Chapter 7 – The p Block Elements Questions and Answers: NCERT The p Block Elements for Class 12 Chemistry
Class 12 Chemistry chapter 7 - The p Block Elements - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
7.1. Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalidcs?
Ans: The group 15 elements have 5 e-1 s in their valence shell. It is difficult to lose 3e-1s to form E3+ and even more difficult to lose 5e-1 s to form E5+. Thus, they have very little tendency to form ionic compounds. Further, since the elements in +5 state have less tendency to lose e-1s than in the +3 state, elements in +5 state have more tendency to share e-1 s and hence pentahalides are more covalent than trihalides.
7.2. Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of group 15 elements?
Ans: Down the group, the atomic size of the element (E) increases and the bond length of the corresponding E—H bond also increases. This adversely affects the bond dissociation enthalpy. This means that amongst the trihydrides of the members of nitrogen family, the bond dissociation enthalpy of Bi—H bond is the least. Therefore, BiH3 is the strongest reducing agent among the hydrides of group 15 elements.
7.3. Why is N2 less reactive at room temperature?
Ans: Due to presence of triple bond between two N-atoms (N = N), the bond dissociation energy of N2 is very high. As a result, N2 becomes less reactive at room temperature.
7.4. Mention the conditions required to maximise the yield of ammonia.
Ans: Ammonia is prepared by Haber’s process as given below:

7.5. How does ammonia react with a solution of Cu2+?
Ans:
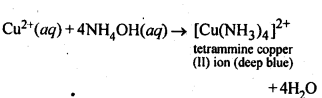
7.6. What is the covalence of nitrogen in N2O5 ?
Ans: In N2O5 , each N-atom has four shared pairs of e-1 s as shown:
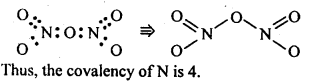
7.7. Why is bond angle in PH+4 ion higher than in PH3 ?
Ans: In both PH3 and PH+4 ion, the phosphorus atom is sp3 hybridised. However, in PH3 the central atom has apyramidal structure due to the presence of lone electron pair on the phosphorus atom.
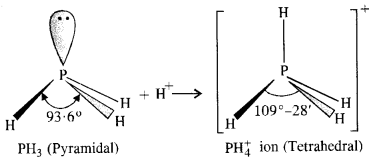
Because of lone pair : shared pair repulsion which is more than that of shared pair : shared pair repulsion, the bond angle in PH3 is nearly 93-6°. In PH+4 ion, there is no lone electron pair on the phosphorus atom. It has a tetrahedral structure with bond angle of 109°-28′. Thus, the bond angle in PH+4 ion is higher than in PH3.
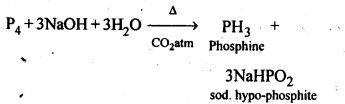
7.8. What happens when white phosphorus is heated with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2?
Ans:
7.9. What happens when Pcl5 is heated?
Ans:

7.10. Write a balanced equation for the hydrolytic reaction of PC is in heavy water.
Ans:
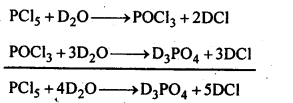
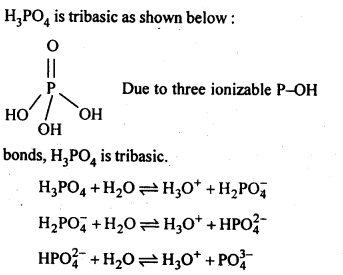
7.11. What is the basicity of H3PO4?
Ans:
7.12. What happens when H3PO4 is heated?
Ans: On heating, H3PO3 disproportionates to form PH3 and H3PO4 with O.S. of-3and + 5.
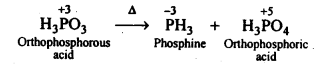
7.13. List the important sources of sulphur.
Ans: Sulphur mainly occurs in the combined states in earth’s crust in the form of sulphates and sulphides.
Sulphates : gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O); epsom (MgSO4.7H2O); baryte (BaSO4), etc.
Sulphides : Galena (PbS); zinc blende (ZnS); copper pyrites (CuFeS2); iron pyrites (FeS2), etc. Traces of sulphur occur’as H2S and in organic materials such as eggs, proteins, garlic, onion, mustard, hair and wool.
7.14. Write the order of thermal stability of the – hydrides of Group 16 elements.
Ans: The thermal stability of hydrides of group 16 elements decreases down the group. This is because down the group, size of the element (M) increases, M-H bond length increases and thus, stability of M-H bond decreases so that it can be broken down easily. Hence, we have order of thermal stability as H2O > H2S > H2Se > H2Te > H2PQ
7.15. Why is H2O a liquid and H2S a gas?
Ans: Due to high electronegativity of O than S, H2O undergoes extensive intermolecular H-bonding. As a result, H2O exists as an associated molecule in which each O is tetrahedrally surrounded by four H2O molecules. Therefore, H2O is a liquid at room temperature.On the other hand,H2S does not undergo H- bonding. It exists as discrete molecules which are held together by weak van der waals forces of attraction. A small amount of energy is required to break these forces of attraction. Therefore, H2S is a gas at room temperature.
7.16. Which of the following does not react with oxygen directly? Zn, Ti, Pt, Fe
Ans: Platinum (Pt) is a noble metal and does not react with oxygen directly.
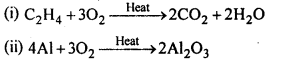
7.17. Complete the following reactions:
(i)C2H2 + O2 -> (ii) 4Al + 3 O2 ->
Ans:
7.18. Why does O3 act as a powerful oxidising agent?
Ans: On heating, O3 readily decomposes to give O2 and nascent oxygen.
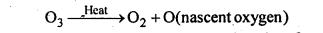
Since nascent oxygen is very reactive, therefore, O3 acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
7.19. How is O3 estimated quantitatively?
Ans: When O3 is treated with excess of KI solution buffered with borate buffer (pH = 9.2), I2 is liberated quantitatively.
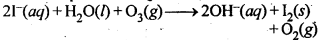
The I2 thus liberated is titrated against a standard solution of sodium thiosulphate using starch as an indicator
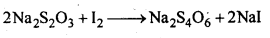
7.20. What happens when sulp’hur dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt?
Ans: SO2 acts as a reducing agent and reduces aqueous solution of Fe (III)salt to Fe (II) salt.
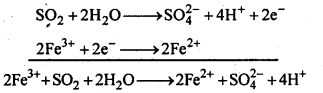
7.21. Comment on the nature of two S-O bonds formed in S02 molecule. Are the two S-O bonds in this molecule equal ?
Ans: SO2 exists as an angular molecule with OSO bond angle of 119.5°. It a resonance hybrid of two canonical-forms:
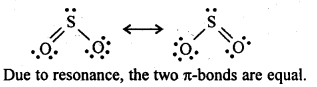
7.22. How is the presence of SO2 detected?
Ans: SO2 is a pungent smelling gas. It can be detected by two test:
7.23. Mention three areas in which H2SO4 plays an important role.
Ans: (i) Sulphuric acid is used for the manufacture of a number of chemicals like hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, nitric acid along with a large number of organic compounds.
(ii) A mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of explosives like picric acid, T.N.T, dynamite etc.
(iii) Dilute solution of acid is employed in petroleum refining in order to remove the unwanted impurities of sulphur.
Last Updated on: January 14, 2026
