The Smart Cities project can be regarded as one of the most ambitious plans that Prime Minister Narendra Modi has for revolutionising India. The tagline of the project is "Smarter Solutions for a Better Tomorrow", which perhaps throws light on what the project wants to achieve for the common people of India. As part of this project, the Indian Government shall be developing satellite towns in the vicinity of existing major cities and getting them up to an all new level.
There are lots of expectations surrounding the project. The Prime Minister has already expressed his willingness for the cities to have technology-based governance systems and has also suggested that these setups be monitored constantly so that they can function well and improve in the due course of time. The social facilities on offer at these cities are expected to be far better than the regular cities. Features like access to Wi-Fi could become the norm rather than the exception at these cities. They are also supposed to look spanking clean and this means that the days of garbage on roads may be a distant memory very soon.
What is the aim of the project?
In the last few years it has been seen that with growing population increasing numbers of people have been moving away from the rural areas to the urban locations. Experts have also predicted that in the next few years people will be migrating to the urban locations at the rate of 25 to 30 people per minute. The main aim for their movement will be better lifestyles as well as opportunities for work. Now, by this rate, all the cities in the country will have 843 million people living in them by 2050. One of the major aims of the project is to make sure that India is able to deal well with this huge influx of people.
One of the various problems plaguing India as a country is open defecation. Available statistics say that approximately 67 per cent of people in the rural areas defecate in the open. This also means that India is responsible for half of the open defecation that goes on around the world. The Smart Cities project will also look to tackle this issue. The Smart Cities plan will also be looking to deal with the issue of pollution emanating from the various modes of transport in India. As part of the project the government will look to come up with cities that are well-equipped from a technological perspective and the idea is to make sure that access is not limited only to the privileged sections of the society. The government will try to make these cities in such a way that they generate little waste and have proper waste recycling facilities that will deal with the waste generated. All the cities are also supposed to be centres of education where people will be able to access the very best in primary as well as higher education. However, this is not where it all stops.
The cities built/upgraded as part of the Smart Cities project shall have the very best in recreational facilities as well with sports stadia, open centres and plazas to go with centres of culture. As a result, it is being expected that the people in these cities will thoroughly enjoy their time over here.
What will be the costs?
The Indian government has approved an amount of Rs 980 billion for rejuvenating 500 cities and developing 100 smart cities. In the Union Budget of 2014, Arun Jaitley - the Union Finance Minister - earmarked an amount of Rs 7060 crore. However, till the month of February 2015 only around Rs 9.24 billion was spent from the amount. That's why only Rs 1.43 billion has been allocated by the Union budget of India for 2015, for the project.
When will the project be completed?
The project is supposed to be completed in the next two decades.
Which areas will be covered by the project?
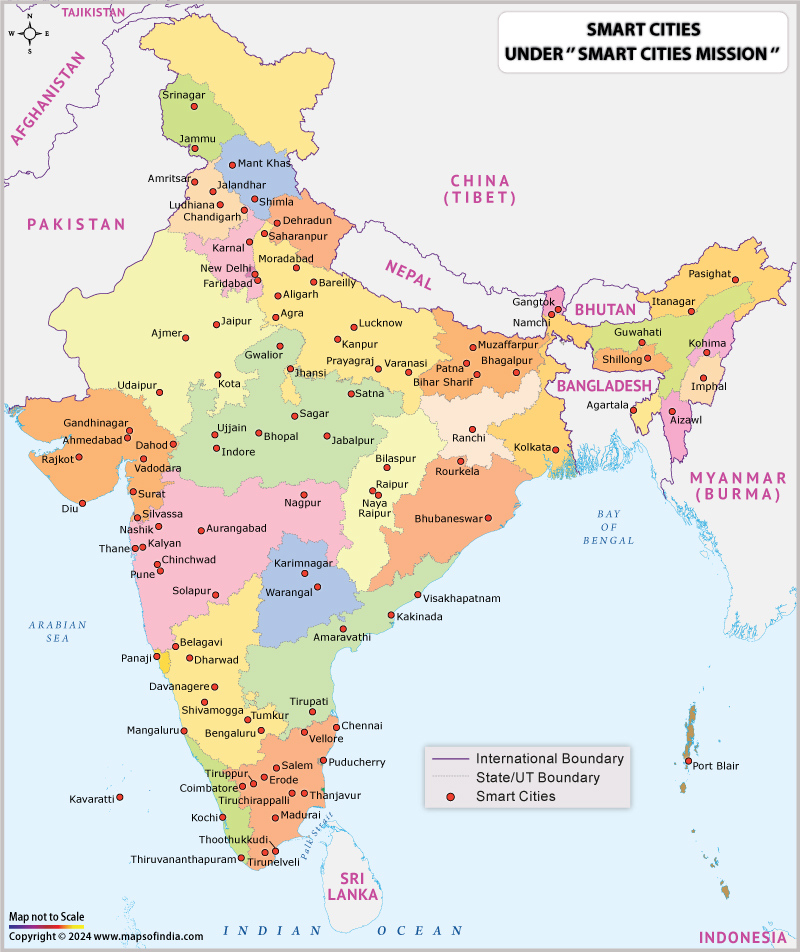
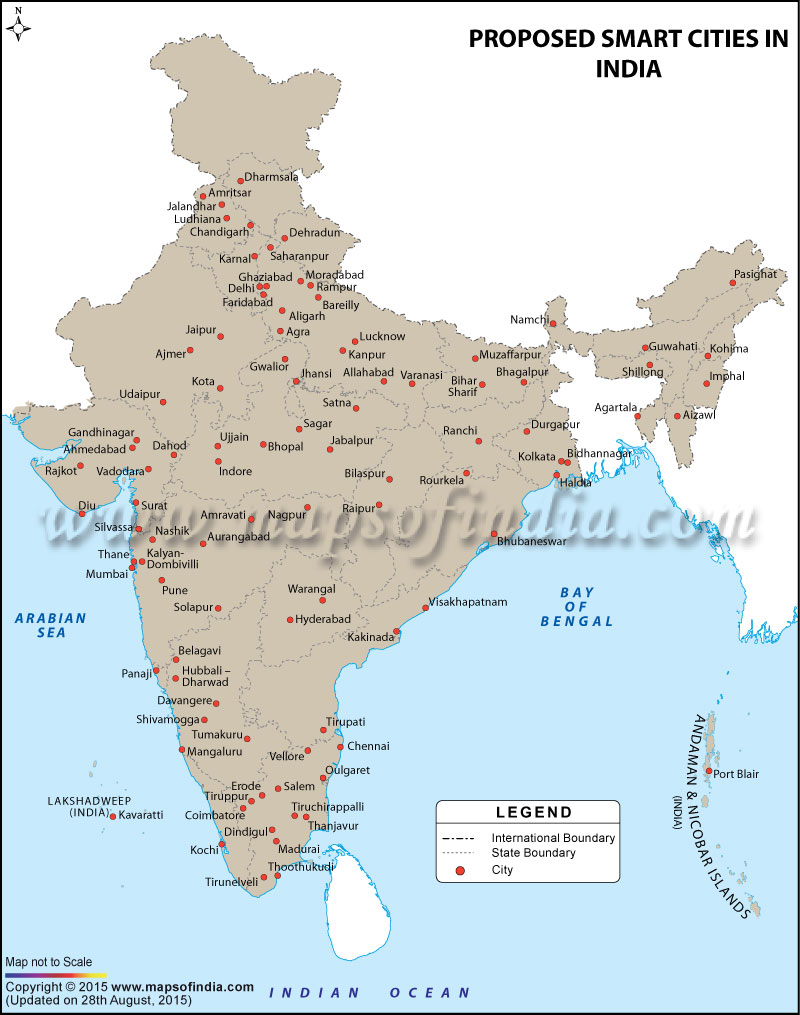
The project is aiming to cover 100 cities in a span of 20 years. In January 2016, the government announced the list of 20 cities to be developed into smart cities in the first phase the plan to make over 100 smart cities by 2022. These 20 cities are - Bhubaneswar, Pune, Jaipur, Surat, Kochi, Ahmedabad, Jabalpur, Visakhapatnam, Solapur, Bhuvanagiri, Indore, Coimbatore, Kakinada, Belgaum, Udaipur, Guwahati, Chennai, Ludhiana and Bhopal as well as the area under the NDMC in New Delhi.
In May, the central government selected 13 urban cities to develop as a smart city. These include Lucknow, New Town in Kolkata, Bhagalpur, Dharamsala, Chandigarh, Faridabad, Raipur, Ranchi, Warangal, Agartala, Imphal, Port Blair and Panaji.
How will the project be implemented?
As has been stated already the project will look to make sure that the complexities and pressure faced by the people living in the cities are far lesser and their costs come down as well. The programme will also try to make the target cities more efficient than ever before. The Indian Government has taken a number of steps in order to carry the project out with the aim being to bring about phenomenal changes in areas such as transportation, health, public security, and energy resources.
It has relaxed the rules and regulations for foreign direct investment that is supposed to play a significant role in the project's ultimate success. The government has also allocated $83 million for the Digital India programme and is looking to use the public private partnership (PPP) model for improving the infrastructure in around 500 urban locations in the country.
The Ministry of Urban Development, which has been entrusted with carrying out the project, is looking to develop at least two smart cities each in the 29 states of India. The Delhi Mumbai Industrial Corridor Development Corporation Ltd (DMICDC) is looking to come up with seven such cities in the 1500 km area covered by the said corridor. This will cover six states and in all the required investment will be in the region of 100 billion US dollars.
As part of the project, India will develop its own low cost smart meters by the end of the ongoing year. It will also operate 8 smart grid pilot projects and the investment needed for the same will be $10 million. As part of the Twelfth Five Year Plan (2012-17), the government will add 88,000 megawatt power. India also needs to make sure that it is able to generate electricity amounting to 250-400 gigawatt by 2030. The Power Grid Corporation of India is planning to put in 26 billion dollars in the project in the next five years. By 2021, it will also need to install 130 million smart meters.
One of the cornerstones of the project is supposed to be smart environment and one important way to achieve this will be to use renewable energy. As part of the project the Union Ministry of New and Renewable Energy is planning to add 30,000 megawatt to the existing capacity. This will be done in the Twelfth Five Year Plan. Management of water resources and waste materials is also going to be an important part of the endeavour. For this, the Indian Government is looking to invest 50 billion US dollars in the water sector. This will be done in a phased manner in the years to come.
The Yamuna Action Plan Phase III, which will be carried out in Delhi, has already met with the necessary approval. The project is supposed to cost in the region of USD 276 million. In order to better execute the sanitation programmes enshrined in the Smart Cities project, the World Bank is lending 500 million US dollars to the Indian Government. With this amount, the Rural Water Supply and Sanitation or RWSS project will be carried out in states such as Assam, Jharkhand, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
As part of the Green Transport module, the Government of India will be providing 4.13 billion US dollars. This is expected to provide the much needed fillip in the production of hybrid and electric cars. The Ministry of Urban Development will also look to invest at least 20 billion US dollars in the years ahead and the money is supposed to be spent for various projects pertaining to metro rail.
A high speed railway line between Mumbai and Ahmedabad has been proposed already. This will cover a distance of 534 km and the total investment needed to realise this project will be in the range of Rs 97,636 crore. The Indian Government will also start a project named Safe City whereby 333 million dollars will be spent in order to get Delhi, Ahmedabad, Mumbai, Bangalore, Kolkata, Hyderabad and Chennai - the major cities of India - to place greater emphasis in terms of improvement in technology.
The Government of India has also inked a disaster management agreement with the World Bank and as per this agreement 236 million US dollars will be provided in order to make the coastal villages in Puducherry and Tamil Nadu better suited to deal with any occurrence of natural disaster.
One of the cornerstones of the Smart Cities project is improving the healthcare services in India. For this purpose, the Indian Government has increased its health budget by 27 per cent in the ongoing fiscal and taken it up to 5.86 billion US dollars. The major focus of this budgetary addition would be to make sure that affordable housing can be provided to the common people. The government will also try to make sure that it can provide similarly economical and efficient healthcare services to common people in the country.
A unique aspect of the Smart Cities project is that the various projects will be done in such a way that they suit the requirements of the particular city/region. As an example, it may be stated that the policy of land pooling will be followed in Delhi.
Facts regarding the project
It is being expected that the Smart Cities project shall lead to an increase of 10 to 15 per cent in job openings, which can be termed as a positive development for the economy. All the households in the Smart Cities will have electricity for at least 8 hours a day and this will be available by 2017.
It is being expected that by dint of the Smart Cities project India will have the third biggest market for construction by 2020. This will be achieved with a yearly growth rate of 11.5 million homes ever year. As of now, the value of the market for intelligent building management systems has been estimated at 621 million US dollars. In the next couple of years, this is supposed to go up to 1891 million US dollars. The benefit of the smart buildings is that they will operate on 30 per cent less water, 40per cent less energy and costs for building maintenance will also come down by 10-30per cent.
As part of its smart health plans, the government will be setting up four new institutes that will be built like AIIMS and 12 medical colleges will also be established across the nation.
What are the issues with the project?
As things stand now, the biggest problem with the Smart Cities project is the huge aggregate cost - Rs 7 lakh crore in a span of 20 years. It is almost impossible for the Indian Government to finance it completely and that is why it is looking for cooperation from the private sector.
WBSM20.12.2014
EBVD
Complete List of 99 Smart Cities (Selected)
| State/UT | City Name |
|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Island | Port Blair |
| Andhra Pradesh | Kakinada |
| Andhra Pradesh | Tirupati |
| Andhra Pradesh | Visakhapatnam |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Pasighat |
| Assam | Guwahati |
| Bihar | Bhagalpur |
| Bihar | Bihar Sharif |
| Bihar | Muzaffarpur |
| Bihar | Patna |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| Chhattisgarh | Bilaspur |
| Chhattisgarh | Naya Raipur |
| Chhattisgarh | Raipur |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu | Silvassa |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu | Diu |
| Delhi | New Delhi |
| Goa | Panaji |
| Gujarat | Ahmedabad |
| Gujarat | Dahod |
| Gujarat | Gandhinagar |
| Gujarat | Rajkot |
| Gujarat | Surat |
| Gujarat | Vadodara |
| Haryana | Faridabad |
| Haryana | Karnal |
| Himachal Pradesh | Dharamasala |
| Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Jammu |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar |
| Jharkhand | Ranchi |
| Karnataka | Bangalore |
| Karnataka | Belgaum |
| Karnataka | Davangere |
| Karnataka | Mangalore |
| Karnataka | Shimoga |
| Karnataka | Tumakuru |
| Kerala | Kochi |
| Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal |
| Madhya Pradesh | Gwalior |
| Madhya Pradesh | Indore |
| Madhya Pradesh | Jabalpur |
| Madhya Pradesh | Sagar |
| Madhya Pradesh | Satna |
| Madhya Pradesh | Ujjain |
| Maharashtra | Amravati |
| Maharashtra | Aurangabad |
| Maharashtra | Hubli-Dharwad |
| Maharashtra | Kalyan |
| Maharashtra | Nagpur |
| Maharashtra | Nashik |
| Maharashtra | Pimpri Chinchwad |
| Maharashtra | Pune |
| Maharashtra | Solapur |
| Maharashtra | Thane |
| Manipur | Imphal |
| Mizoram | Aizawl |
| Nagaland | Kohima |
| Odisha | Bhubaneswar |
| Odisha | Raurkela |
| Puducherry | Oulgaret |
| Punjab | Amritsar |
| Punjab | Jalandhar |
| Punjab | Ludhiana |
| Rajasthan | Ajmer |
| Rajasthan | Jaipur |
| Rajasthan | Kota |
| Rajasthan | Udaipur |
| Sikkim | Gangtok |
| Sikkim | Namchi |
| Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| Tamil Nadu | Coimbatore |
| Tamil Nadu | Erode |
| Tamil Nadu | Madurai |
| Tamil Nadu | Salem |
| Tamil Nadu | Thanjavur |
| Tamil Nadu | Thoothukudi |
| Tamil Nadu | Tiruchirappalli |
| Tamil Nadu | Tirunelveli |
| Tamil Nadu | Tiruppur |
| Tamil Nadu | Vellore |
| Telangana | Karimnagar |
| Telangana | Warangal |
| Tripura | Agartala |
| Uttar Pradesh | Agra |
| Uttar Pradesh | Aligarh |
| Uttar Pradesh | Allahabad |
| Uttar Pradesh | Bareilly |
| Uttar Pradesh | Jhansi |
| Uttar Pradesh | Kanpur |
| Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow |
| Uttar Pradesh | Moradabad, |
| Uttar Pradesh | Saharanpur |
| Uttar Pradesh | Varanasi |
| Uttarakhand | Dehradun |
| West Bengal | New Town Kolkata |
Note:- *Jammu and Kashmir has asked for more time to decide on the potential Smart City.
** 12 cities have been shortlisted from Uttar Pradesh against 13 cities allocated to the State.
Last Updated on : February 28, 2024
Government Schemes and Campaigns