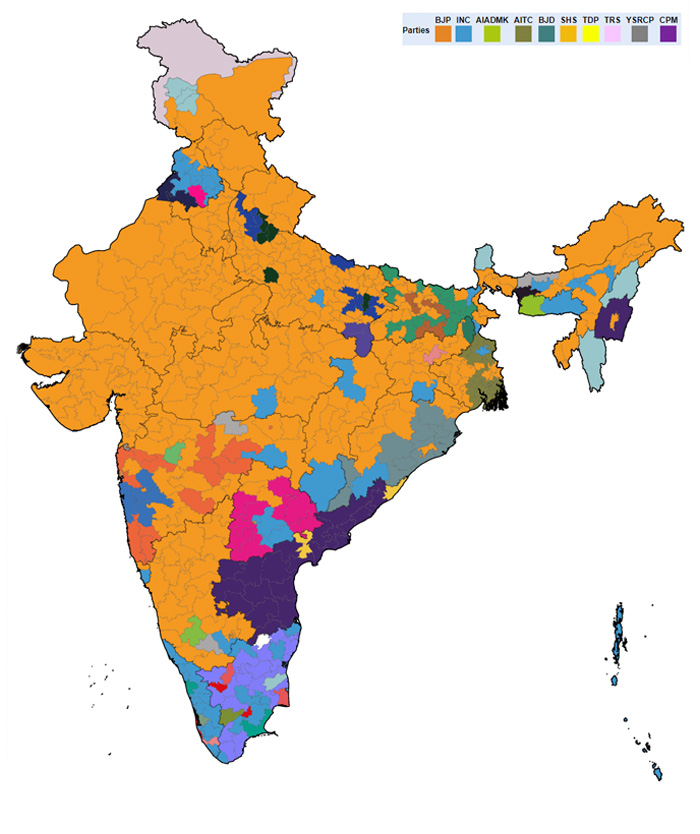
Andaman and Nicobar
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3)
Andhra Pradesh
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):42
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):294
Lok Sabha Election Dates:30 April (Phase 7), 7 May (Phase 8)
Assembly Elections Dates:30 April (Phase 1), 07 May (Phase 2)
Arunachal Pradesh
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):2
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):60
Lok Sabha Election Dates:09 April (Phase 2)
Assembly Elections Dates:09 April
Asom (Assam)
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):14
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):126
Lok Sabha Election Dates:07 April (Phase 1), 12 April (Phase 4), 24 April (Phase 6)
Bihar
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):40
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):243
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6), 30 April (Phase 7), 07 May (Phase 8), 12 May (Phase 9)
Chandigarh
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3)
Chhattisgarh
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):11
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):90
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6)
Dadra and Nagar Haveli
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
Lok Sabha Election Dates:30 April (Phase 7)
Daman and Diu
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
Lok Sabha Election Dates:30 April (Phase 7)
Delhi
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):7
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):70
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3)
Goa
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):2
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):40
Lok Sabha Election Dates:12 April (Phase 5)
Gujarat
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):26
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):182
Lok Sabha Election Dates:30 April (Phase 7)
Haryana
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):10
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):90
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3)
Assembly Elections Dates:Not declared
Himachal Pradesh
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):4
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):68
Lok Sabha Election Dates:07 May (Phase 8)
Jammu And Kashmir
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):6
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):87
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6), 30 April (Phase 7), 07 May (Phase 8)
Jharkhand
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):14
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):81
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6)
Karnataka
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):28
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):224
Lok Sabha Election Dates:17 April (Phase 5)
Kerala
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):20
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):140
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3)
Lakshadweep
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3)
Madhya Pradesh
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):29
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):230
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6)
Maharashtra
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):48
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):288
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6)
Assembly Elections Dates:Not declared
Manipur
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):2
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):60
Lok Sabha Election Dates:09 April (Phase 2), 17 April (Phase 5)
Meghalaya
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):2
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):60
Lok Sabha Election Dates:09 April (Phase 2)
Mizoram
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):40
Lok Sabha Election Dates:09 April (Phase 2)
Nagaland
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):60
Lok Sabha Election Dates:09 April (Phase 2)
Odisha
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):21
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):147
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5)
Assembly Elections Dates:10 April (Phase 1), 17 April (Phase 2)
Puducherry
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):30
Lok Sabha Election Dates:24 April (Phase 6)
Punjab
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):13
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):117
Lok Sabha Election Dates:30 April (Phase 7)
Rajasthan
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):25
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):200
Lok Sabha Election Dates:17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6)
Sikkim
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):1
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):32
Lok Sabha Election Dates:12 April (Phase 4)
Assembly Elections Dates:12 April
Tamil Nadu
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):39
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):234
Lok Sabha Election Dates:24 April (Phase 6)
Tripura
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):2
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):60
Lok Sabha Election Dates:07 April (Phase 1), 12 April (Phase 4)
Uttarakhand (Uttaranchal)
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):5
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):70
Lok Sabha Election Dates:07 May (Phase 8)
Uttar Pradesh
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):80
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):403
Lok Sabha Election Dates:10 April (Phase 3), 17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6), 30 April (Phase 7), 07 May (Phase 8), 12 May (Phase 9)
West Bengal
No. of Parliamentary Constituencies (seats):42
No. of Assembly Constituencies (seats):294
Lok Sabha Election Dates:17 April (Phase 5), 24 April (Phase 6), 30 April (Phase 7), 07 May (Phase 8), 12 May (Phase 9)
The Constitution of India was adopted by the Constituent Assembly on November 26, 1949. Drafted by a committee led by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, it took effect from January 26, 1950, and the date is celebrated as the Republic Day of India. India was declared as a democratic republic, with Dr. Rajendra Prasad becoming the first President of India. The first constitutional elections in India were held in 1952, in which the INC won by majority and India got its first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru. The first Lok Sabha was formed and Dr. Rajendra Prasad was re-elected as the President of India.
Election Commission of India
The Election Commission of India (ECI) is established constitutionally as an autonomous federal authority. The prime responsibility of the ECI is to administer and supervise all electoral processes under the Indian Constitution, maintaining the principles and rules ensuring free and fair polling.
The Chief Election Commissioner, appointed by the President of India, heads the commission. The President also appoints two Election Commissioners. According to Conditions of Service Rules 1992, salaries and allowances of the Chief Election Commissioner and the two Election Commissioners are at par with that of Judges of the Supreme Court of India. The Parliament of India can remove the Chief Election Commissioner on grounds of incapacity or misbehavior only if it attains support of two-third majority in Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha. The President of India has the power to remove the two election commissioners on recommendation of the Chief Election Commissioner.
Purpose of Elections
In a democracy, the government is formed by people's representation. India is a democratic republic where governance is elected by people both centrally as well as regionally. In case of regional governance, i.e., state government, geographies are demarcated for appropriate representation of the people in various Vidhan Sabhas. For the central government, every state sends their representatives in the Lok Sabha by clubbing certain number of Vidhan Sabha constituencies to represent populace of such demography. Election is a process which allows people to exercise their right in choosing a representative either of specific political and economic ideals or independent personality by casting votes. Thus, election is required for representation by the people right from Gram Panchayat, Municipalities & Corporations, Vidhan Sabha and Lok Sabha, so that the whole country from village-level upwards is represented through a fair process.
The Electoral Process
- Constituencies are segregated as per the number of seats in Lok Sabha and Vidhan Sabha elections.
- The voters' list of the demarcated constituencies is prepared and published.
- The Election Commission declares dates of election, date of filing nomination papers and the last date of withdrawing nomination.
- Nominations are filed.
- Nomination papers are verified on a fixed date. The commission has power to reject a nomination if the papers are not in order.
- Campaigns are held by political parties through public meetings, distribution of posters, processions, and use of media like radio and television.
- Campaigning closes 48 hours prior to election date.
- The election law in India prohibits a candidate from:
- Threatening or bribing a voter
- Campaigning using government resources
- Influencing or appealing voters on religion and caste
- Spending over Rs. 25 lakhs and Rs. 10 lakhs for one-time Lok Sabha or Vidhan Sabha election, respectively.
- All political parties abide by the Model Code of Conduct.
- Elections are conducted in selected government colleges and schools with respective District Collectors taking charge of polling.
- Government employees are inducted in the polling booths.
- Vote is cast either by ballot boxes or through the Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs).
- The ballot boxes and EVMs are thereafter transferred to strong rooms until counting is undertaken at pre-fixed centre.
- The candidate receiving majority votes is declared as elected from the constituency.
- Election may be re-held if complaint from a candidate is found to be valid.
- The party or coalition that has won by majority forms the government.
- General or Lok Sabha Elections: The General elections are held every 5 years. The candidates elected become Members of Parliament or MPs. The Lok Sabha has a maximum of 552 seats and currently there are 544 MPs in the house. The maximum number of seats can be altered if the parliament approves such an amendment. The party or coalition achieving majority in the house forms the government and chooses the Prime Minister. The candidate thus chosen must be a member of either the Lok Sabha or the Rajya Sabha. If he/she is not, then six months time is given for him/her to get elected to either of the houses.
- Rajya Sabha Elections: Rajya Sabha is the upper house of the Indian Parliament. There can be a maximum of 250 members, of which 12 are nominated by the President of India. These 12 members are generally renowned and knowledgeable personalities from different walks of life such as art, social service, science, literature or sports. The state and territorial legislatures representing 29 states and 2 Union Territories elect the rest of the members. Members are elected every six years with two-third retiring every two years. The two houses, namely the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha, can meet to resolve any conflicting legislation between the two.
- Election of the President: The President of India is officially the head of the judiciary, legislature and state of the Indian Republic. He is the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. He is indirectly elected by the people of India through Electoral College consisting of elected members of the Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha, Vidhan Sabhas and Vidhan Parishads and serves a term of five years. Re-election takes place if the incumbent resigns or in case of his/her death. Any Indian citizen who has attained 35 years of age and is qualified for Lok Sabha elections is an eligible candidate for the Presidential post. However, he should not hold any office of profit or a seat in parliament or state assembly.
- State Assembly Elections: The Legislative or State Assembly elections are held in 29 states and 2 Union Territories out of the 7 Union Territories of India. The candidates elected become Members of the legislative assembly or Vidhan Sabha of the respective states. They are known as MLAs. The party or coalition holding majority in the state forms the government and chooses the Chief Minister of the state. The MLAs of the winning party hold different offices as ministers of state. The state assembly elections are held every 5 years.
Last Updated on : April 11, 2019