The .solubility of a solute in a given solvent follows the rule ‘ Like dissolves like’.Glucose contains five and sucrose contains eight -OH groups. These -OH groups form H-bonds with water. As a result of this extensive intermoleeular H-bonding, glucose and sucrose are soluble in water.On the other hand, benzene and cyclohexane do not contain -OH bonds and hence do not form H-bonds with water. Moreover, they are non-polar molecules and hence do not dissolve in polar water molecules.
14.2. What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose?
Ans: Lactose being a disaccharide gives two molecules of monosaccharides Le. one molecule each of D-(+) – glucose and D-(+)-galactbse.
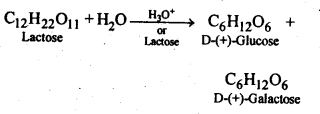
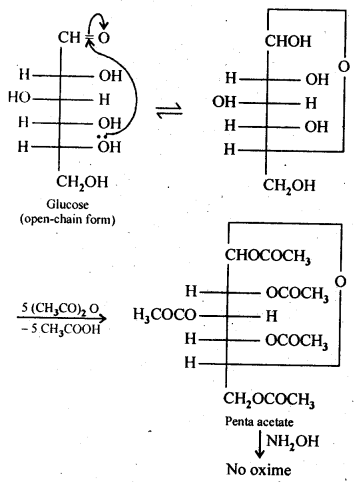
14.3. How do you explain the absence of aldehyde group in the pentaacetate of D-glucose?
Ans: The cyclic hemiacetal form of glucose contains an -OH group at C-l which gets hydrolysed in aqueous solution to produce open chain aldehydic form which then reacts with NH2OH -to form corresponding oxime. Thus, glucose contains an aldehydic group. However, when glucose is reacted with acetic anhydride, the -OH group at C-l along with the other -OH groups at C-2, C-3, C-4 and C-6 form a pentaacetate.Since the penta acetate of1 glucose does not contain a free -OH group at C-l, it cannot get hydrolysed in aqueous solution to produce open chain aldehydic form and hence glucose pentaacetate does not react with NH2OH to form glucose oxime. The reactions are shown as:
14.4. The melting points and solubility in water of a-amino acids are generally higher than those of corresponding haloacids. Explain.
Ans: a-amino acids as we all know, are dipolar in nature (N+H3-CHR-COO–) and have strong dipolar interactions. As a result, these are high melting solids. These are also involved in intermolecular hydrogen bonding with the molecules of water and are therefore, water soluble. On the contrary, the haloacids RCH(X)COOH are not dipolar like a-amino acids. Moreover, only the carboxyl group of haloacids are involved in hydrogen bonding with the molecules of water and not the halogen atoms. These have therefore, comparatively less melting points and are also soluble in water to smaller extent.
14.5. Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg?
Ans: When egg is boiled, proteins first undergo denaturation and then coagulation and the water present in the egg gets absorbed in coagulated protein, probably through H- bonding
14.6. Why cannot Vitamin C be stored in our body?
Ans: Vitamin C cannot be stored in the body because it is water soluble and is, therefore, easily excreted in urine.
14.7. Which products would be formed when a nucleotide from DNA containing thymine is hydrolysed?
Ans: Upon hydrolysis, nucleotide from DNA would form 2-deoxyribose and phosphoric acid along-with thymine.
14.8. When RNA is hydrolysed, there is no relationship among the quantities of different bases obtained. What does this fact suggest about the structure of RNA?
Ans: A DNA molecule has two strands in which the four complementary bases pair each other, i.e., cytosine (C) always pair with guanine (G) while thymine (T) always pairs with adenine (A). Thus, when a DNA molecule is hydrolysed, the molar amounts of cytosine is always equal to that of guanine and that of adenine is always equal to thymine.In RNA, there is no relationship between the quantities of four bases (C, G, A and U) obtained, therefore, the base pairing principle, i.e. A pairs with U and C pairs with G is not followed. Therefore, unlike DNA, RNA has a single strand.
Last Updated on: January 14, 2026
