Chapter 15 – Polymers Questions and Answers: NCERT Polymers for Class 12 Chemistry
Class 12 Chemistry chapter 15 - Polymers - Questions and Answers of NCERT Book Solutions.
15.1. What are polymers?
Ans: Polymers are high molecular mass substances (103 — 107u) consisting of a very large number of simple repeating structural units joined together through covalent bonds in a linear fashion. They are also called macromolecules. Ex: polythene, nylon 6,6, bakelite, rubber, etc.
15.2. How are polymers classified on the basis of structure?
Ans: On the basis of structure, polymers are classified into three types. These are linear chain polymers, branched chain polymers and crossedlinkedpolymers.
1. Linear chain polymers: In this case, the monomer units are linked to one another to form long linear chains. These linear chains are placed one above the other and are closely packed in space. The close packing results in high densities, tensile strength and also high melting and boiling points. High density polyethene is a very common example of this type. Nylon, polyesters and PVC are also linear chain polymers.
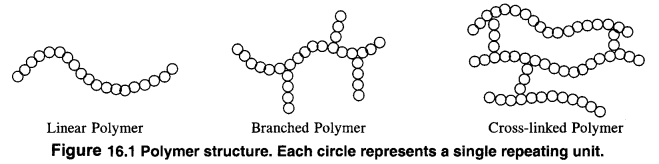
2. Branched chain polymers: In this type of polymers, the monomer units are linked to form long chains which have also side chains or branched chains of different Lengths attached to them. As a result of branching, these polymers are not closely packed in space. They have low densities, low tensile strength as well as low melting and boiling points. Some common examples of such polymers are ; low density polyethene, amylopectin, starch, glycogen etc.
3. Cross: linked polymers. In these polymers, also called net—work polymers, the monomer units are linked together to form three dimensionaL net—work as shown in the figure. These are expected to be quite hard, rigid and brittle. Examples of cross linked polymers are bakelite, glyptal. melamine formaldehyde polymer etc.
15.3. Write the names of the monomers of the following polymers:
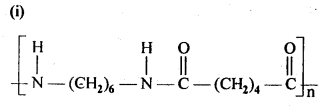
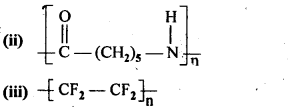
Ans: (i) Hexamethylene diamine NH2-(CH2)6NH2 and adipic acid HOOC – (CH2)4 – COOH
(ii) Caprolactum
(iii) Tetrafluoroethene F2C = CF2
15.4. Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers:
Terylene, Bakelite, Polyvinyl chloride,Polythene
Ans: Addition polymers: Polyvinyl chloride, Polythene
Condensation polymers : Terylene, bakelite.
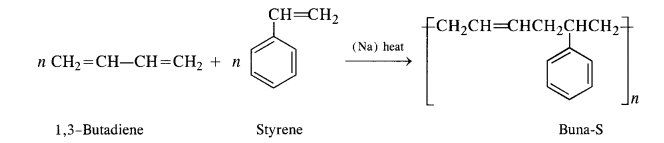
15.5. Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S.
Ans: Both Buna-N and Buna-S are synthetic rubber and are co-polymers in nature. They differ in their constituents.
Buna-N: Constituents are : buta-1, 3-diene and acrylonitrile.
Buna-S: Constituents are : buta-1, 3-diene, and styrene. They condense in the presence of Na.
Buna – S: It is a co—polymer of 1. 3 – butadiene and styrene and is prepared by the polymerisation of these components in the
ratio of 3 : 1 in the presence of sodium.
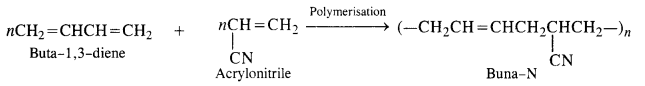
15.6. Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their intermolecuiar forces.
(i) Nylon 6,6, Buna-S, Polythene
(ii) Nylon 6, Neoprene, Polyvinyl chloride
Ans: On the basis of intermolecuiar forces, polymers are classified as elastomers, fibres and plastics. The increasing order of intermolecuiar forces is:
Elastomer < Plastic < fibre.
Thus, we have
(i)Buns-S < Polythene < Nylon 6,6
(ii)Neoprene < Polyvinyl chloride < Nylon 6.
Last Updated on: January 14, 2026
